Mnemonics: Electromagnetic Induction | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Key Laws of Electromagnetic Induction |

|
| 2. Types of Induction |

|
| 3. Factors Affecting Induced EMF |

|
| 4. Units in Electromagnetic Induction |

|
| 5. Applications of Electromagnetic Induction |

|
1. Key Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
Types: Faraday’s First Law, Faraday’s Second Law, Lenz’s Law
Mnemonic: "Funny Friends Love-magnets"
Funny – Faraday’s First Law
Friends – Faraday’s Second Law
Love-magnets – Lenz’s Law
This mnemonic helps you remember the three main laws in electromagnetic induction:
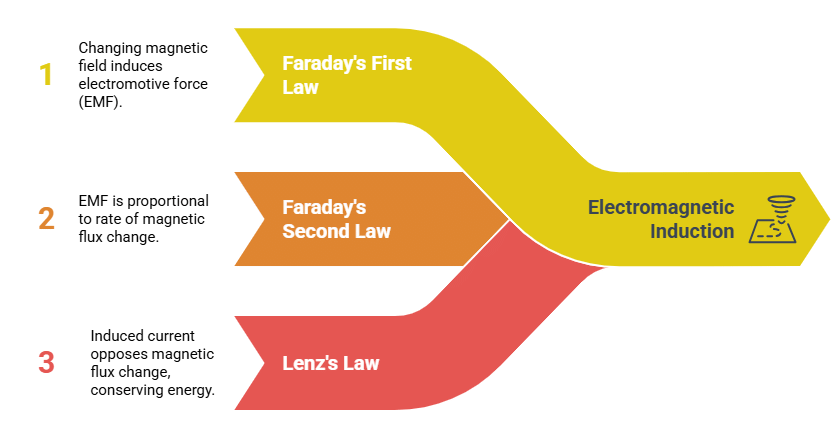
Faraday’s First Law: A changing magnetic field induces an EMF.
Faraday’s Second Law: The induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
Lenz’s Law: The direction of the induced current opposes the change in magnetic flux, conserving energy.
2. Types of Induction
Types: Self Induction, Mutual Induction
Mnemonic: "Selfie Mode"
Selfie – Self Induction
Mode – Mutual Induction
This mnemonic helps you easily remember the two main types of electromagnetic induction:
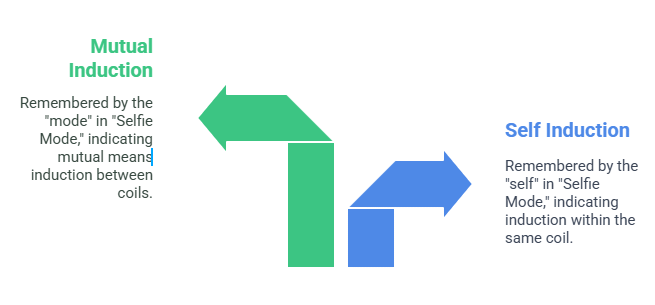
Self Induction: When a changing current in a coil induces EMF in the same coil.
Mutual Induction: When a changing current in one coil induces EMF in a nearby coil.
“Selfie Mode” links the idea of “self” and “interaction with others,” just like self-induction affects itself, and mutual induction involves others.
3. Factors Affecting Induced EMF
Types: Number of Turns, Area of Coil, Magnetic Field Strength, Angle, Time
Mnemonic: "Nina Always Makes Amazing Tea"
Nina – Number of Turns
Always – Area of Coil
Makes – Magnetic Field Strength
Amazing – Angle (between field and area vector)
Tea – Time (rate of change)
This mnemonic helps recall all key factors that influence the induced EMF in a coil:
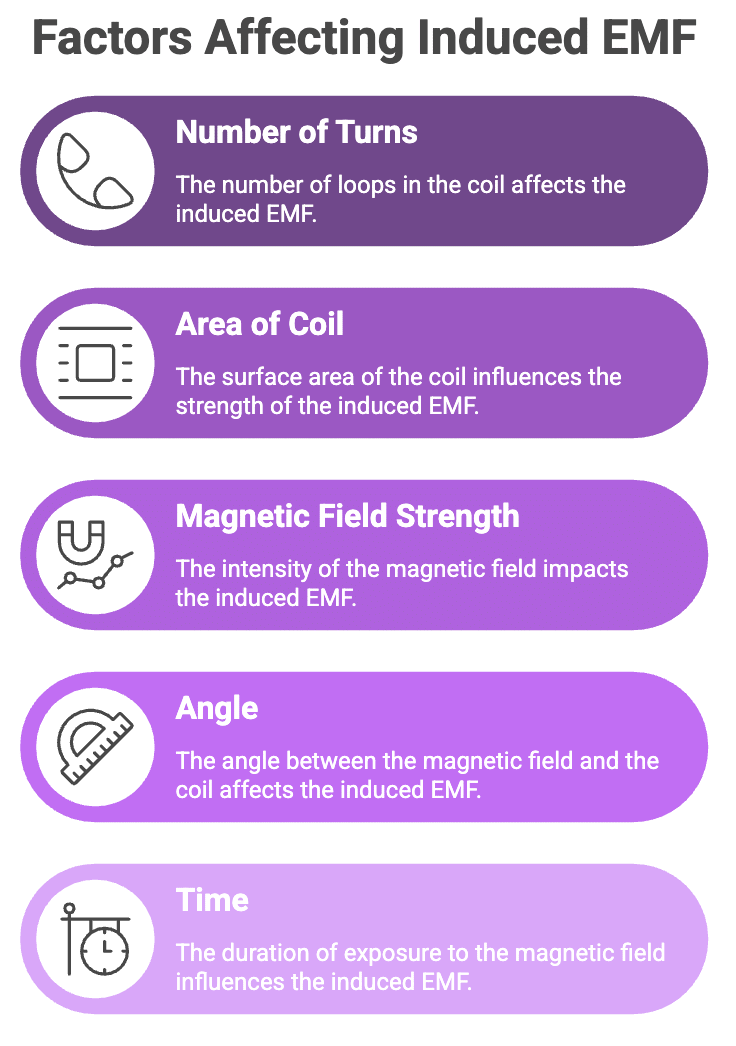
Number of Turns: More turns → more EMF
Area of Coil: Larger area → greater flux
Magnetic Field Strength: Stronger field → higher EMF
Angle: EMF depends on the angle between magnetic field and area vector
Time: Faster change → greater EMF
4. Units in Electromagnetic Induction
Types: Volt, Weber, Henry, Ampere
Mnemonic: "Victor Was Hugging Alligators"
Victor – Volt
Was – Weber
Hugging – Henry
Alligators – Ampere
This mnemonic helps lock in the four essential SI units used in electromagnetism:
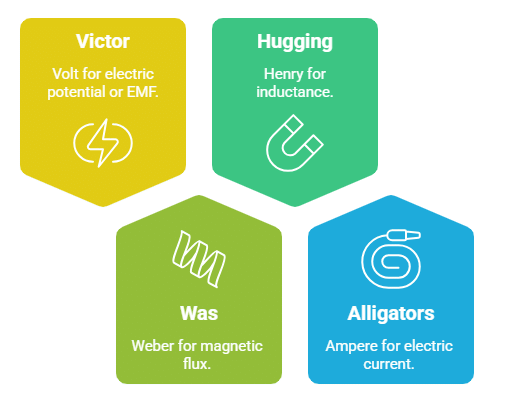
Volt (V) – for electric potential or EMF
Weber (Wb) – for magnetic flux
Henry (H) – for inductance
Ampere (A) – for electric current
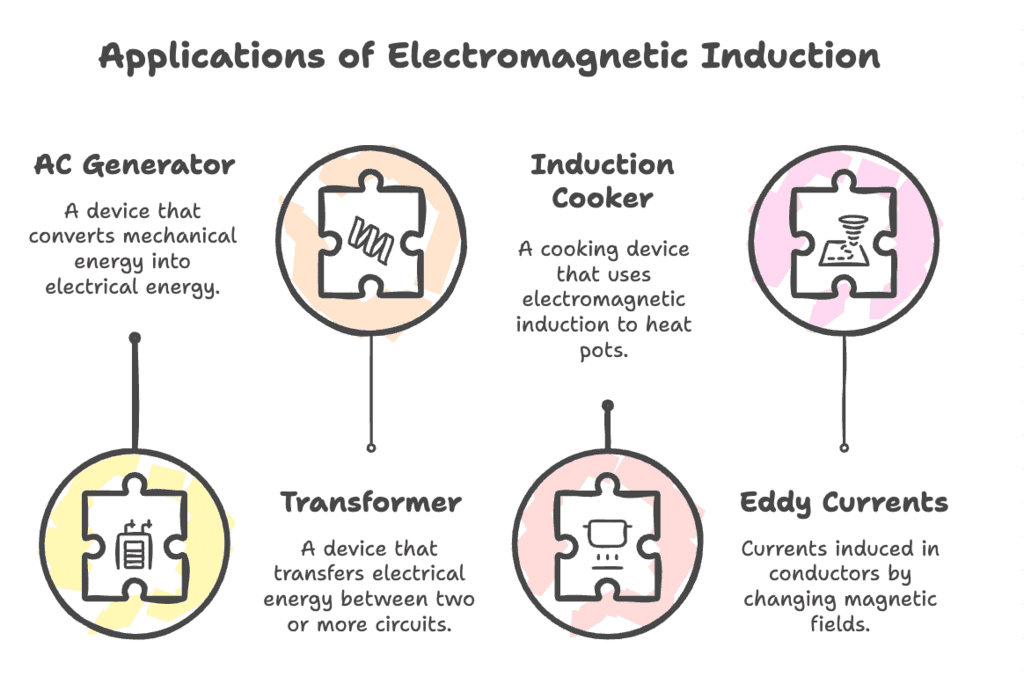
5. Applications of Electromagnetic Induction
Types: AC Generator, Transformer, Induction Cooker, Eddy Currents
Mnemonic: "Aman Took Icecream Eagerly"
Aman – AC Generator
Took – Transformer
Icecream – Induction Cooker
Eagerly – Eddy Currents
This mnemonic helps you quickly recall devices and effects related to electromagnetic induction:
AC Generator – Produces alternating current using magnetic induction
Transformer – Steps voltage up or down in AC circuits
Induction Cooker – Uses changing magnetic fields to heat metal vessels
Eddy Currents – Circular currents induced in conductors, useful or wasteful based on application
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Electromagnetic Induction - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 2. What are the applications of electromagnetic induction in daily life? |  |
| 3. How does Faraday's law relate to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 4. What is Lenz's law and how does it apply to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 5. What are some common misconceptions about electromagnetic induction? |  |




















