Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Mathematics Class 6 ICSE > Revision Notes: Data Handling Including Pictograph and Bar Graph
Revision Notes: Data Handling Including Pictograph and Bar Graph | Mathematics Class 6 ICSE PDF Download
Data Handling (Statistics and Graphs)
- Each number collected for required information is called "data"
- Statistical data can be represented in many ways, e.g. in the form of a table, pictures, graphs, figures, etc.
- In general Bar graphs [Column Graph], Pie graph [Pie chart], Line graph, Pictograph, Histogram are used for representation of data.
Various Types of Graphical Representation of Data
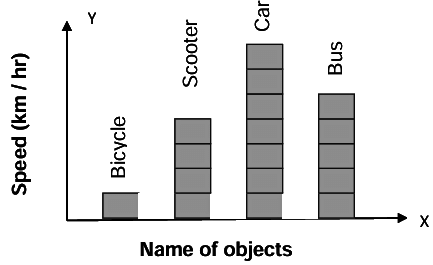
Bar graph- It is the simplest and most widely used graph, in which data is represented by heigth of rectangular cubes
- Take parameters along x-axis and y-axis
- All bars should be of same width.
- Same spaces should be left between the consecutive bars.

Pie graph
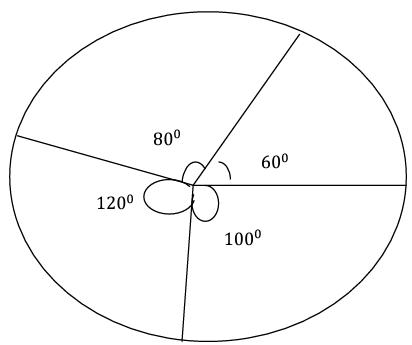
- It is a pictorial representation of numerical data, where the data is represented by sectors of circle.
- An angle whose vertex is a central angle is called "central angle
- Calculate the central angle for each component. = (value of each component / Total value of all components) × 360

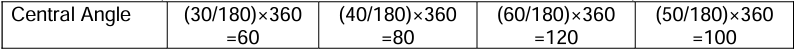
Line graph
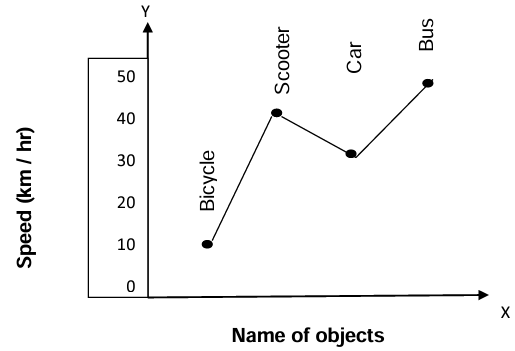
- It is a pictorial representation of numerical data, where the data is represented by points (thick points) and then joined by line segments
- An angle whose vertex is a central angle is called "central angle
- Calculate the central angle for each component. = (value of each component / Total value of all components) × 360

The document Revision Notes: Data Handling Including Pictograph and Bar Graph | Mathematics Class 6 ICSE is a part of the Class 6 Course Mathematics Class 6 ICSE.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
44 videos|201 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Data Handling Including Pictograph and Bar Graph - Mathematics Class 6 ICSE
| 1. What is a pictograph, and how is it used in data handling? |  |
Ans. A pictograph is a type of graph that uses pictures or symbols to represent data. Each picture or symbol corresponds to a specific quantity. For example, if one apple symbol represents 5 apples, then three apple symbols would represent 15 apples. Pictographs are helpful for visualizing data in a simple and engaging way, making it easier for people to understand and interpret the information presented.
| 2. How do you create a bar graph? |  |
Ans. To create a bar graph, follow these steps:
1. Determine the data you want to represent.
2. Choose a scale that suits your data range.
3. Draw two axes: a vertical axis (y-axis) for the values and a horizontal axis (x-axis) for the categories.
4. Label each axis appropriately.
5. Draw bars for each category, making sure the height of each bar corresponds to the value it represents.
6. Finally, add a title to your graph to indicate what the data represents.
| 3. What are the advantages of using bar graphs over pictographs? |  |
Ans. Bar graphs have several advantages over pictographs. They can represent a larger range of data values and allow for easier comparison between different categories, as the height of the bars can be precisely measured. Bar graphs can also include negative values, which pictographs cannot easily depict. Additionally, bar graphs can accommodate more complex data sets, making them versatile for various types of analysis.
| 4. How can you interpret data from a pictograph? |  |
Ans. To interpret data from a pictograph, first identify the symbols used and what each symbol represents in terms of quantity. Then, count the number of symbols present for each category and multiply by the value represented by each symbol. This will give you the total quantity for each category. Lastly, compare these totals to understand trends, differences, or similarities in the data presented.
| 5. What should you consider when choosing between a pictograph and a bar graph? |  |
Ans. When choosing between a pictograph and a bar graph, consider the complexity of your data, the audience, and the clarity needed for interpretation. If your data is simple and has a limited range, a pictograph may be more visually appealing and easier to understand. However, if your data requires precise comparisons or includes a wider range of values, a bar graph would be more appropriate. Always consider the audience's familiarity with the graph type as well.
Related Searches
















