Textbook Solution: The Number System | Year 6 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Getting started |

|
| Exercise 1.1 |

|
| Exercise 1.2 |

|
| Check your progress |

|
Getting started
Q1: What is the value of the digit 9 in these numbers?
(a) 809.46
Ans: 9 ones
(b) 2021.89
Ans: 9 hundredths
(c)123 456.95
Ans: 9 tenths
Q2: write these numbers in words and digits
(a) 200 000 + 5000 + 400 + 8 + 0.9
Ans: two hundred and five thousand, four hundred and eight point nine (205 408.9)
(b) 500 000 + 70 000 + 30 + 6 + 0.01
Ans: five hundred and seventy thousand thirty six point zero one (570 036.01)
Q3: (a) What number is ten times bigger than 0.01?
Ans: 0.1
(b) What number is one hundred times smaller than 555?
Ans: 5.55
Q4: What is the missing number?
100 x 10 = 10 000 ÷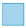
Ans: 10
Q5: Round these lengths to the nearest whole number.
(a) 6.2 m
Ans: 66m
(b) 36.5 cm
Ans: 376m
(c) 12.3 m
Ans: 12m
(d) 10.6 cm
Ans: 11m
Q6: A number with 1 decimal place is rounded to the nearest whole number.
(a) What is the smallest number that rounds to 100?
Ans: 99.5
(b) What is the largest number that rounds to 10?
Ans: 10.4
Exercise 1.1
Q1: What is the value of the digit 7 in these numbers?
(a) 6703.46
Ans: 7 hundred
(b) 213.807
Ans: 7 thousandths
(c) 456.702
Ans: 7 tenths
(d) 60.078
Ans: 7 hundredths
Q2: Sonia has these five cards.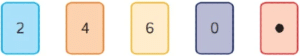 What is the smallest number, greater than 1, she can make usina all her cards?
What is the smallest number, greater than 1, she can make usina all her cards?
Ans: 2.046
Q3: Find the odd one out.
Explain your answer.
Ans: Odd one out is 12.34. All the others are equivalent to 1.234.
Q4: Add these numbers together and write the total number in words and digits.
(a) 2 + 0.1 + 0.03 + 0.009
Ans: two point one three nine (2.139)
(b) -900-9-0.9-0.009
Ans: negative nine hundred and nine point nine zero nine (−909.909)
(c) 20 + 5 + 0.4 + 0.03 + 0.001
Ans: twenty-five point four three one (25.431)
(d) -3-0.4-0.08-0.001
Ans: negative three point four eight one (-3.481)
Swap books with your partner and check their answer.
Read the numbers to each other
Q5: Copy and complete.
37.844 = 30 + 7 +  + 0.04 +
+ 0.04 +
Ans: 0.8 or 8/10 and 0.004 or 4/1000
Q6: Petra is regrouping decimal numbers. She spills ink on her work.
What number is under each ink blot?
(a) 0.546 = 0.4 + +0.006
+0.006
Ans: 0.14
(b) 0.789 - 0.7 + 0.07 +
Ans: 0.019
Q7: Find the missing numbers.
(a) 7.2 x 1000 =
Ans: 7200
(b) 0.85 x 100 = 
Ans: 85
(c) 4.28 x 10 = 
Ans: 42.8
(d) 670 ÷ 100 = 
Ans: 6.7
(e) 151 ÷ 1000 = 
Ans: 0.151
(f) 5.5 ÷ 10 = 
Ans: 0.55
Q8: Look at these number cards.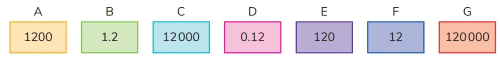 Write the letter of the card that is:
Write the letter of the card that is:
(a) one thousand times bigger than 12
Ans: C
(b) one hundredth of 12
Ans: D
(c) one thousandth of 120 000
Ans: E
Q9: Mira divides a number by 10, then by 10 again and then by 10 again.
Her answer is 0.005
What number did she start with?
Ans: 5
Exercise 1.2
Q1: Round these decimals to the nearest whole number.
4.09 7.89 2.55 7.45
Ans: 4 8 3 7
Q2: Leo bought a book costing $14.65.What is the cost of the book to the nearest dollar?
Ans: $15
Q3: Which of these numbers rounds to 5 when rounded to the nearest whole number?
4.35 4.05 4.5 5.05 4.55 5.35 5.5 5.53
Check your answers to questions 1 to 3 with your partner.
Ans: 4.5 5.05 4.55 5.35
Q4: Round these numbers to the nearest tenth.
4.52 7.81 2.35 9.07
Ans: 4.5 7.8 2.4 9.1
Q5: Which of these numbers rounds to 7.5 when rounded to the nearest tenth?
7.35 7.05 7. 51 7.55 7.49 7.56 7.53
Check your answers to questions 4 and 5 with your partner.
Ans: 7.51 7.49 7.53
Q6: Correct all the statements that are false.
(A) 3.04 is 3 when rounded to the nearest whole number and the nearest tenth.
Ans: False, 3.04 is 3.0 when rounded to the nearest tenth
(B) 5.03 is 5 when rounded to the nearest whole number and 5.0 when rounded to the nearest tenth.
Ans: True
(C) 6.95 is 7 when rounded to the nearest whole number and 6.9 when rounded to the nearest tenth.
Ans: False, 6.95 is 7.0 when rounded to the nearest tenth.
Discuss your answers with your partner.
Make sure you explain the reasons you have given.
Q7: Round these measures to the nearest tenth.
55.55 litres 12.22 metres 35.45 kilograms
Ans: 55.6 litres 12.2 metres 35.5 kilograms
Q8: Choose the smallest number from this list that rounds to
1. 0.55 0.99 1.9 1.45 0.5 1.05 0
Ans: 0.5
Q9: Jasper says, ‘7.97 is 8 when rounded to the nearest whole number and is also 8 when rounded to the nearest tenth
Is Jasper correct?
Explain your answer.
Ans: 7.97 is 8 when rounded to the nearest whole number. 7.97 is 8.0 when rounded to the nearest tenth.
The 7 in the hundredths place increases the tenths by one so 7.9 becomes 8.0.
If the number is rounded to the nearest tenth, there must be a digit in the tenths place, even if it is zero.
Think like a mathematician
Q1: The sides of a rectangle are measured in centimetres to 2 decimal places using a micrometer (an instrument for measuring length accurately).
Ans: 5 cm is between 4.50 and 5.49 cm
Q2: The measurements are rounded to the nearest whole number. They are 5 cm and 6 cm.
Ans: 6 cm is between 5.50 and 6.49 cm
Q3: What is the smallest possible perimeter of the rectangle?
Ans: Smallest possible perimeter = 4.50 + 4.50 + 5.50 +5.50 = 20.00 cm
Check your progress
Q1: Copy and complete.
87.655 = 80 + 7 + 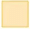 +
+  +
+ 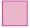
Ans: 0.6 + 0.05 + 0.005
Q2: What decimal number is represented by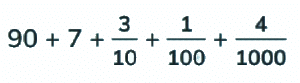
Ans: 97.314
Q3: How many times bigger is the value of the digit 6 in 64.53 than the value of the digit 6 in 0.367?
Ans: 1000
Q4: (a) What is 3.08 rounded to the nearest tenth?
Ans: 3.1
(b) What is 9.55 rounded to the nearest whole number?
Ans: 10
Q5: Find the missing numbers.
(a) 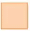 x 0.9 = 9
x 0.9 = 9
Ans: 10
(b) 705 ÷ 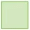 = 7.05
= 7.05
Ans: 100
(c) 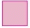 x 0.16 = 160
x 0.16 = 160
Ans: 1000
(d) 34 ÷ 1000 = 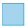
Ans: 0.034
Q6: The announcer said, ‘Ingrid won the 100 metre race in 13.9 seconds.’  Her time was originally measured to 2 decimal places.
Her time was originally measured to 2 decimal places.
What was the slowest time she could have run?
Ans: 13.94 second
|
63 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solution: The Number System - Year 6 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 6
| 1. What is the number system and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of number systems? |  |
| 3. How do you convert a decimal number to a fraction? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of prime numbers in the number system? |  |
| 5. How can understanding the number system help in real-life applications? |  |




















