Mnemonics: Thermodynamics | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Types of Systems |

|
| First Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| State Functions |

|
| Types of Processes |

|
| Spontaneous Processes |

|
| Second Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| Third Law of Thermodynamics |

|
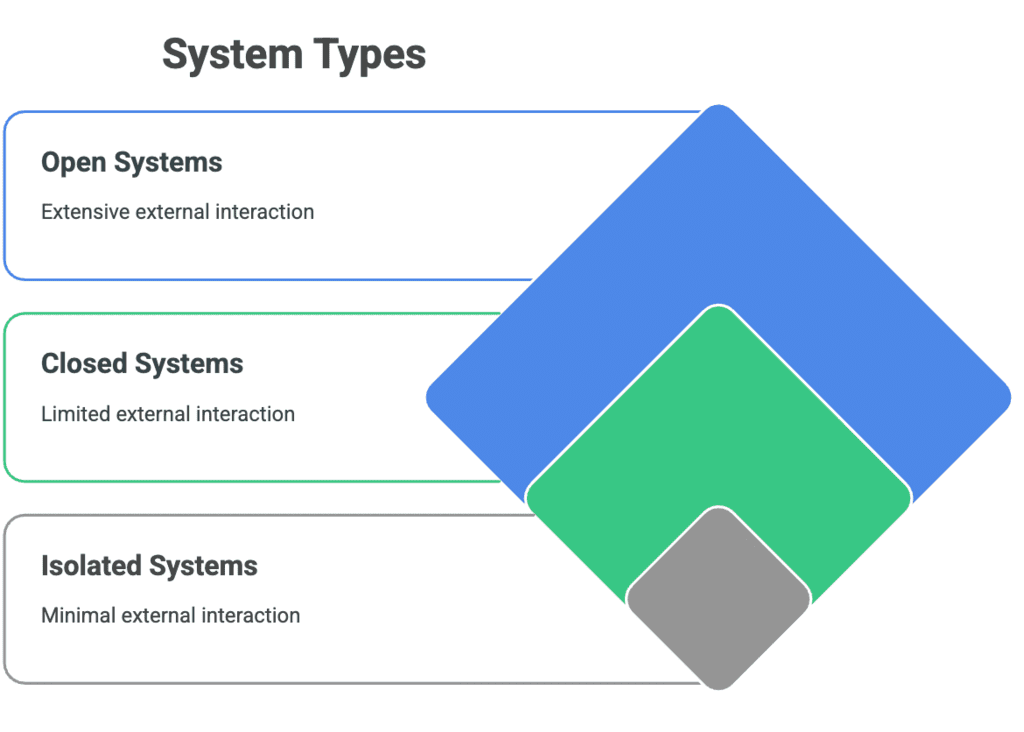
Types of Systems
Types: Open, Closed, Isolated
Mnemonic:"Open, Closed, Isolated—Systems Defined, Energy Controlled!"
Explanation:
Open = Open system allows both energy and matter to be exchanged with the surroundings.
Closed = Closed system allows only energy to be exchanged, not matter.
Isolated = Isolated system does not exchange either energy or matter with the surroundings.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Mnemonic: "Energy’s Conserved, Heat and Work, Together Preserved!"
Explanation:
Energy’s Conserved = The first law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted.
Heat and Work = Energy is transferred as heat or work between the system and surroundings.
Together Preserved = The change in internal energy (ΔU) equals the heat added to the system (Q) minus the work done by the system (W): ΔU = Q - W.
State Functions
Types: Pressure, Volume, Temperature, Enthalpy
Mnemonic: "Pipes Vent To Engines"
Breakdown:
- Pipes - Pressure
- Vent - Volume
- To - Temperature
- Engines - Enthalpy
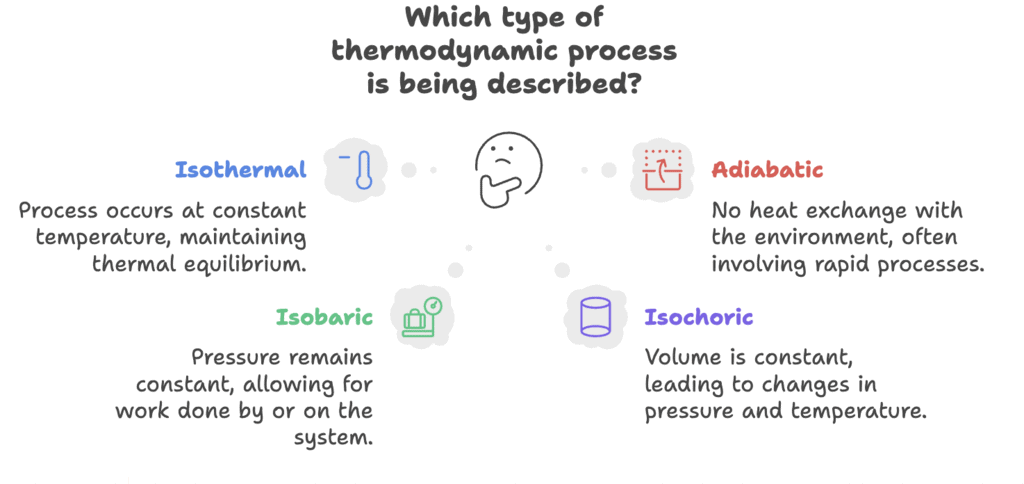
Types of Processes
Types: Isothermal, Adiabatic, Isobaric, Isochoric
Mnemonic: "Isha Adds Ice Cubes"
Breakdown:
- Isha - Isothermal
- Adds - Adiabatic
- Ice - Isobaric
- Cubes - Isochoric
Spontaneous Processes
Mnemonic: "Spontaneity’s Flow, Energy Goes Low!"
Explanation:
Spontaneity’s Flow = A spontaneous process occurs naturally without external influence.
Energy Goes Low = For a process to be spontaneous, the system must move towards a state of lower energy.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Mnemonic:"Entropy’s Rise, Disorder’s the Prize!"
Explanation:
Entropy’s Rise = The second law states that the entropy (disorder) of the universe always increases.
Disorder’s the Prize = In any spontaneous process, the total entropy of the system and surroundings increases.
Third Law of Thermodynamics
Mnemonic:"Zero Entropy at Absolute Zero—Energy’s Free to Go!"
Explanation:
Zero Entropy at Absolute Zero = The third law states that the entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero (0 K) is zero.
Energy’s Free to Go = At absolute zero, the system has no disorder and no energy to be transferred.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Thermodynamics - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic laws of thermodynamics that I need to remember for NEET? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively use mnemonics to remember thermodynamic concepts for NEET? |  |
| 3. What are some common thermodynamic processes I should study for NEET? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding entropy important in thermodynamics for NEET? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of thermodynamics in real life that I should be aware of for NEET? |  |















