Mnemonics: Biotechnology & its Applications | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
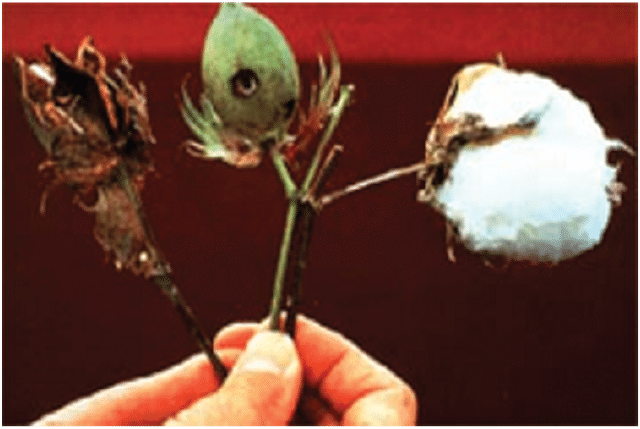
1. Bt Cotton and Cry Genes
Concepts: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) produces Cry proteins (toxins) that kill insects (lepidopterans, coleopterans, dipterans); Cry genes (cryIAc, cryIIAb, cryIAb) cloned into crops like cotton; inactive protoxin activates in insect gut (alkaline pH), forming pores, causing cell lysis; Bt cotton resists pests, reducing insecticide use.
Mnemonic: "Bt’s Cry Toxin Rips Bollworms’ Guts, Cotton Booms"
Breakdown:
Bt’s → Bacillus thuringiensis, the bacterium producing Cry proteins.
Cry Toxin → Cry genes (cryIAc, cryIIAb for cotton bollworms; cryIAb for corn borer) encode toxic proteins, inactive as protoxins in Bt.
Rips → Protoxin activates in insect gut (alkaline pH), forming pores in midgut epithelial cells, causing swelling, lysis, and death.
Bollworms’ Guts → Specifically targets lepidopterans (e.g., tobacco budworm, armyworm), also coleopterans (beetles), dipterans (flies).
Cotton → Bt cotton, genetically modified with Cry genes, resists pests without chemical insecticides.
Booms → Bt cotton boosts yields by preventing pest damage, supporting the Green Revolution.

2. RNA Interference (RNAi)
Concepts: RNAi silences mRNA using double-stranded RNA (dsRNA); used in transgenic tobacco to resist nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita); Agrobacterium vectors introduce nematode-specific genes, producing sense/anti-sense RNA to form dsRNA, blocking nematode mRNA translation.
Mnemonic: "RNAi Mutes Nema, Tobacco Grows"
Breakdown:
RNAi → RNA interference, a eukaryotic defense mechanism.
Mutes → dsRNA binds and silences specific mRNA, preventing translation.
Nema → Meloidogyne incognita, a nematode reducing tobacco yield.
Tobacco → Transgenic tobacco uses Agrobacterium to express dsRNA.
Grows → dsRNA kills nematodes, protecting tobacco roots.

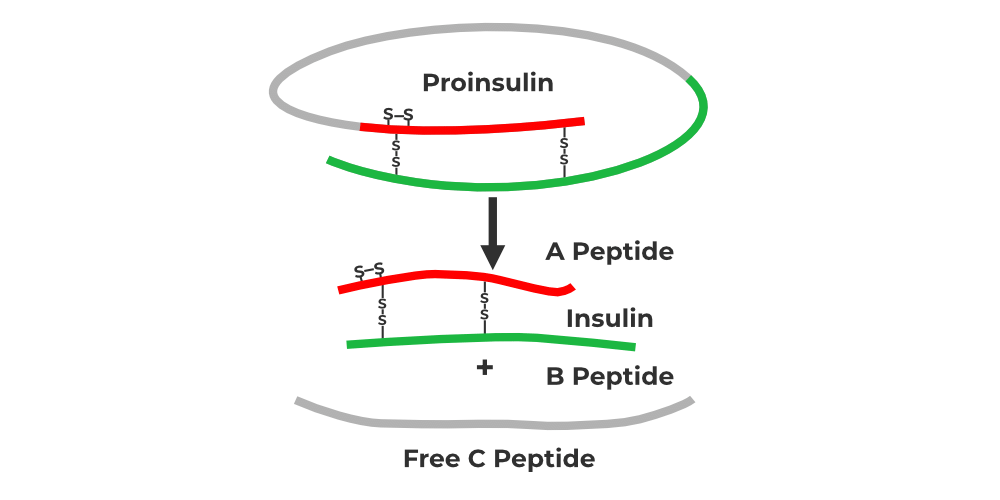
3. Genetically Engineered Insulin
Concepts: Recombinant DNA produces human insulin in E. coli; insulin has A and B chains linked by disulfide bonds; pro-insulin with C peptide is matured by removing C peptide; Eli Lilly (1983) used plasmids to produce A and B chains separately, then combined them.
Mnemonic: "E. coli Builds Insulin, Chains Bond"
Breakdown:
E. coli → Bacterium engineered for human insulin production.
Builds → Eli Lilly (1983) used plasmids to produce A and B chains in E. coli.
Insulin → Mature insulin lacks C peptide, unlike pro-insulin.
Chains → A and B chains are produced separately.
Bond → Chains combine via disulfide bonds, forming functional insulin.
4. Patents and Biopiracy
Concepts: Patents on biotech products (e.g., Basmati rice, turmeric, neem) raise ethical issues; biopiracy is unauthorized use of bio-resources/traditional knowledge without compensation; Basmati rice patent (1997) by a US company claimed Indian varieties; Indian Patents Bill and GEAC prevent biopiracy.
Mnemonic: "Basmati, Neem, Turmeric Nabbed, Patents Snatch, Laws Defend"
Breakdown:
Basmati → 27 Indian Basmati varieties patented by a US company (1997).
Neem → Indian neem, targeted for patenting traditional uses.
Turmeric → Indian turmeric, subject to biopiracy for medicinal applications.
Nabbed → Biopiracy steals bio-resources and traditional knowledge without authorization.
Patents → Unfair patents claim Indian resources as “novelties,” restricting farmers.
Snatch → Patents aggressively take control of traditional bio-resources.
Laws → Indian Patents Bill and GEAC defend against exploitation.
Defend → Legal measures protect India’s biodiversity and knowledge.
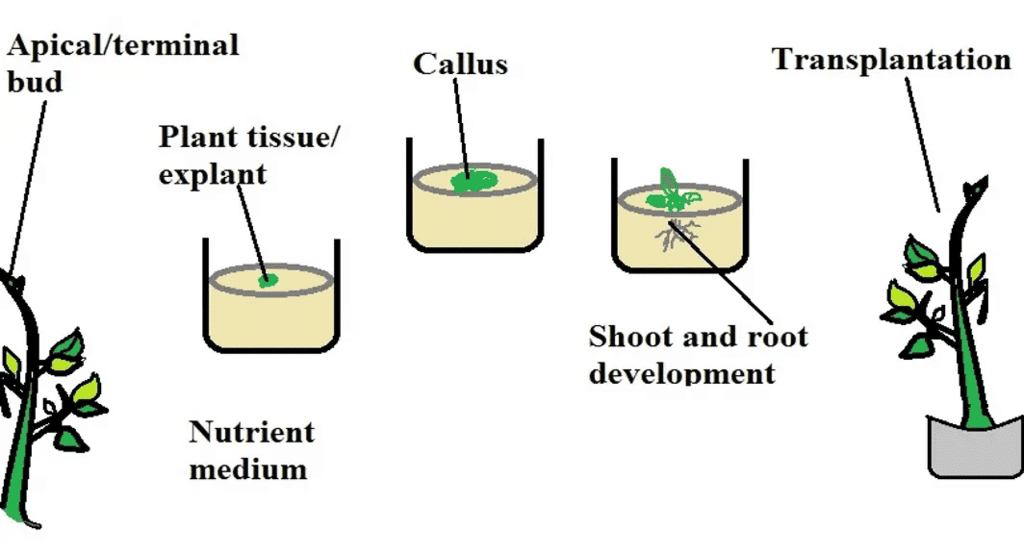
5. Tissue Culture and Micropropagation
Concepts: Tissue culture regenerates plants from explants via totipotency; micropropagation produces identical somaclones; uses nutrient media with sucrose, salts, vitamins, auxins, cytokinins; meristem culture yields virus-free plants (e.g., banana, sugarcane).
Mnemonic: "Explant Grows, Clones Bloom, Meristem Cleans"
Breakdown:
Explant → Any plant part (e.g., cell, tissue) used in tissue culture.
Grows → Totipotency allows explants to regenerate whole plants in nutrient media (sucrose, auxins, cytokinins).
Clones → Micropropagation produces identical somaclones (e.g., tomato, banana).
Bloom → Thousands of plants grow rapidly for commercial use.
Meristem → Apical/axillary meristems, virus-free, cultured to produce healthy plants (e.g., sugarcane).
Cleans → Meristem culture removes viruses, yielding disease-free plants.
6. Gene Therapy
Concepts: Gene therapy corrects genetic defects by inserting normal genes; first used in 1990 for adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency; functional ADA cDNA introduced into lymphocytes via retroviral vectors; embryonic gene insertion could be permanent.
Mnemonic: "ADA Gene Fixes Immune, Lymphocytes Heal"
Breakdown:
ADA → Adenosine deaminase deficiency, a hereditary immune disorder.
Gene → Functional ADA cDNA corrects the defective gene.
Fixes → Gene therapy inserts normal genes to restore function.
Immune → ADA is crucial for immune system function.
Lymphocytes → Engineered lymphocytes receive ADA cDNA via retroviral vectors.
Heal → Periodic infusions treat patients; embryonic therapy could be permanent.
7. Transgenic Animals
Concepts: Transgenic animals (e.g., mice) have foreign genes; used to study physiology, diseases (cancer, Alzheimer’s), biological products (α-1-antitrypsin), vaccine safety (polio), and toxicity testing; Rosie (transgenic cow) produced human alpha-lactalbumin milk.
Mnemonic: "Mice Genes Probe Disease, Rosie Milks Proteins"
Breakdown:
Mice → Over 95% of transgenic animals are mice.
Genes → Foreign genes inserted to study physiology (e.g., insulin-like growth factor).
Probe → Transgenic animals model diseases (cancer, cystic fibrosis).
Disease → Study gene roles in disease development.
Rosie → Transgenic cow producing human alpha-lactalbumin milk (2.4 g/L).
Milks → Biological products (e.g., α-1-antitrypsin for emphysema) and vaccine/toxicity testing.
Proteins → Human proteins from transgenic animals aid medical treatments.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Biotechnology & its Applications - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is biotechnology and how is it applied in various fields? |  |
| 2. What are some common techniques used in biotechnology? |  |
| 3. How does biotechnology contribute to medicine? |  |
| 4. What are the ethical concerns surrounding biotechnology? |  |
| 5. What role does biotechnology play in environmental conservation? |  |
















