Mnemonics: Ecosystem | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Upright vs. Inverted Pyramids |

|
| 2. Steps of Decomposition |

|
| 3. Detritus Food Chain (DFC) |

|
| 4. Grazing Food Chain (GFC) |

|
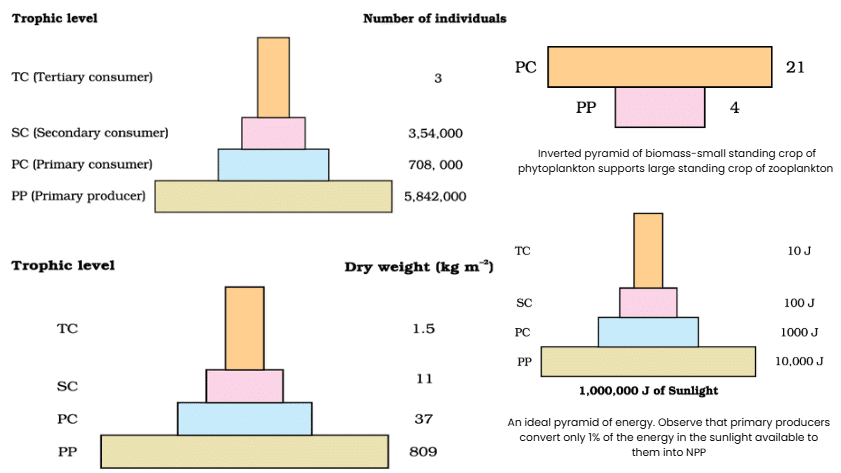
1. Upright vs. Inverted Pyramids
Types: Number Pyramid, Biomass Pyramid, Energy Pyramid
Mnemonic: "Nice Big Elephants"
Breakdown:
Nice → Number Pyramid (upright in grasslands/forests, inverted in tree-based ecosystems)
Big → Biomass Pyramid (upright in forests, inverted in aquatic ecosystems)
Elephants → Energy Pyramid (always upright, never inverted)
Orientation Mnemonic: "Energy Never Inverts, Biomass Sometimes, Numbers Rarely"
Energy Never Inverts: Energy pyramid is always upright.
Biomass Sometimes: Biomass pyramid is inverted in aquatic ecosystems (e.g., phytoplankton < zooplankton).
Numbers Rarely: Number pyramid is inverted in tree-based ecosystems (e.g., one tree supports many insects).
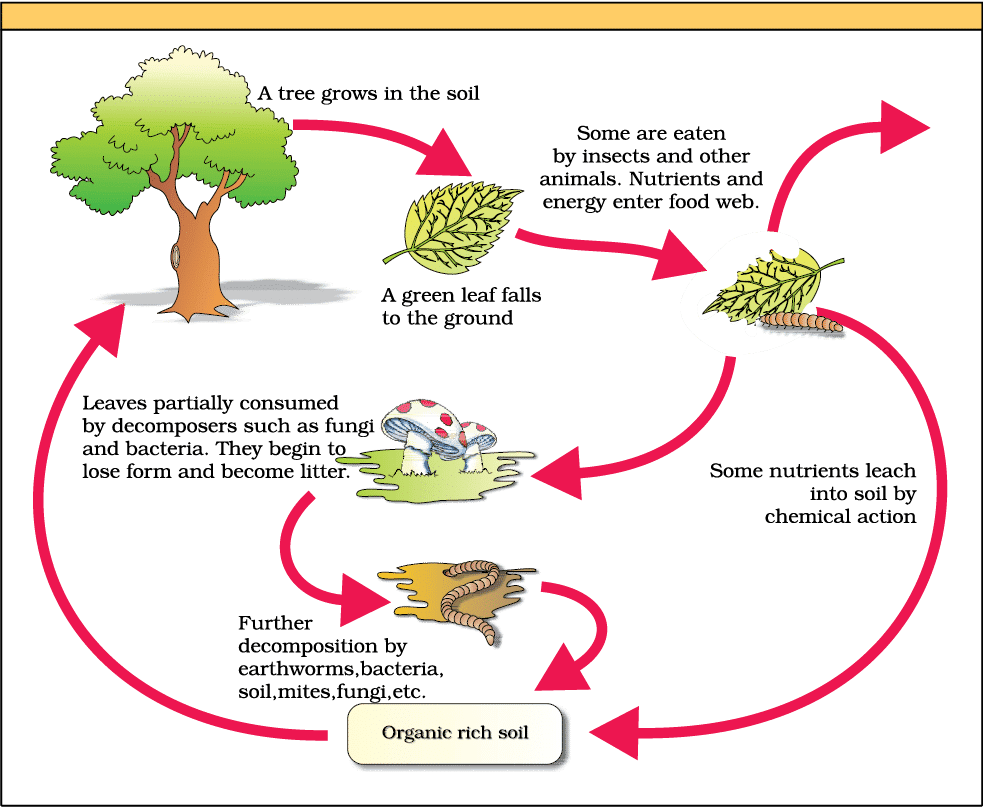
2. Steps of Decomposition
Steps: Fragmentation, Leaching, Catabolism, Humification, Mineralisation
Mnemonic: "Funny Lions Can Hunt Mice"
Breakdown:
Funny → Fragmentation (detritivores break detritus into smaller particles)
Lions → Leaching (water-soluble nutrients wash into soil)
Can → Catabolism (enzymes degrade detritus into simpler substances)
Hunt → Humification (formation of humus, a nutrient reservoir)
Mice → Mineralisation (microbes release inorganic nutrients)
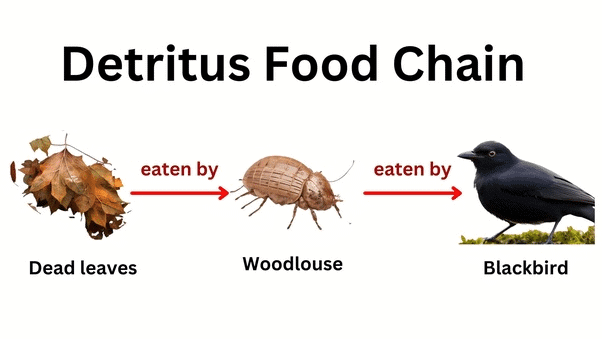
3. Detritus Food Chain (DFC)
Components: Dead Matter, Decomposers, Degradation, Nutrient Return
Mnemonic: "Dead Days Decompose Deeply"
Breakdown:
Dead → Dead Matter (detritus, starting point of DFC)
Days → Decomposers (fungi, bacteria break down detritus)
Decompose → Degradation (breakdown into simpler substances)
Deeply → Nutrient Return (nutrients recycled to producers)
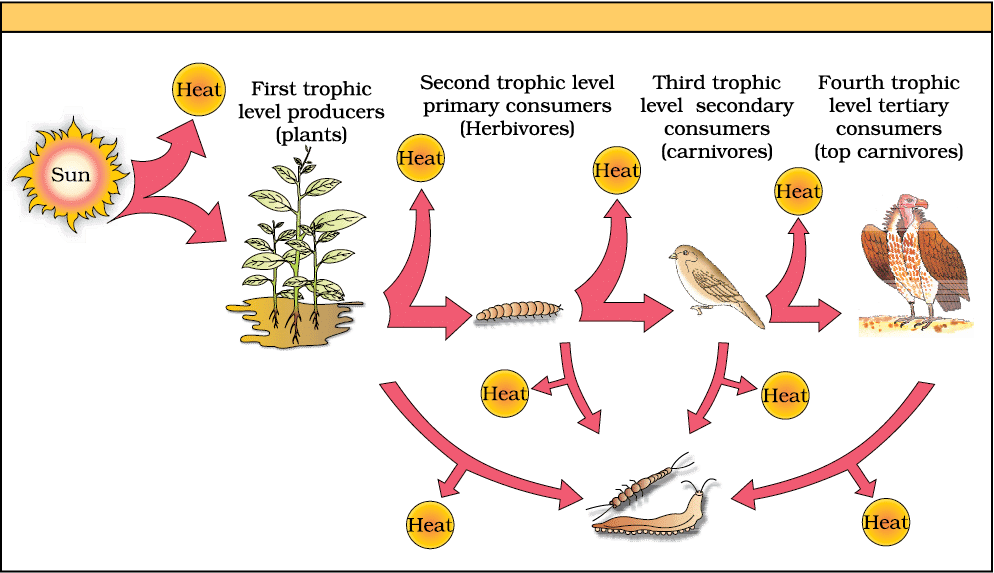
4. Grazing Food Chain (GFC)
Components: Producers, Primary Consumers, Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers
Mnemonic: "Green Goats Make Meat"
Breakdown:
Green → Producers (plants, start of GFC)
Goats → Primary Consumers (herbivores, e.g., goats)
Make → Secondary Consumers (primary carnivores, e.g., frogs)
Meat → Tertiary Consumers (top carnivores, e.g., snakes)
Tip to Remember:
GFC starts with Green (living plants).
DFC starts with Dead (non-living organic matter).
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Ecosystem - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is an ecosystem and why is it important for the NEET exam? |  |
| 2. How do energy flow and nutrient cycling occur in an ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of ecosystems covered in the NEET syllabus? |  |
| 4. How does human activity impact ecosystems? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of ecological succession that NEET students should know? |  |




















