Mnemonics: Semiconductor Electronics | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Semiconductor Materials |

|
| Energy Bands in Solids |

|
| p-n Junction Diode Operations |

|
| Simple Circuits with Diodes |

|
| Transistor Configurations |

|
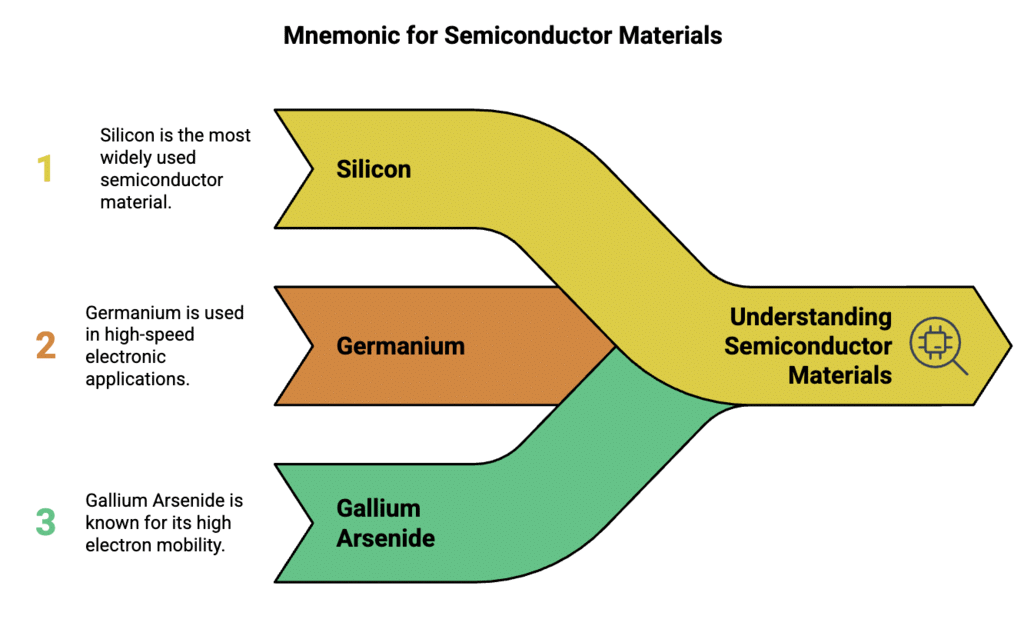
Semiconductor Materials
Types: Silicon, Germanium, Gallium Arsenide
Mnemonic: "Sonia Grips Glowing Arcs"
Breakdown:
- Sonia - Silicon
- Grips - Germanium
- Glowing Arcs - Gallium Arsenide
Silicon (Si) and Germanium (Ge) are the most commonly used elemental semiconductors.
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is a compound semiconductor, used in high-speed devices like LEDs and lasers.
These materials have 4 valence electrons and form crystalline structures that can conduct electricity under specific conditions.
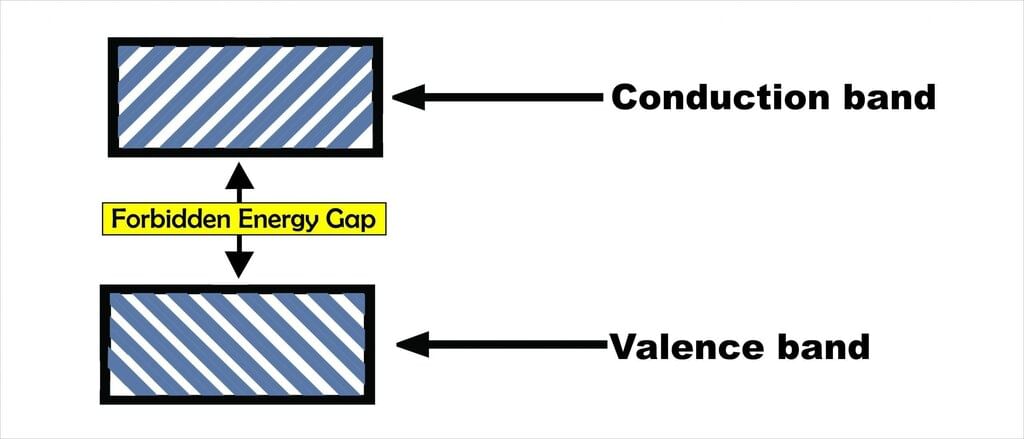
Energy Bands in Solids
Types: Valence Band, Conduction Band, Forbidden Gap
Mnemonic: "Vicky Conducts Funky Grooves"
Breakdown:
- Vicky - Valence Band
- Conducts - Conduction Band
- Funky Grooves - Forbidden Gap
Valence Band: Contains electrons involved in bonding; lower energy band.
Conduction Band: Where free electrons move and conduct electricity.
Forbidden Gap: The energy difference between valence and conduction bands.
Conductors: No gap or overlapping bands.
Insulators: Large gap.
Semiconductors: Small gap (e.g., 0.7 eV for Ge, 1.1 eV for Si).
This concept explains why semiconductors conduct only under certain conditions (like heat or light input).
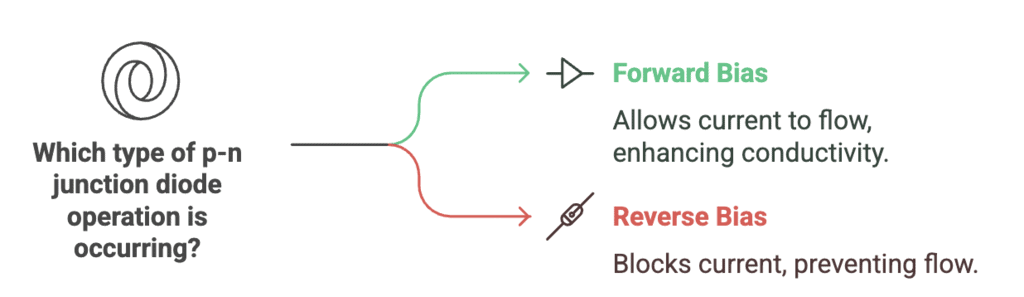
p-n Junction Diode Operations
Types: Forward Bias, Reverse Bias
Mnemonic: "Forwards Flies, Reverse Replies: No!"
Breakdown:
Forwards Flies → Forward Bias → Current flies (flows).
Reverse Replies: No! → Reverse Bias → No current (except leakage).
Forward Bias: p-side connected to positive terminal and n-side to negative. Current flows. Depletion region narrows.
Reverse Bias: p-side to negative, n-side to positive. No significant current, but reverse saturation current flows. Depletion region widens.
This is the working principle behind rectifiers and Zener diodes.
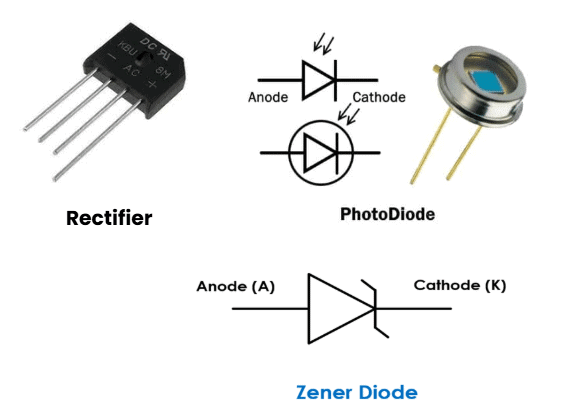
Simple Circuits with Diodes
Types: Rectifier, Zener Diode, Photodiode
Mnemonic: "Ravi Zerox Photon Beams"
Breakdown:
- Ravi - Rectifier
- Zerox - Zener Diode
- Photon Beams - Photodiode
Rectifier: Converts AC to DC using diodes. Half-wave and Full-wave types.
Zener Diode: Special diode used in reverse bias to maintain constant voltage → voltage regulation.
Photodiode: Converts light into current, used in sensors and optical devices.
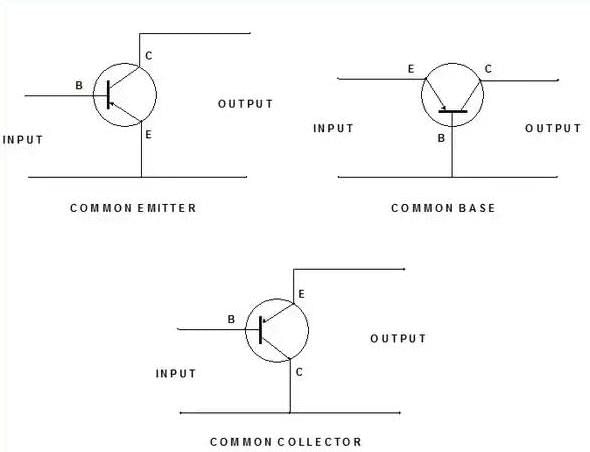
Transistor Configurations
Types: Common Emitter, Common Base, Common Collector
Mnemonic: "Clever Engineers Build Circuits"
Breakdown:
- Clever Engineers - Common Emitter
- Build - Common Base
- Circuits - Common Collector
These are three ways to connect transistors in circuits, each with unique characteristics:
Common Emitter (CE):
Most commonly used.
High voltage and current gain.
Phase shift of 180°.
Common Base (CB):
Low input impedance, high voltage gain.
No phase shift.
Used in high-frequency applications.
Common Collector (CC):
High input impedance, low output impedance.
No voltage gain, used for buffering.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Semiconductor Electronics - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic components of a semiconductor? |  |
| 2. How does doping affect the conductivity of semiconductors? |  |
| 3. What is the role of p-n junctions in semiconductor devices? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of semiconductors in electronics? |  |
| 5. How do temperature changes affect semiconductor behavior? |  |




















