Mnemonics: Wave Optics | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
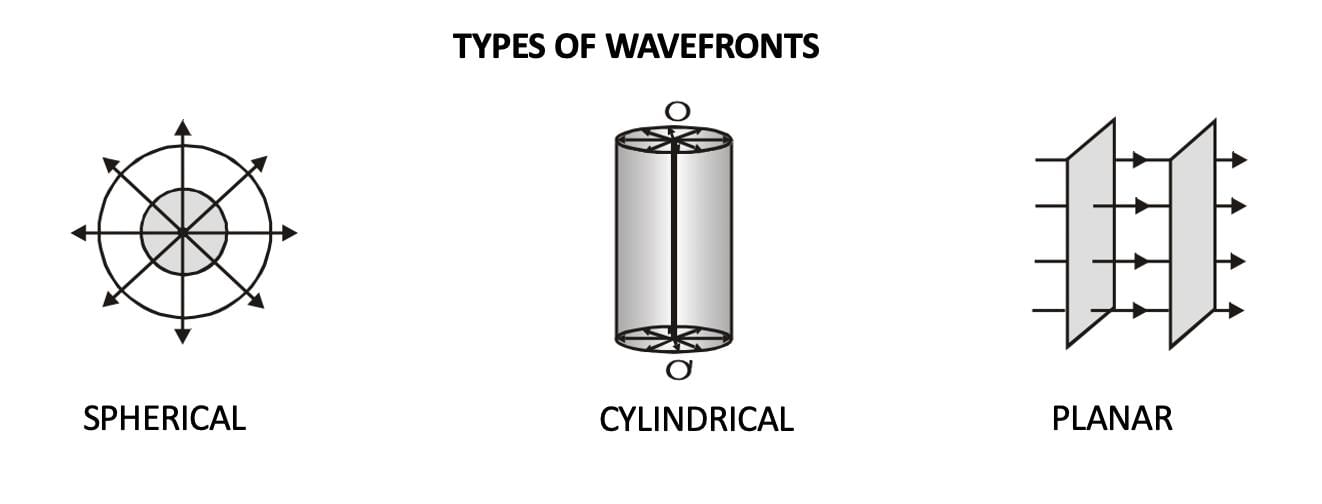
1. Types of Wavefronts
Mnemonic: "Sunny Cities Party"
Breakdown:
Sunny → Spherical Wavefront
Formed by a point source. Waves spread out equally in all directions, creating concentric spherical surfaces.Cities → Cylindrical Wavefront
Formed by a line source. Waves spread out in cylinders around the line, like ripples around a long straight object.Party → Plane Wavefront
Formed when waves from a distant or collimated source move in parallel, making the wavefront flat — like light from a laser.
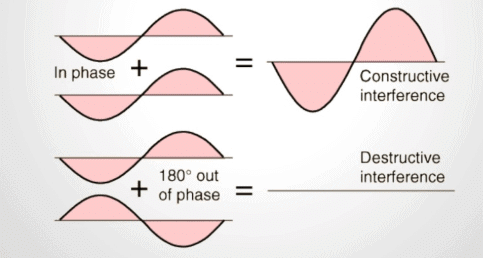
2. Interference Conditions (Constructive & Destructive)
Mnemonic: "Same Crest, Add Best; Opposite Crest, Rest."
Breakdown:
Same Crest → Waves are in-phase → Constructive interference
Add Best → Their amplitudes add up → Bright fringe
Opposite Crest → Out-of-phase waves → Destructive interference
Rest → Cancel each other → Dark fringe
Constructive: Δx=nλ
Destructive: Δx=(2n+1)λ/2
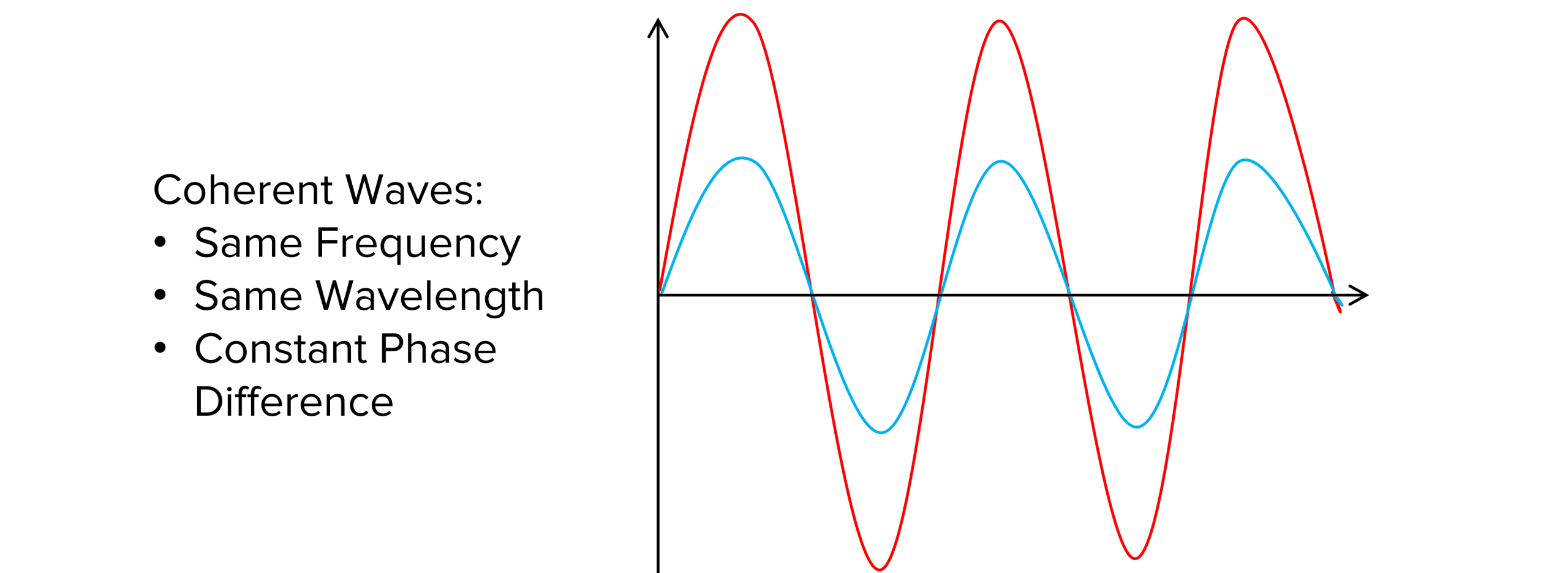
3. Coherent Source Conditions
Mnemonic: "Same Freq, Fixed Phase: Friends Forever."
Breakdown :
Same Freq → Identical frequencies required
Fixed Phase → Constant phase difference
Friends Forever → Like coherent sources, always "in sync"
Coherent sources are essential for stable interference — they must vibrate together with the same rhythm and a fixed phase link, just like best friends always in step.
4. Brewster’s Law (Polarising Angle)
Mnemonic: "Tan Uncle Brew = n"
Breakdown:
Tan → Tangent
Uncle Brew → Brewster’s angle θB
n → Refractive index
Formula: tan θB = μ
At Brewster’s angle, the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular, and the reflected light becomes completely polarised. This law gives the angle where this happens, using the tangent of the angle equal to the refractive index.
5. Applications of Interference and Diffraction
Mnemonic: "Tiny New Discoveries Rule"
Breakdown:
Tiny → Thin Film Colors
Caused by interference in light reflected from thin layers (e.g., soap bubbles, oil films), producing vibrant colors.New → Newton’s Rings
Circular interference patterns formed by a lens placed on a flat glass surface — useful in measuring wavelength or lens properties.Discoveries → Diffraction Grating
An optical device with many narrow slits that splits light into sharp spectral lines — key for analyzing light in labs and spectrometers.Rule → Resolving Power
The ability of instruments to distinguish closely spaced objects — improved by interference and diffraction effects.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Wave Optics - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is wave optics and how does it differ from geometrical optics? |  |
| 2. What are the key principles of interference in wave optics? |  |
| 3. How does diffraction occur in wave optics? |  |
| 4. What is polarization and what are its applications in wave optics? |  |
| 5. How do lenses behave in wave optics compared to geometrical optics? |  |