Mnemonics: Work, Energy, and Power | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
1. Work
Mnemonic: "Wizards Perform Clever Calculations"
Wizards – Work Done (W = F · d)
Perform – Positive Work (Force and displacement in the same direction)
Clever– Conservative Forces (Work is path-independent)
Calculations – Constant Force Work (W = F.d cosθ)
Work Done (W = F · d): Work is done when a force causes a displacement. It is calculated as the force multiplied by the displacement.
Positive Work: When force and displacement are in the same direction, the work is positive, meaning energy is being transferred to the object.
Conservative Forces: The work done by conservative forces, like gravity or spring forces, is path-independent; it depends only on the initial and final positions, not the path taken.
Constant Force Work: When the force is constant, the work done is the product of the force, the displacement, and the cosine of the angle between them.
2. Energy Types
Mnemonic: "Kangaroos Play Every Game"
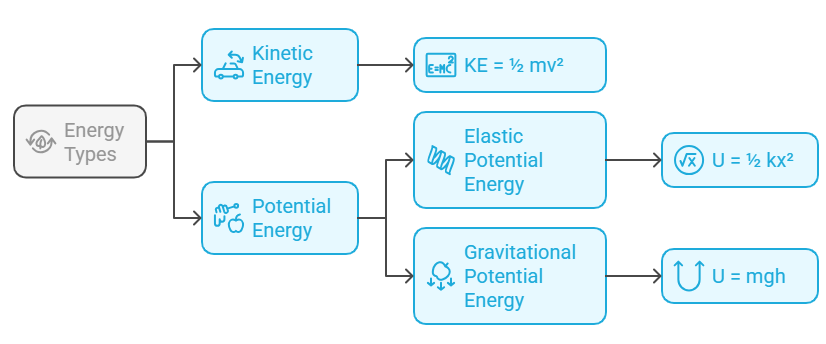
- Kangaroos – Kinetic Energy (KE = ½ mv²)
- Play – Potential Energy (gravitational, elastic)
- Every– Elastic Potential Energy (U = ½ kx²)
- Game – Gravitational Potential Energy (U = mgh)
Kinetic Energy (KE = ½ mv²): Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Any object that is moving has kinetic energy, which depends on the mass (m) and the velocity (v) of the object. The formula is KE = ½ mv², where v is the speed of the object.
Potential Energy (Gravitational, Elastic): Potential energy is stored energy. The two main types of potential energy are gravitational (due to an object's position above the ground) and elastic (stored in objects like springs or rubber bands).
Elastic Potential Energy (U = ½ kx²): This type of potential energy is stored in stretched or compressed springs (or any elastic material). The formula U = ½ kx² represents the elastic potential energy, where k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Gravitational Potential Energy (U = mgh): Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. The formula U = mgh shows how the potential energy depends on mass (m), height (h), and the acceleration due to gravity (g).
|
95 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Work, Energy, and Power - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the relationship between work, energy, and power in physics? |  |
| 2. How can mnemonics help in remembering formulas related to work, energy, and power? |  |
| 3. What are some common formulas related to work, energy, and power that NEET students should memorize? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate work done when the force is applied at an angle? |  |
| 5. What are some tips for effectively using mnemonics to study for the NEET exam on work, energy, and power? |  |





















