Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Physics Class 6 ICSE > Revision Notes: Force
Revision Notes: Force | Physics Class 6 ICSE PDF Download
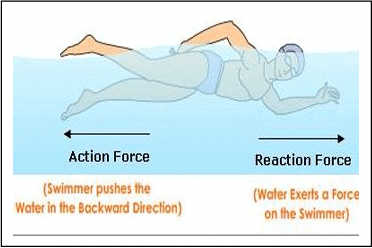
Force is a push or pull that can
a. Change the state of motion (a and b)
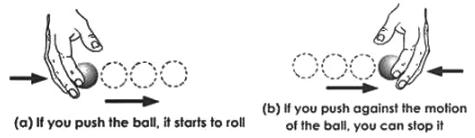 b. Change the shape
b. Change the shape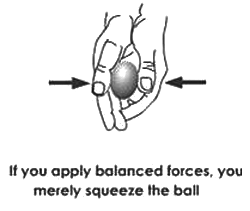
Types of forces
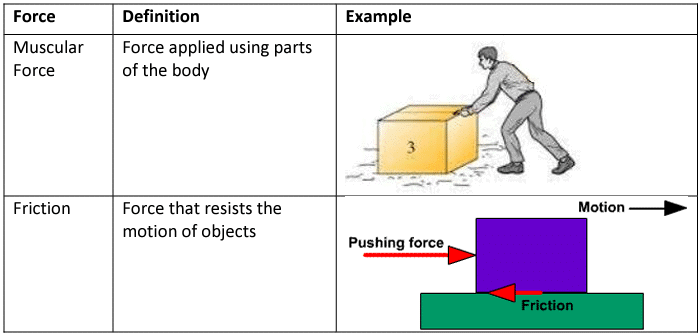
a. Contact forces
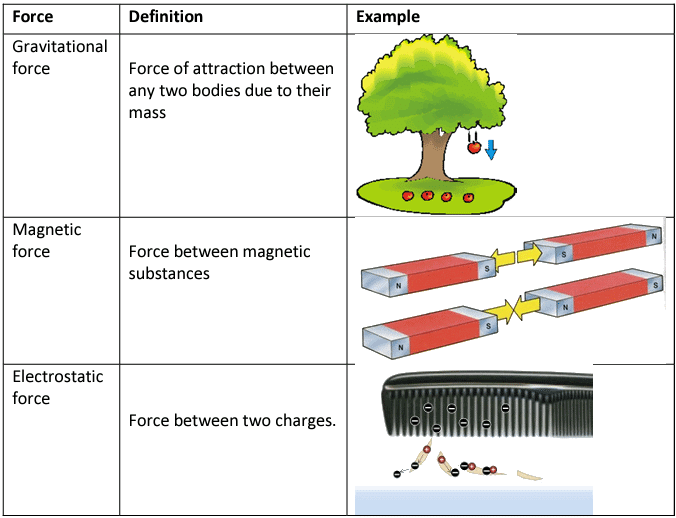
b. Non-contact forces
SI unit : newton (N)
1 newton is that much force which produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 in a body of mass 1 kg
Non- SI unit :
- Kilogram force
1 kgf = 1000 gf
1 kgf = 9.8 N
Measurement of Force (weight)

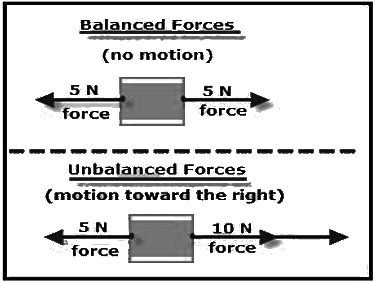
Net effect of Force
The document Revision Notes: Force | Physics Class 6 ICSE is a part of the Class 6 Course Physics Class 6 ICSE.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
8 videos|45 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Force - Physics Class 6 ICSE
| 1. What is force and how is it defined in physics? |  |
Ans. Force is a push or pull acting upon an object as a result of its interaction with another object. It is defined as any influence that can change the motion of an object, including starting, stopping, or changing its direction. The standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) is the Newton (N).
| 2. What are the different types of forces? |  |
Ans. There are several types of forces, including contact forces and non-contact forces. Contact forces require physical contact between objects and include friction, tension, and normal force. Non-contact forces, on the other hand, act at a distance and include gravitational force, magnetic force, and electrostatic force.
| 3. How does mass affect the force experienced by an object? |  |
Ans. The mass of an object affects the amount of force required to change its motion. According to Newton's second law of motion, the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = m × a). Therefore, a heavier object (greater mass) requires more force to achieve the same acceleration as a lighter object.
| 4. What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces? |  |
Ans. Balanced forces occur when two or more forces acting on an object cancel each other out, resulting in no change in motion. Unbalanced forces occur when the forces acting on an object do not cancel out, causing the object to accelerate or change direction. For example, if a box is pushed with equal force from both sides, it remains still (balanced). If more force is applied on one side, it will move (unbalanced).
| 5. How can we observe the effects of force in our daily lives? |  |
Ans. We observe the effects of force in various everyday activities. For instance, when we push a shopping cart, we apply a force that moves it forward. Similarly, when we kick a ball, our foot applies a force that sends the ball flying. Even simple actions like opening a door or lifting a backpack demonstrate the application of force in real life.
Related Searches





















