Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Accountancy Class 11 > Mind Map: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
Mind Map: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
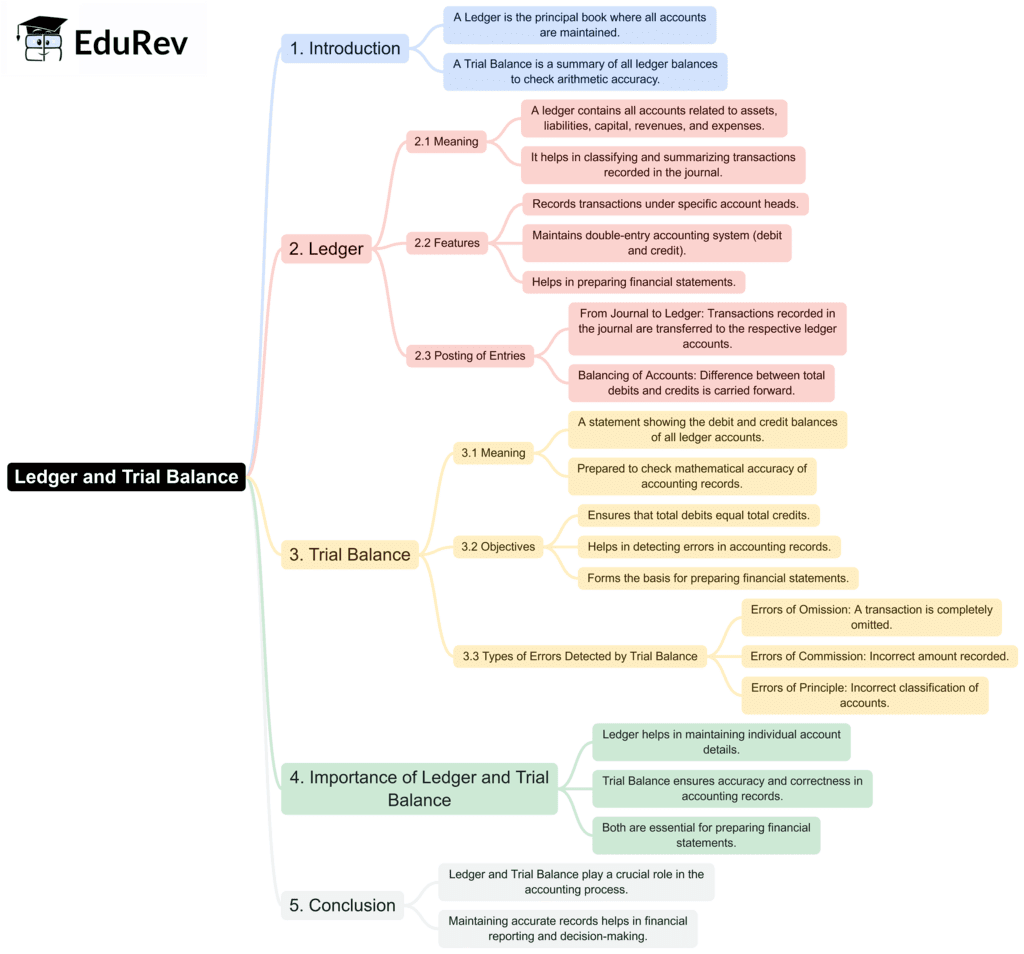
The document Mind Map: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Accountancy Class 11.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
61 videos|220 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is a trial balance and why is it important in accounting? |  |
Ans. A trial balance is an accounting report that lists the balances of all general ledger accounts of a business at a specific point in time. It serves as a tool for ensuring that the total debits equal total credits, which is essential for verifying the accuracy of the bookkeeping process. The trial balance is important because it helps identify any discrepancies in the accounts before preparing financial statements.
| 2. What are common types of errors that can occur in accounting? |  |
Ans. Common types of errors in accounting include:
1. <b>Errors of omission</b>: Failing to record a transaction.
2. <b>Errors of commission</b>: Recording a transaction incorrectly.
3. <b>Errors of principle</b>: Violating accounting principles while recording a transaction.
4. <b>Compensating errors</b>: Two or more errors offsetting each other.
5. <b>Transposition errors</b>: Mistakes in the order of digits in numbers.
| 3. How can errors in the trial balance be rectified? |  |
Ans. Errors in the trial balance can be rectified through various methods:
1. <b>Identifying the error</b>: Review account balances and transactions to locate discrepancies.
2. <b>Adjusting journal entries</b>: Make the necessary journal entries to correct the identified errors.
3. <b>Re-preparing the trial balance</b>: After making corrections, prepare a new trial balance to ensure that debits and credits are equal.
4. <b>Using a suspense account</b>: If an error cannot be identified immediately, it can be temporarily placed in a suspense account until further investigation.
| 4. What is the difference between a trial balance and a balance sheet? |  |
Ans. A trial balance is an internal report used by accountants to ensure that debits equal credits in the ledgers, while a balance sheet is an external financial statement that presents a company's financial position at a specific date. The balance sheet includes assets, liabilities, and equity, providing stakeholders with insights into the company's financial health, whereas the trial balance is primarily a tool for detecting errors in accounting records.
| 5. Can a trial balance show that the books are correct even if there are errors? |  |
Ans. Yes, a trial balance can show that the books are correct even if there are errors. This is because the trial balance only verifies that total debits equal total credits. It does not guarantee the accuracy of individual account balances or the correctness of transactions. Errors such as compensating errors or errors of principle can result in a balanced trial balance despite inaccuracies in the accounts.
Related Searches





















