Mnemonics: Molecular Basis of Inheritance | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
1. Key Experiments for Genetic Material
4 Experiments: Griffith’s Transformation, Avery-Mac Leod-Mc Carty’s Biochemical Characterization, Hershey-Chase’s Bacteriophage Experiment, Meselson-Stahl’s Semiconservative Replication.
Mnemonic: "Griffith Transforms, Avery Finds, Hershey Chases, Meselson Proves"
Breakdown:
- Griffith Transforms → Griffith’s 1928 experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae showed transformation (R to S strain via a “transforming principle”).
- Avery Finds → Avery-MacLeod-McCarty (1933-44) identified DNA as the transforming principle by showing DNase inhibits transformation.
- Hershey Chases → Hershey-Chase (1952) used radioactive phosphorus (DNA) and sulfur (protein) to prove DNA enters bacteria during bacteriophage infection.
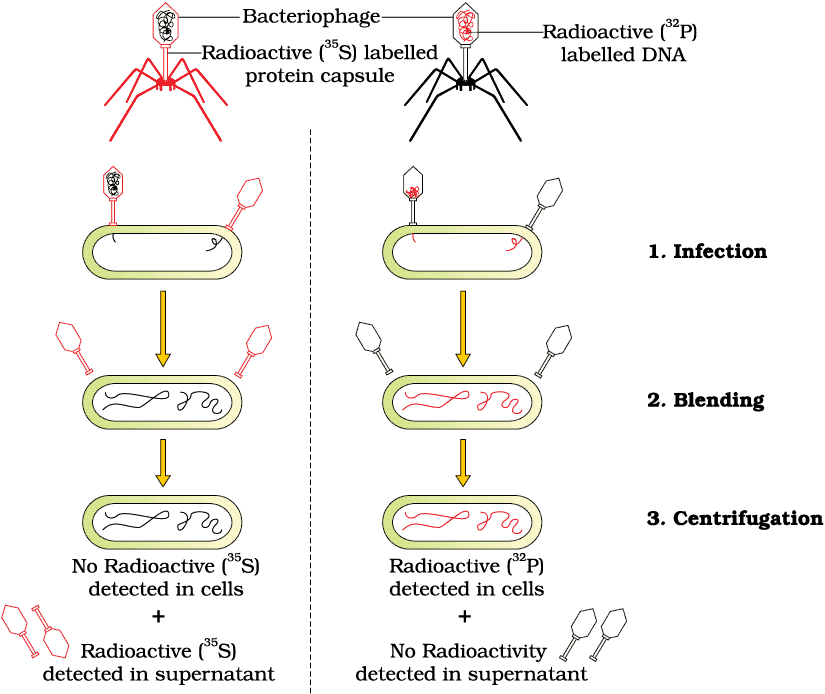 The Hershey-Chase experiment
The Hershey-Chase experiment
- Meselson Proves → Meselson-Stahl (1958) confirmed semiconservative replication using heavy (15N) and light (14N) nitrogen in E. coli.
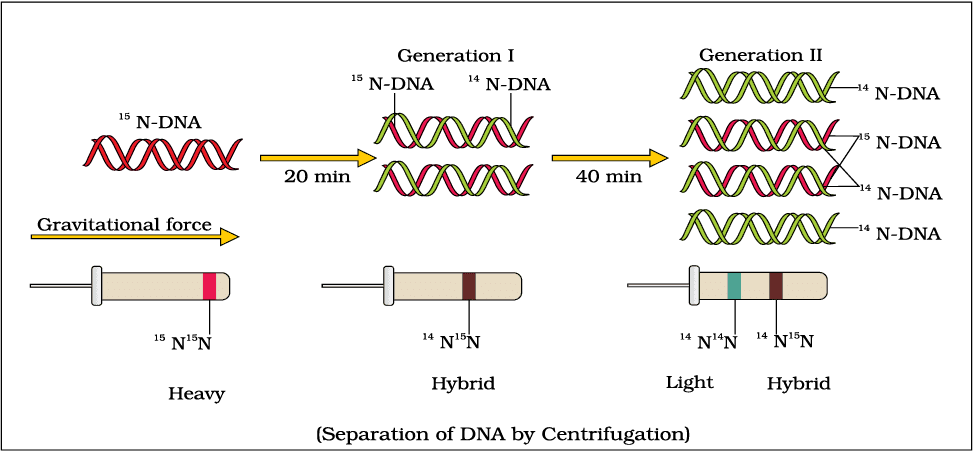 Meselson and Stahl’s Experiment
Meselson and Stahl’s Experiment
2. Polysaccharides (in Griffith’s Experiment)
Concept: Polysaccharide coat distinguishes smooth (S) and rough (R) strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Griffith’s transformation experiment.
Mnemonic: "Smooth Coats Kill, Rough Don’t"
Breakdown:
- Smooth → S strain has a polysaccharide (mucous) coat, making it virulent (kills mice).
- Coats → The polysaccharide coat is key to the S strain’s virulence.
- Kill → S strain causes pneumonia, leading to death in mice.
- Rough Don’t → R strain lacks the polysaccharide coat, is non-virulent, and doesn’t kill mice.
3. DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
Concepts: Semiconservative replication, replication fork, DNA-dependent DNA polymerase, continuous/discontinuous synthesis, DNA ligase, occurs in cytosol.
Mnemonic: "Fork Opens, Poly Builds Fast"
Breakdown:
Fork → Replication fork where DNA strands separate.
Opens → Strands act as templates (3’→5’ for continuous, 5’→3’ for discontinuous synthesis).
Poly → DNA-dependent DNA polymerase catalyzes 5’→3’ polymerization.
Builds → Semiconservative replication produces two daughter DNAs (one parental, one new strand).
Fast → Rapid process in the cytosol.
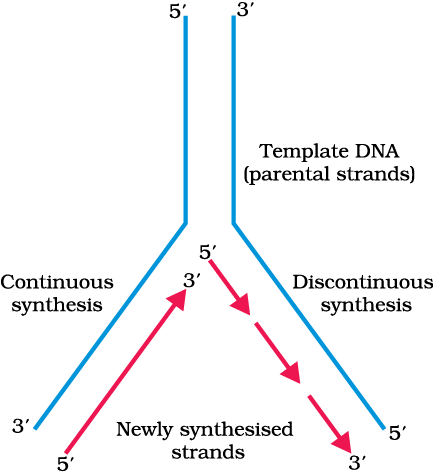 Replicating Fork
Replicating Fork
4. DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
Concepts: Semiconservative replication, replication fork, DNA polymerase, occurs in nucleus during S-phase, coordinated with cell cycle.
Mnemonic: "Forks Move, Nucleus Works Slow"
Breakdown:
Forks → Replication forks form where strands separate.
Move → Strands are templates for semiconservative replication.
Nucleus → Replication occurs in the nucleus at S-phase.
Works → DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands (5’→3’).
Slow → Slower due to larger genome and cell cycle coordination.
5. Transcription in Prokaryotes
Concepts: Single RNA polymerase, promoter, template strand, polycistronic mRNA, no processing, coupled with translation, cytosolic.
Mnemonic: "One Pen Copies, mRNA Goes"
Breakdown:
One → Single DNA-dependent RNA polymerase transcribes all RNAs.
Pen → Promoter (5’-end) binds polymerase to start transcription.
Copies → Template strand (3’→5’) is copied into RNA (A-U, G-C pairing).
mRNA → Polycistronic mRNA codes for multiple proteins.
Goes → mRNA is functional immediately, used in cytosolic translation (coupled).
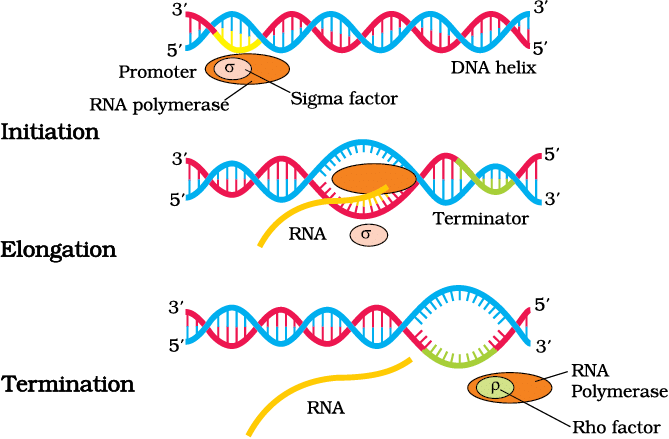 Process of Transcription in Bacteria
Process of Transcription in Bacteria
6. Transcription in Eukaryotes
Concepts: Three RNA polymerases, nuclear transcription, monocistronic hnRNA, splicing, capping, tailing, transport to cytoplasm.
Mnemonic: "Three Pens Slice, Cap, Send"
Breakdown:
Three → Three RNA polymerases: I (rRNAs), II (hnRNA), III (tRNA, 5S rRNA, snRNAs).
Pens → Promoter-driven transcription in the nucleus.
Slice → Splicing removes introns, joining exons in hnRNA.
Cap → 5’-methyl guanosine cap and 3’-poly-A tail added.
Send → Mature, monocistronic mRNA is transported to cytoplasm.
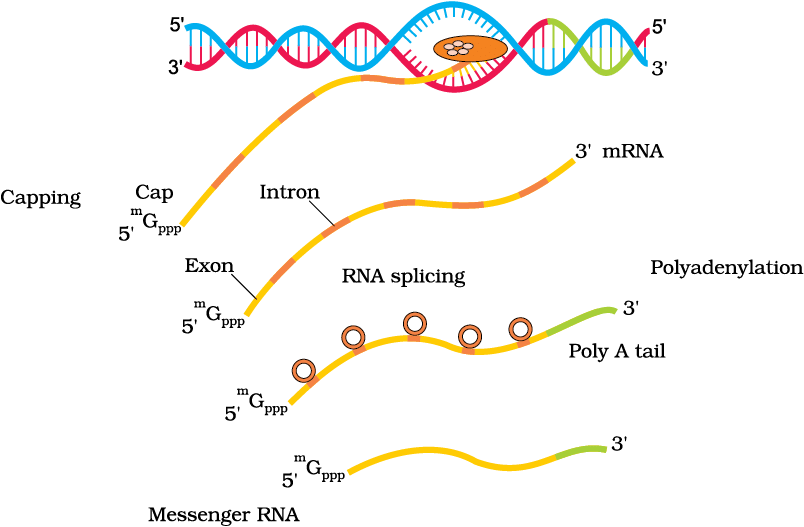 Process of Transcription in Eukaryotes
Process of Transcription in Eukaryotes
7. Translation in Prokaryotes
Concepts: 70S ribosomes, initiator tRNA (AUG), polycistronic mRNA, coupled with transcription, cytosolic, peptide bond formation.
Mnemonic: "Small Ribs Read, Proteins Form"
Breakdown:
Small → 70S ribosomes (50S + 30S).
Ribs → Ribosomes read mRNA codons, with rRNA as a ribozyme (peptide bonds).
Read → Initiator tRNA recognizes AUG, starting translation.
Proteins → Polycistronic mRNA produces multiple proteins.
Form → Peptide bonds form in initiation, elongation, termination (stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA).
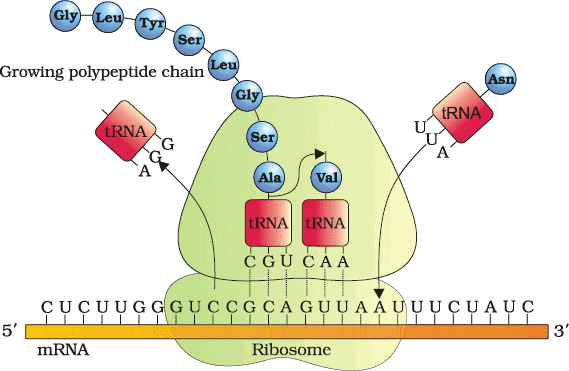 Translation
Translation
8. Translation in Eukaryotes
Concepts: 80S ribosomes, initiator tRNA (AUG), monocistronic mRNA, cytoplasmic, peptide bond formation, UTRs.
Mnemonic: "Big Ribs Scan, Proteins Build"
Breakdown:
Big → 80S ribosomes (60S + 40S).
Ribs → Ribosomes read mRNA, with rRNA as a ribozyme.
Scan → Initiator tRNA recognizes AUG, with UTRs aiding initiation.
Proteins → Monocistronic mRNA codes for one protein.
Build → Peptide bonds form in initiation, elongation, termination (stop codons).
9. Lac Operon
Concepts: Regulatory gene (i), structural genes (z, y, a), promoter, operator, repressor, inducer (lactose), negative regulation.
Mnemonic: "Lactose Frees O, Genes Make Milk"
Breakdown:
Lactose → Lactose acts as the inducer, binding the repressor.
Frees O → Repressor (from i gene) is inactivated, freeing the operator.
Genes → Structural genes z (beta-galactosidase), y (permease), a (transacetylase) are transcribed.
Make → RNA polymerase binds promoter, transcribes genes for lactose metabolism.
Milk → Refers to lactose (milk sugar) breakdown into galactose and glucose.
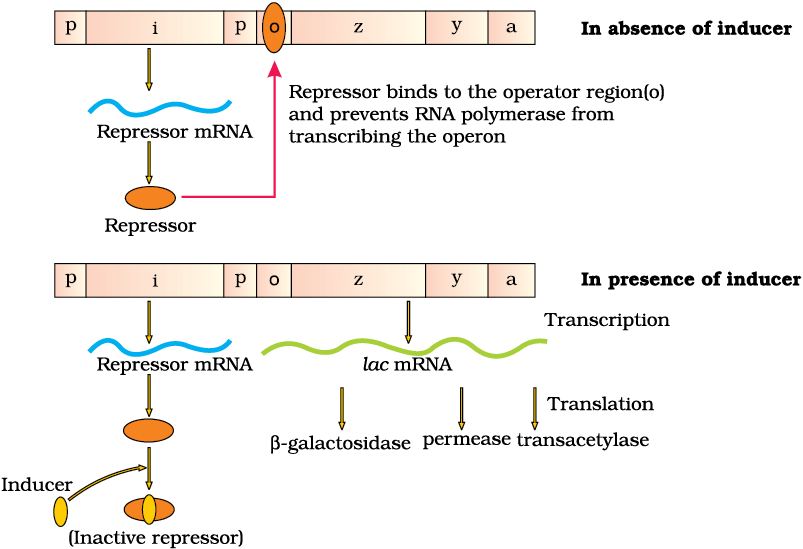 The lac Operon
The lac Operon
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the molecular basis of inheritance? |  |
| 2. How does DNA replication occur? |  |
| 3. What are the roles of RNA in the molecular basis of inheritance? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of mutations in inheritance? |  |
| 5. How do Mendel's laws relate to molecular genetics? |  |

















