Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > Infographic: Light
Infographic: Light | Science Class 8 PDF Download
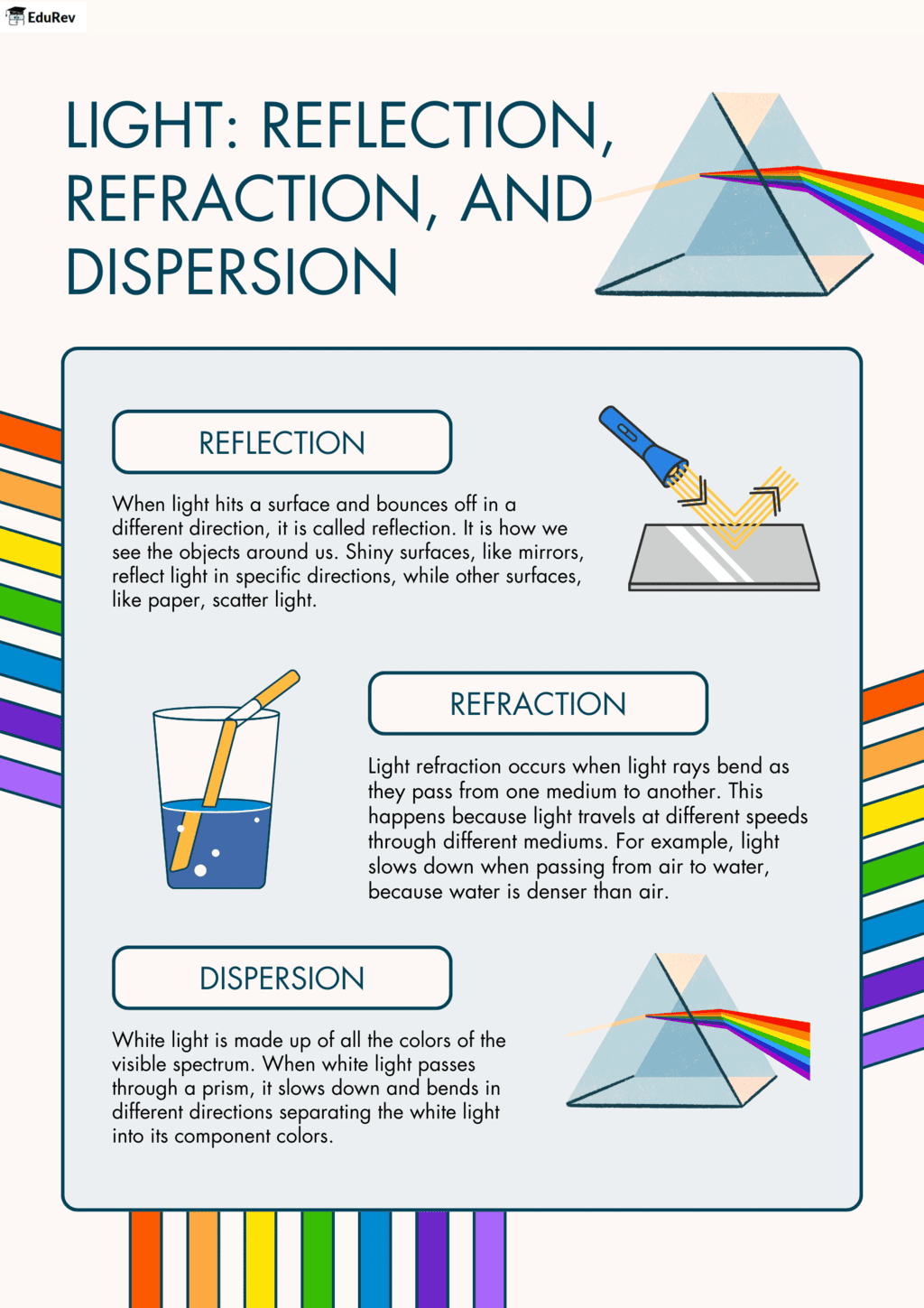
The document Infographic: Light | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Infographic: Light - Science Class 8
| 1. What is light and how does it behave as both a particle and a wave? |  |
Ans. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It exhibits both particle-like and wave-like behavior, a phenomenon known as wave-particle duality. As a wave, light can exhibit interference and diffraction, while as a particle, it can be thought of as photons that carry energy.
| 2. What are the different types of light sources? |  |
Ans. Light sources can be classified into natural and artificial types. Natural sources include the sun, stars, and fire, while artificial sources encompass electric bulbs, LEDs, and lasers. Each type of light source emits light through different processes, such as incandescence, fluorescence, and phosphorescence.
| 3. How does light travel through different mediums? |  |
Ans. Light travels at different speeds depending on the medium it passes through. In a vacuum, light travels at its maximum speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s). When light enters denser mediums like water or glass, it slows down, which can lead to refraction and changes in the direction of light.
| 4. What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum in relation to light? |  |
Ans. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared light, radio waves, and X-rays. Each type of radiation has different wavelengths and frequencies, and understanding the spectrum helps us grasp how light interacts with matter and its various applications in technology and medicine.
| 5. How do our eyes perceive light and color? |  |
Ans. Our eyes perceive light through specialized cells called photoreceptors, which include rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to low light levels and help us see in dim conditions, while cones are responsible for color vision and function best in bright light. The brain interprets signals from these cells to produce the perception of color based on the wavelengths of light that are absorbed.
Related Searches
















