Revision Notes: The Living World | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction to the Living World
Biology is the science of life forms and living processes. The living world is characterized by a vast variety of organisms, from microscopic to large, found in diverse habitats such as mountains, forests, oceans, deserts, and hot springs. Early humans distinguished between living and non-living entities, often deifying inanimate objects like wind and fire, and certain plants and animals due to awe or fear. The recognition that all organisms are interrelated led to humility and movements for biodiversity conservation.
Diversity in the Living World
- Variety of organisms includes visible organisms like plants, animals, and birds, and microscopic ones, with diversity increasing in larger observation areas, such as dense forests.
- Each distinct kind of organism represents a species. Approximately 1.7–1.8 million species are known, with new ones continuously identified.
- Biodiversity refers to the number and types of organisms on Earth, vital for understanding ecological interactions.

Need for Classification
- Local names for organisms vary across regions, causing confusion in communication.
- A universal system is needed to assign a single, globally recognized name to each organism.
Taxonomy and Systematics
- Taxonomy is the science of identification, nomenclature, and classification of organisms based on external and internal structure, cell structure, development, and ecological information.
- Systematics studies the diversity and evolutionary relationships among organisms, including identification, nomenclature, and classification.
- Systematics originated from the Latin word "systema" (systematic arrangement). Linnaeus’s Systema Naturae laid the foundation for modern systematics.
Nomenclature
The purpose of nomenclature is to provide a standardized, universal name for each organism to avoid confusion.
- Binomial nomenclature, developed by Carolus Linnaeus, gives each organism a two-part name: Genus (first word, capitalized) and specific epithet (second word, lowercase). Example: Mangifera indica (mango).
- Rules of nomenclature:
- Names are in Latin or Latinized, written in italics (or underlined if handwritten).
- Genus starts with a capital letter; specific epithet with a lowercase letter.
- Author’s name (abbreviated) may follow the scientific name, e.g., Mangifera indica Linn.
- International codes:
- ICBN: International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (for plants).
- ICZN: International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (for animals).
Classification
Classification is the grouping of organisms into categories (taxa) based on observable characteristics to simplify the study of millions of organisms.
- Taxa are scientific categories like plants, animals, mammals, dogs, etc. Taxa represent different hierarchical levels, e.g., "dogs" is a lower taxon than "mammals."
- Taxonomy processes:
- Characterization: Studying organism features.
- Identification: Determining the correct organism for a name.
- Nomenclature: Naming organisms.
- Classification: Grouping organisms into taxa.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
A ranked system of categories (taxa) from species to kingdom, forming a hierarchy. A taxon is a unit of classification representing a rank.
- Hierarchical levels (in ascending order):
- Species: Group of individuals with fundamental similarities, distinguishable by morphological differences. Example: Mangifera indica (mango), Homo sapiens (human).
- Genus: Group of related species with more common characters than species of other genera. Example: Solanum tuberosum (potato) and Solanum melongena (brinjal) belong to Solanum.
- Family: Group of related genera with fewer similarities than genus/species. Example: Solanum, Petunia, Datura in Solanaceae (plants); Panthera, Felis in Felidae (animals).
- Order: Group of related families with fewer similar characters. Example: Solanaceae and Convolvulaceae in Polymoniales (plants); Felidae and Canidae in Carnivora (animals).
- Class: Group of related orders. Example: Primata and Carnivora in Mammalia (animals).
- Phylum/Division: Group of related classes. Example: Chordata (animals with notochord); Angiospermae (plants).
- Kingdom: Highest category, including all related phyla/divisions. Example: Animalia (animals), Plantae (plants).
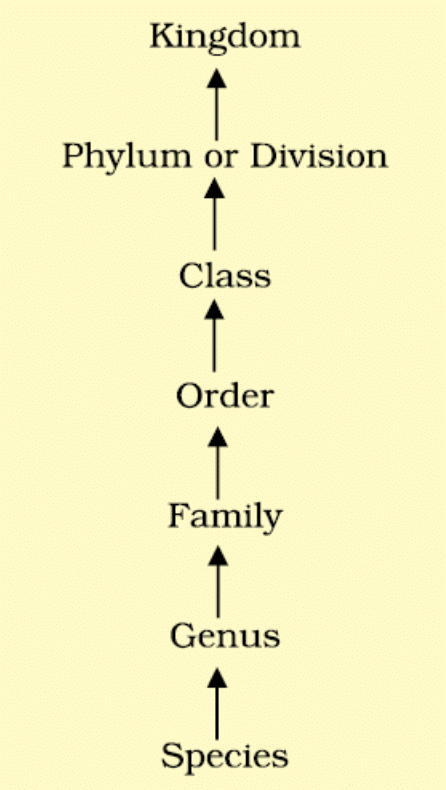
- Trend in hierarchy: As you move from species to kingdom, the number of shared characteristics decreases. Lower taxa (e.g., species) have more common features; higher taxa (e.g., kingdom) are harder to relate.
Examples of Taxonomic Categories
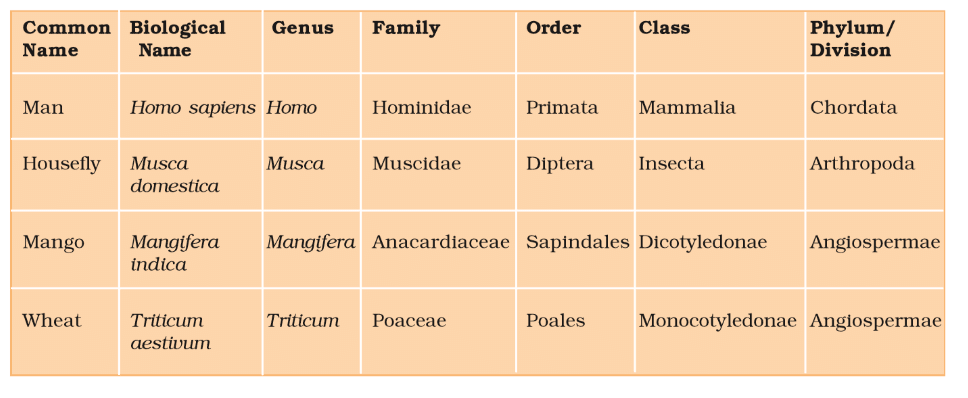
Key Contributions
Ernst Mayr (1904–2004), called "The Darwin of the 20th century," was a Harvard evolutionary biologist who defined the modern concept of a biological species. He made species diversity a central question in evolutionary biology and received the Balzan Prize (1983), International Prize for Biology (1994), and Crafoord Prize (1999).
Summary
The living world is diverse, with millions of species, many still undiscovered. Taxonomy facilitates studying this diversity through identification, nomenclature, and classification. Binomial nomenclature ensures universal naming. The taxonomic hierarchy organizes organisms from species to kingdom, with decreasing shared characteristics as you move up. Systematics explores evolutionary relationships, building on taxonomy.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: The Living World - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the importance of classification in biology? |  |
| 2. What are the main features of the taxonomic hierarchy? |  |
| 3. How do scientists assign names to organisms using nomenclature? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of taxonomic categories? |  |
| 5. Who are some key contributors to the field of taxonomy and systematics? |  |






















