Mnemonics: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Laws of Reflection |

|
| 2. Laws of Refraction |

|
| 3. Mirror Formula |

|
| 4. Nature of Images in Mirrors |

|
| 5. Power of Lens Depends On |

|
| 6. Optical Instruments – Devices |

|
1. Laws of Reflection
Types: Incident Ray, Reflected Ray, Normal, Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
Mnemonic: "Inaya Really Needs Apples"
Breakdown:
- Inaya – Incident Ray
- Really – Reflected Ray
- Needs – Normal
- Apples – Angle Equality (θi = θr)
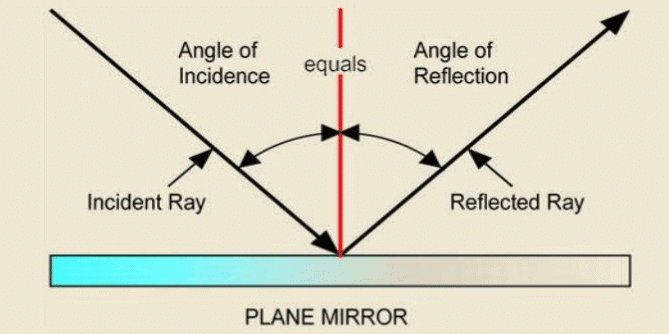
The laws of reflection govern how light behaves when it reflects off a surface. According to these laws:
The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
2. Laws of Refraction
Types: Incident Ray, Refracted Ray, Normal, Snell’s Law
Mnemonic: "Inaya Reads Notes Slowly"
Breakdown:
- Inaya – Incident Ray
- Reads – Refracted Ray
- Notes – Normal
- Slowly – Snell’s Law
The laws of refraction explain how light bends when it passes from one medium to another.
According to Snell’s Law, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant and depends on the refractive indices of the two media. The incident ray, refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
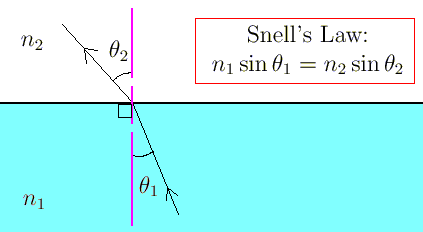
3. Mirror Formula
Types: Object Distance (u), Image Distance (v), Focal Length (f), Radius of Curvature (R)
Mnemonic: "Uncle Victor Found Roses"
Breakdown:
- Uncle – Object Distance (u)
- Victor – Image Distance (v)
- Found – Focal Length (f)
- Roses – Radius of Curvature (R)
This mnemonic helps remember the components involved in the mirror formula. The mirror formula relates these quantities:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
Where f is the focal length, u is the object distance, and v is the image distance. Additionally, the radius of curvature R is related to the focal length by the formula R=2f.
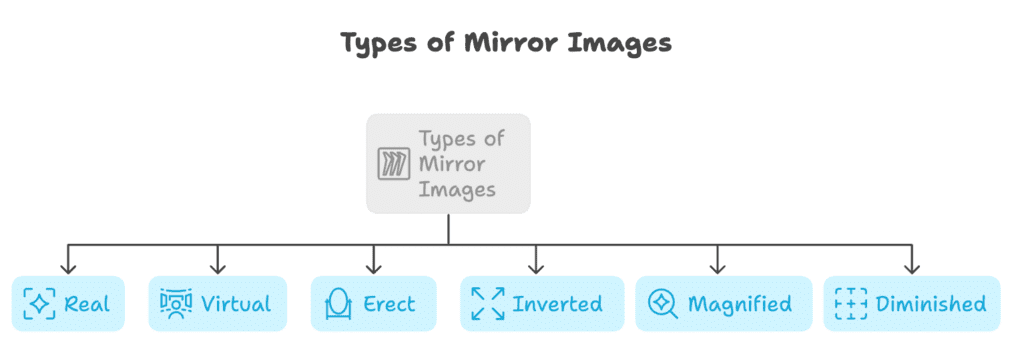
4. Nature of Images in Mirrors
Types: Real, Virtual, Erect, Inverted, Magnified, Diminished
Mnemonic: "Ravi Visited Every Interesting Market Daily"
- Ravi – Real
- Visited – Virtual
- Every – Erect
- Interesting – Inverted
- Market – Magnified
- Daily – Diminished
This mnemonic helps you remember the different types of images formed by mirrors.
Real images are formed by converging light rays and can be captured on a screen. They are typically inverted.
Virtual images are formed by diverging light rays and cannot be captured on a screen. They are typically erect.
The image may also be either magnified (larger than the object) or diminished (smaller than the object) depending on the mirror type and the object's position relative to the mirror.
5. Power of Lens Depends On
Types: Focal Length, Medium, Radius of Curvature, Refractive Index
Mnemonic: "Fat Monkeys Run Rapidly"
- Fat – Focal Length
- Monkeys – Medium
- Run – Radius of Curvature
- Rapidly – Refractive Index
The power of a lens is determined by the combination of these factors:
The focal length dictates how strongly the lens bends light, with shorter focal lengths corresponding to more powerful lenses.
The medium (such as air or water) surrounding the lens impacts the bending of light.
The radius of curvature of the lens surfaces influences the lens's ability to converge or diverge light.
The refractive index of the lens material affects how light slows down when passing through it.
Mathematically, it is given by P = 1/f, where P is the power and f is the focal length.
6. Optical Instruments – Devices
Types: Simple Microscope, Compound Microscope, Astronomical Telescope, Terrestrial Telescope
Mnemonic: "Some Children Admire Telescopes"
- Some – Simple Microscope
- Children – Compound Microscope
- Admire – Astronomical Telescope
- Telescopes – Terrestrial Telescope
This mnemonic helps recall the four main optical instruments:
A simple microscope has one lens and magnifies objects at a small scale.
A compound microscope uses two lenses, providing higher magnification and is used for studying microscopic objects.
An astronomical telescope is for viewing distant stars and planets, utilizing large lenses or mirrors.
A terrestrial telescope is mainly used for observing faraway objects on Earth, providing a clear, upright image.
7. Total Internal Reflection Conditions
Mnemonic: "Dense to Rare, Critical Care"
Breakdown:
Dense to Rare – The light must travel from a denser medium (e.g., water, glass) to a rarer medium (e.g., air).
Critical Care – The angle of incidence must be greater than or equal to the critical angle for total internal reflection to occur.
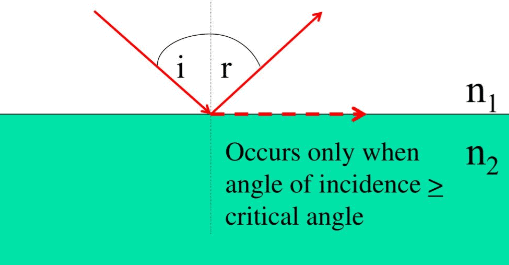
Total internal reflection happens when light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium and the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle. This phenomenon is commonly seen in optical fibers and prisms. The critical angle is the minimum angle at which light can strike the boundary between two media and still reflect entirely within the denser medium.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic principles of ray optics? |  |
| 2. How do lenses work in optical instruments? |  |
| 3. What are the types of mirrors used in ray optics? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the focal length in optical instruments? |  |
| 5. How can mnemonics help in studying ray optics for the NEET exam? |  |




















