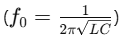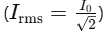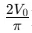Mnemonics: Alternating Current | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
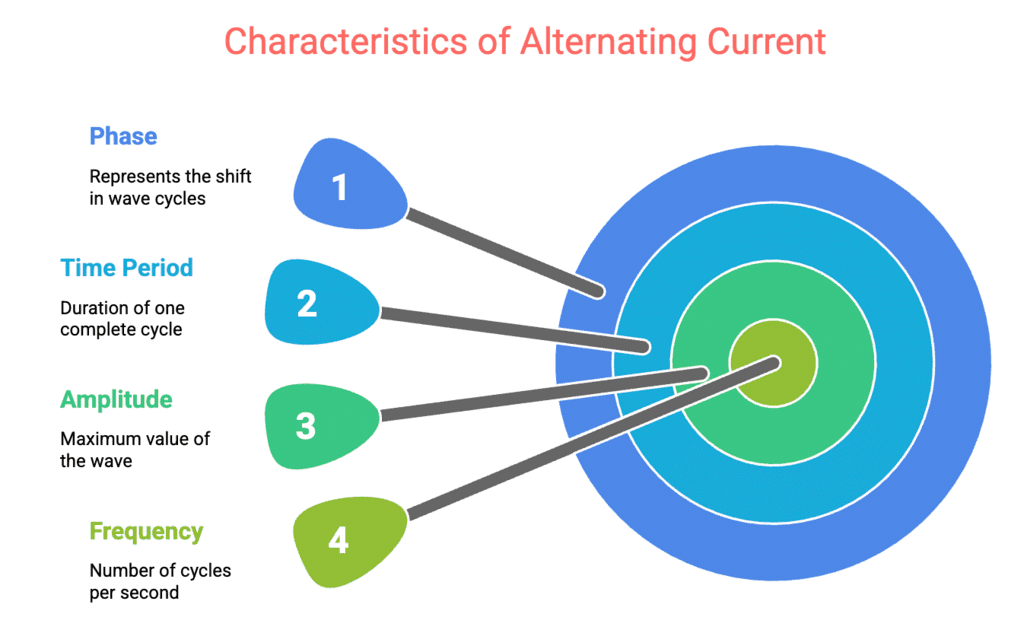
1. Characteristics of Alternating Current
Types: Frequency, Amplitude, Time Period, Phase
Mnemonic: "Frogs Always Take Picnic."
Breakdown:
Frogs → Frequency
Number of complete cycles per second (measured in Hz). It tells how fast the AC alternates.Always → Amplitude
Maximum value of current or voltage. Shows how strong the AC is at its peak.Take → Time Period
Time taken to complete one full cycle. It's the duration of one full wave.Picnic → Phase
Describes the position of the wave in time—shows whether it leads or lags another wave.
AC waves differ from DC by continuously changing direction and magnitude. These four characteristics help define the shape and behavior of an AC waveform.
2. Power in AC Circuits
Types: Instantaneous Power, Average Power, Peak Power, Power Factor
Mnemonic: "Ishaan Always Paints Perfectly"
Breakdown:
Ishaan – Instantaneous Power
Always – Average Power
Paints – Peak Power
Perfectly – Power Factor
Instantaneous Power is the power at any given moment in the AC cycle.
Average Power is the useful power consumed over one complete cycle.
Peak Power is the maximum power value reached during a cycle.
Power Factor shows how efficiently power is used; it depends on the phase difference between voltage and current.
This mnemonic helps you quickly recall the key power types and their roles in analyzing AC circuits, especially useful in exams.
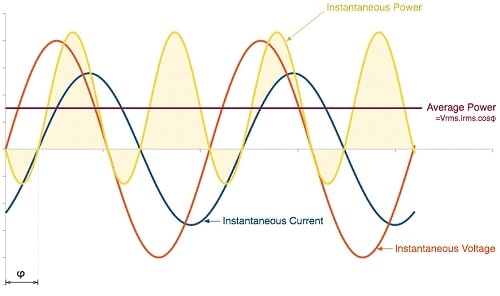
3. Phase Relations in AC Circuits
Types: Voltage in Resistor, Inductor, Capacitor
Mnemonic: "Ravi Is Confident"
Breakdown:
Ravi – Resistor → Voltage and current are in phase.
Is – Inductor → Voltage leads current.
Confident – Capacitor → Voltage lags behind current.
In AC circuits, voltage and current don't always rise and fall together.
In a resistor, they move together (in phase).
In an inductor, voltage gets ahead (leads current).
In a capacitor, voltage is behind (lags current).
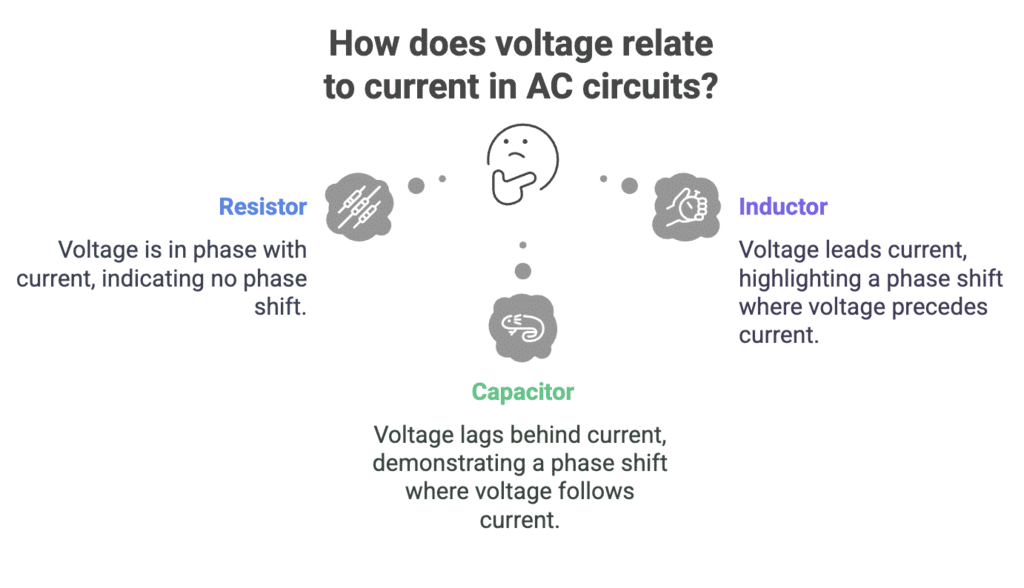
4. Impedance in Series RLC Circuit
Types: Resistance, Inductive Reactance, Capacitive Reactance, Net Impedance
Mnemonic: "Riya Is Cooking Noodles"
Breakdown:
Riya – Resistance (R)
Is – Inductive Reactance (XL= ωL)
Cooking – Capacitive Reactance (XC = 1/ωC)
Noodles – Net Impedance
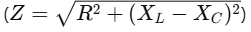
In a series RLC circuit, impedance is the total opposition to the flow of alternating current:
Resistance (R) opposes the current uniformly.
Inductive Reactance (XL) arises due to inductance and causes the current to lag behind the voltage.
Capacitive Reactance (XC) arises due to capacitance and causes the current to lead the voltage.
Net Impedance (Z) is the combination of all these opposing factors, calculated by
, and determines the overall opposition to the AC current.
5. Resonance in AC Circuit
Types: Resonant Frequency, Maximum Current, Impedance Minimum, Power Maximum
Mnemonic: "Ravi Makes Idli Perfect"
Breakdown:
Ravi – Resonant Frequency
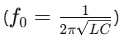
Makes – Maximum Current (occurs at resonance)
Idli – Impedance Minimum (occurs at resonance, Z=R)
Perfect – Power Maximum (maximum power transferred at resonance)
In an AC circuit, resonance occurs when the inductive reactance (XL) equals the capacitive reactance (XC), and the system behaves as if it’s purely resistive:
Resonant Frequency is the frequency at which resonance occurs, given by
At resonance, the maximum current flows because impedance is minimized.
The impedance minimum at resonance means the circuit behaves like a resistor, with Z = R.
Power maximum happens at resonance because the impedance is at its lowest, allowing maximum energy transfer.
6. Root Mean Square (RMS) Concepts
Types: RMS Current, RMS Voltage, Average Value
Mnemonic: "Ritu Visits America"
Breakdown:
Ritu – RMS Current
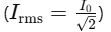
Visits – RMS Voltage
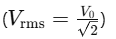
America – Average Value (for a half-wave,
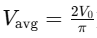 )
)
RMS Current is the effective current value that produces the same heating effect as a DC current. It’s calculated by
RMS Voltage is the effective voltage value, similarly calculated as
, which gives the same power dissipation as DC voltage.
Average Value refers to the mean value of an AC waveform over a half-cycle. For a sine wave, the average value of voltage is
This mnemonic makes it easy to recall the key RMS concepts and their relationships in AC circuits, which is crucial for calculating power and analyzing waveforms.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Alternating Current - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the definition of Alternating Current (AC) ? |  |
| 2. How does Alternating Current differ from Direct Current (DC) ? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using Alternating Current in power systems ? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of frequency in Alternating Current ? |  |
| 5. How is Alternating Current represented mathematically ? |  |