Mnemonics: Thermal Properties of Matter | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Modes of Heat Transfer |

|
| 2. Expansion of Solids |

|
| 3. Newton’s Law of Cooling |

|
| 4. Calorimetry Equation |

|
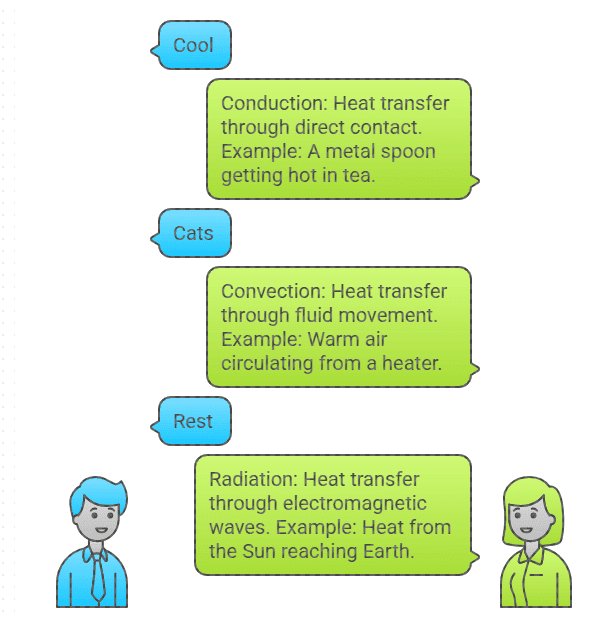
1. Modes of Heat Transfer
Mnemonic: "Cool Cats Rest"
Cool – Conduction
Cats – Convection
Rest– Radiation
Conduction: The process of heat transfer through direct contact between particles of a substance. It occurs in solids when particles vibrate and pass energy to neighboring particles.Example: A metal spoon getting hot when placed in a cup of hot tea.
Convection: Heat transfer through the movement of fluid (liquid or gas) particles. As a fluid heats up, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler fluid sinks.Example: The warm air circulating inside a room from a heater.
Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves (like infrared radiation), which does not require a medium.Example: Heat from the Sun reaching Earth through the vacuum of space.
2. Expansion of Solids
Mnemonic: "Little Ants Venture Everywhere"
Little – Linear Expansion
Ants – Areal Expansion
Venture – Volume Expansion
Everywhere – Expansion Coefficients (α, β, γ)
Linear Expansion: Refers to the change in length of an object when its temperature changes.
Formula: ΔL = αL₀ΔT, where α is the coefficient of linear expansion.Areal Expansion: Refers to the change in the area of an object when its temperature changes.
Formula: ΔA = βA₀ΔT, where β is the coefficient of areal expansion.Volume Expansion: Refers to the change in volume of an object when its temperature changes.
Formula: ΔV = γV₀ΔT, where γ is the coefficient of volume expansion.Expansion Coefficients: These coefficients (α, β, and γ) represent how much the length, area, and volume of a material change per unit temperature change.

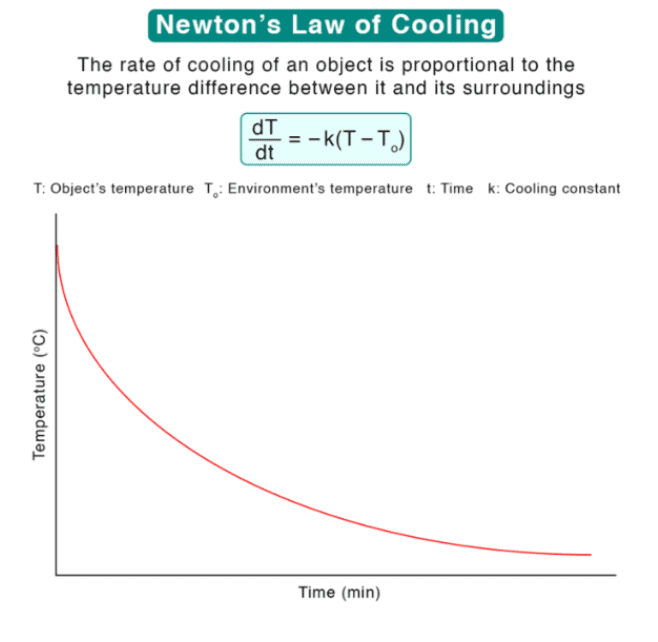
3. Newton’s Law of Cooling
Mnemonic: “Cool Rate Drops”
Cool – Cooling
Rate – Rate ∝ ΔT (temperature difference)
Drops – Decreases over time
Newton's Law of Cooling suggests that the rate at which an object cools is proportional to the difference between its current temperature and the ambient temperature. The greater the difference, the faster the object cools. Over time, as the temperature of the object approaches the surrounding temperature, the cooling rate decreases.
4. Calorimetry Equation
Mnemonic: “Cold Equals Hot”
Cold – mcΔT (cold object)
Equals – Equals
Hot – mcΔT (hot object)
This mnemonic represents the concept of heat exchange between two objects at different temperatures, typically used in calorimetry. When a hot object and a cold object are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter object to the colder one until thermal equilibrium is reached.
The heat gained by the cold object equals the heat lost by the hot object, and can be expressed as:
mcold c ΔTcold = mhot c ΔThot
Where:
m = mass of the object
c = specific heat capacity of the substance
ΔT = change in temperature of the object
This equation reflects the principle of conservation of energy, as the total heat remains constant in an isolated system. The mnemonic helps in recalling this idea that the heat transferred to a cold object equals the heat lost by the hot object.
|
122 videos|493 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Thermal Properties of Matter - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| $1. What are the different temperature scales and how do they compare? |  |
| $2. What are the types of thermal expansion? |  |
| $3. What factors affect specific heat capacity? |  |
| $4. What is latent heat and how does it relate to phase changes? |  |
| $5. What are the modes of heat transfer? |  |