Revision Notes: Structural Organisation in Animals | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Structural Organisation |

|
| Organ and Organ System |

|
| Frogs |

|
| Summary |

|
Introduction to Structural Organisation
In multicellular animals, unlike unicellular organisms where a single cell performs all functions, groups of similar cells with intercellular substances form tissues to carry out specific functions. These tissues organize into organs (e.g., stomach, heart), and multiple organs form organ systems (e.g., digestive, respiratory), exhibiting division of labour for efficient functioning and survival.
Organ and Organ System
Four basic tissue types—epithelial, connective, muscular, and neural—form organs, which associate to create organ systems. This organization ensures coordinated activities of millions of cells. For example, the heart comprises all four tissue types. Complexity in organs and systems reflects an evolutionary trend.
- Morphology: Study of external form and features.
- Anatomy: Study of internal organ morphology.
Frogs
Frogs, class Amphibia (phylum Chordata), exemplified by Rana tigrina in India, are cold-blooded (poikilotherms) with variable body temperature. They exhibit camouflage (mimicry) and undergo aestivation (summer sleep) and hibernation (winter sleep) to avoid extreme conditions.
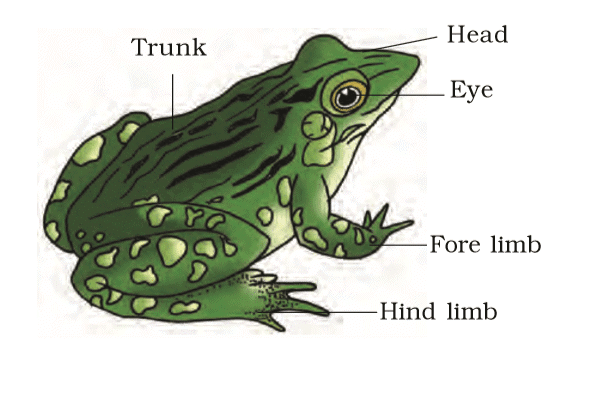
1. Morphology of Frogs
Frogs have smooth, slippery, moist skin due to mucus, with olive-green dorsal side (dark spots) and pale yellow ventral side. They absorb water through skin, not drinking it.
- Body: Divided into head and trunk (no neck or tail).
- Head: Nostrils, bulging eyes with nictitating membrane, tympanum (ear).
- Limbs: Forelimbs (4 digits) and hind limbs (5 webbed digits) for swimming, leaping, burrowing.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males have vocal sacs and copulatory pad on first digit of forelimb; absent in females.
2. Anatomy of Frogs
The body cavity houses well-developed organ systems: digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous, excretory, and reproductive.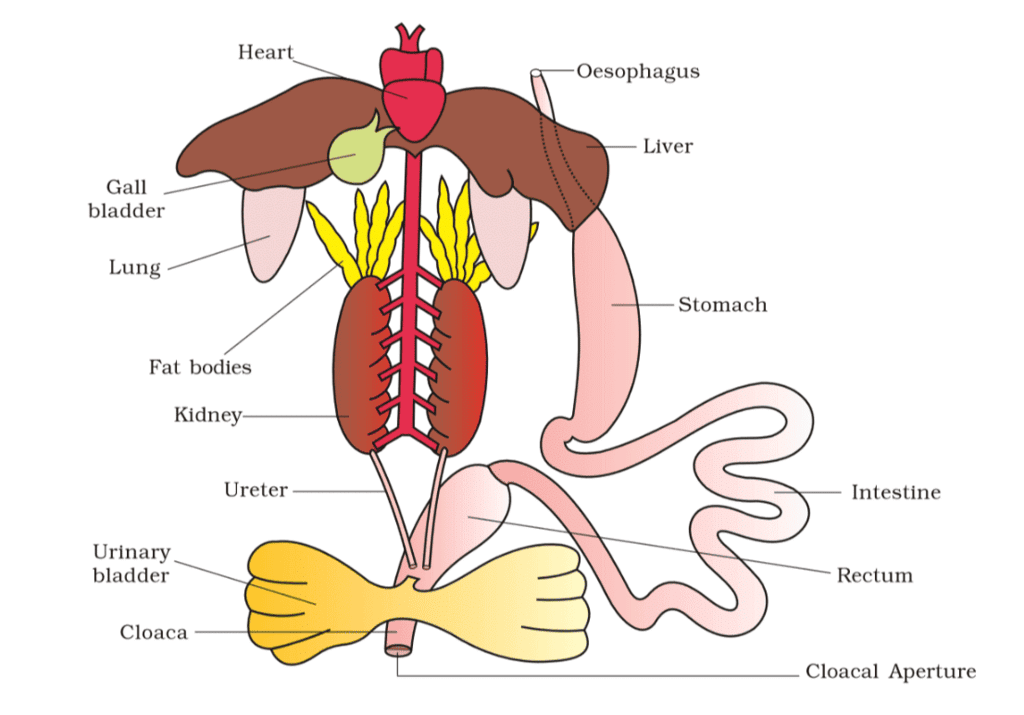
a) Digestive System
- Structure: Short alimentary canal (carnivorous)—mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, intestine, rectum, cloaca; digestive glands (liver, pancreas).
- Process: Bilobed tongue captures food; stomach secretes HCl and gastric juices; chyme enters duodenum, receiving bile (fat emulsification) and pancreatic juice (carbohydrate/protein digestion); intestine (with villi/microvilli) absorbs nutrients; waste exits via cloaca.
b) Respiratory System
- In Water: Cutaneous respiration (skin diffuses dissolved oxygen).
- On Land: Pulmonary respiration (lungs—pink, sac-like in thorax) via nostrils and buccal cavity; skin and buccal cavity also assist; skin respiration during aestivation/hibernation.
c) Circulatory System
- Type: Closed, with heart (3 chambers: 2 atria, 1 ventricle, covered by pericardium), blood vessels, and blood; lymphatic system (lymph, channels, nodes).
- Heart: Sinus venosus feeds right atrium via vena cava; ventricle leads to conus arteriosus; arterial and venous systems distribute/collect blood.
- Special Systems: Hepatic portal (liver-intestine) and renal portal (kidney-lower body).
- Blood: Nucleated RBCs (with haemoglobin), WBCs, platelets; lymph lacks some proteins and RBCs.
d) Excretory System
- Structure: Kidneys (dark red, bean-like, with nephrons), ureters, cloaca, urinary bladder.
- Function: Ureotelic (excretes urea); in males, ureters double as urinogenital ducts; in females, ureters and oviducts open separately into cloaca; waste filtered by kidneys exits via cloaca.
e) Nervous System
- Components: Central (brain, spinal cord), peripheral (10 cranial nerves, spinal nerves), autonomic (sympathetic, parasympathetic).
- Brain: In cranium; forebrain (olfactory lobes, cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon), midbrain (optic lobes), hindbrain (cerebellum, medulla oblongata); spinal cord in vertebral column.
- Endocrine Glands: Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, pineal, pancreatic islets, adrenals, gonads secrete hormones.
f) Sense Organs
- Types: Touch (sensory papillae), taste (taste buds), smell (nasal epithelium), vision (eyes in orbits), hearing/balance (tympanum, internal ears).
g) Reproductive System
- Male: Testes (attached to kidneys via mesorchium), 10-12 vasa efferentia, Bidder’s canal, urinogenital duct to cloaca.
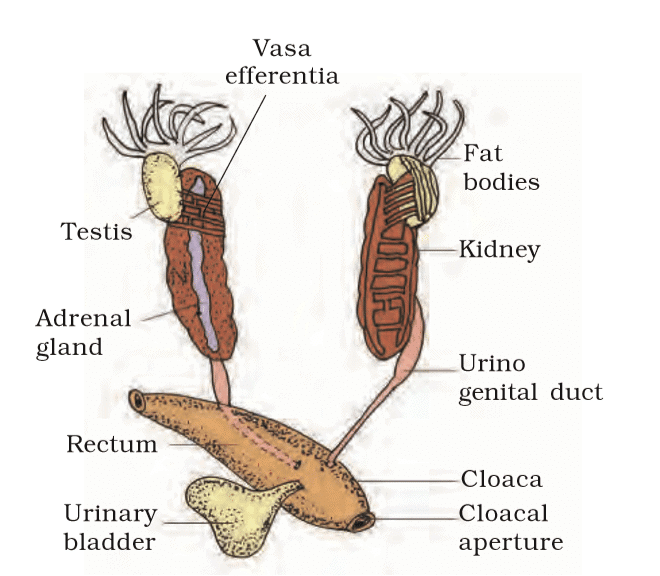 Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System - Female: Ovaries (near kidneys), oviducts to cloaca; lays 2500-3000 ova; external fertilization in water; tadpole larva metamorphoses into adult.
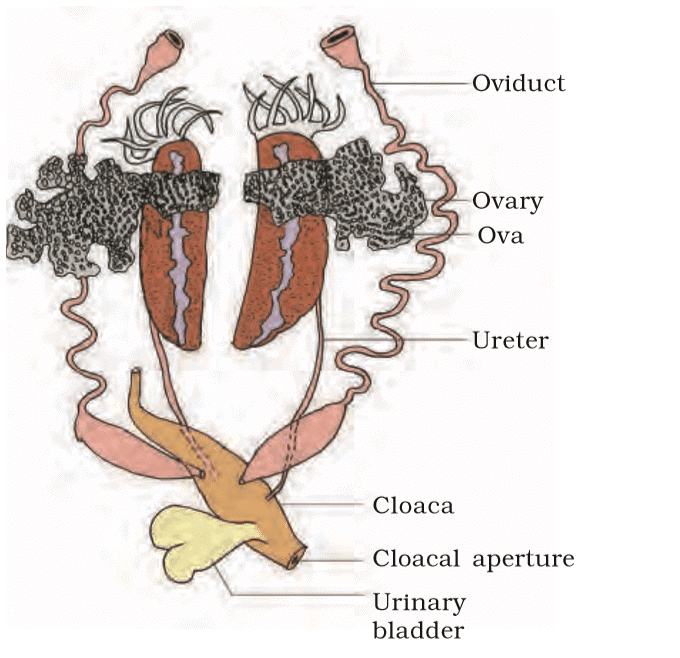 Female Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System - Economic Importance: Insect control, ecological balance (food chain link), frog legs as food.
Summary
Multicellular animals exhibit division of labour via tissues (e.g., epithelial), organs, and organ systems. Frogs (Rana tigrina) have moist skin aiding respiration, a short digestive system, closed circulation with nucleated RBCs, and a complex nervous system. They respire via skin (water) and lungs (land), excrete urea, and reproduce externally, with tadpoles metamorphosing into adults. Frogs contribute to ecosystems and agriculture.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Structural Organisation in Animals - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main levels of organization in animals? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of epithelial tissue in animals? |  |
| 3. How do different types of connective tissues vary in structure and function? |  |
| 4. What are the major functions of muscular tissue in animals? |  |
| 5. How does the nervous system contribute to the structural organization in animals? |  |




















