Living Things Chapter Notes | Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Bones and Skeletons |

|
| Why We Need a Skeleton |

|
| Skeletons and Movement |

|
| Different Kinds of Skeletons |

|
| Medicines and infectious diseases |

|
Bones and Skeletons
 Skeletal Motion
Skeletal Motion
What is a Skeleton?
A skeleton is a strong frame inside the bodies of people and many animals, made up of bones connected together. It supports the body from within, providing structure and stability. The skeletons of extinct animals, like dinosaurs, give us evidence of their existence and form. The human skeleton has 206 bones, which come in various sizes and shapes. Bones are hard and strong, and they can be felt through the skin.
The human Skeleton
Main bones include:
- Skull: Forms the head and protects the brain.
- Jaw: Allows for chewing and speaking.
- Rib cage: Shields the lungs and heart.
- Spine: Supports the back and protects the spinal cord.
- Upper arm bones: Include the humerus.
- Lower arm bones: Include the radius and ulna.
- Thigh bones: Include the femur, the largest bone in the body.
- Lower leg bones: Include the tibia and fibula.
- Hip: Connects the legs to the torso and supports movement.
Arms generally consist of three main bones: humerus (upper arm), radius, and ulna (lower arm). The thigh bone (femur) is much larger than the lower leg bones (tibia and fibula).
Why We Need a Skeleton

The skeleton has four main functions:
- Protection: Skeletons safeguard vital organs that keep us alive and healthy. The skull protects the brain; the rib cage shields the lungs and heart; the spine guards the spinal cord.
- Support: The skeleton forms a strong frame that gives the body shape and prevents it from collapsing. Strong bones ensure the body is firm and resistant to pressure.
- Movement: The skeleton enables activities like walking, running, and more. Muscles attach to bones, and when they contract, they pull on bones to assist movement.
- Growth: The skeleton grows as we age, allowing our bodies to increase in size. An adult's skeleton is larger than a child's and stops growing once adulthood is reached.
Skeletons and Movement
Muscles make us move
- Bones are rigid and cannot bend, but muscles allow the body to move in various ways.
- Muscles attach to bones and are responsible for actions such as sitting, standing, walking, running, bending, stretching, smiling, holding objects, eating, and talking.
- Muscles lie under the skin, covering the skeleton and shaping the body.
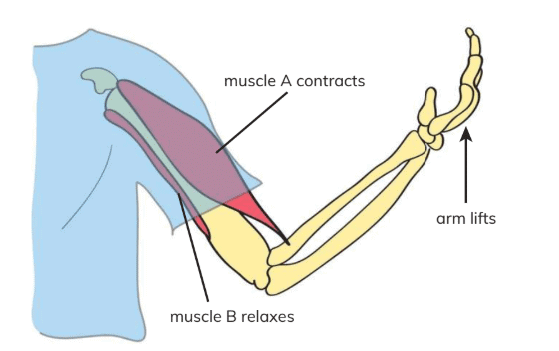
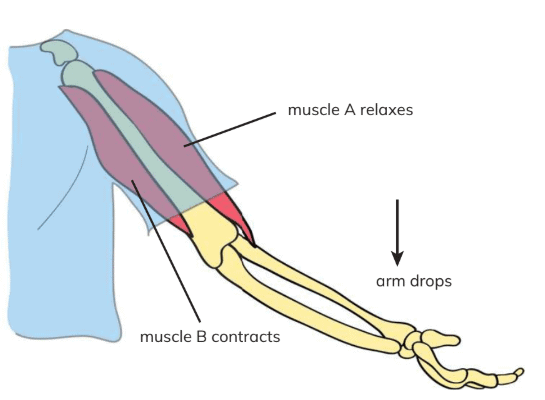
How Muscles Work
- Muscles create movement by pulling on bones, contracting (becoming shorter) and relaxing (becoming longer). When a muscle contracts, it pulls the attached bone, enabling movement.
- When it relaxes, it lengthens, allowing the body to rest. Muscles work in pairs: one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to produce coordinated movement (e.g., muscle A contracts to lift the arm, while muscle B relaxes; muscle B contracts to lower the arm, while muscle A relaxes).
- Contracting muscles become shorter and thicker; relaxing muscles become longer and thinner.
Movement keeps us healthy
Movement through activities like walking, running, dancing, lifting, climbing, and jumping is beneficial for health. Prolonged sitting is harmful.
Benefits of movement include:
- Improved heart and lung function.
- Stronger muscles and bones.
- Increased flexibility and ease of stretching.
- Reduced risk of certain illnesses.
- Enhanced cognitive function.
- Improved mood.
Different Kinds of Skeletons
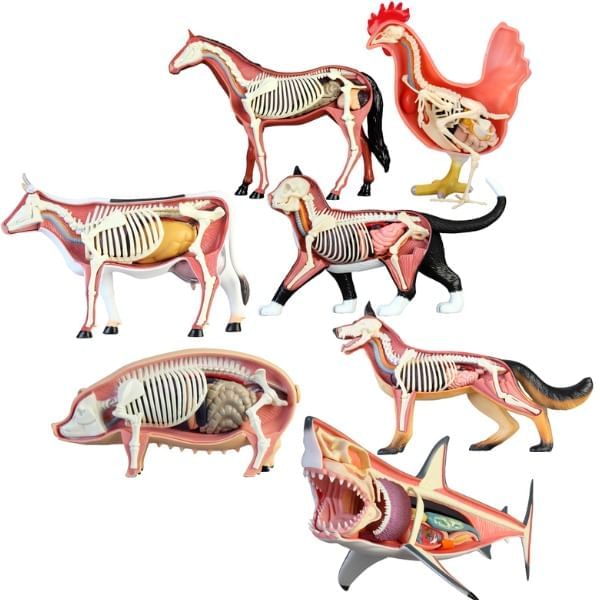

Animals with Bones
Animals with bones possess a skeleton with a backbone inside their bodies, known as vertebrates. The term vertebrate means with a backbone.
Vertebrates can be classified into five groups based on their characteristics:
- Fish: Live in water, have fins instead of arms and legs, and their bodies are covered with scales.
- Amphibians: Live both in water and on land (e.g., frogs), with smooth, wet skin.
- Reptiles: Include snakes, lizards, tortoises, and crocodiles; covered with dry scales. Most live on land, but some, like crocodiles, can be found in water.
- Birds: Covered with feathers and have wings instead of arms. Most can fly, but some, like ostriches, cannot.
- Mammals: Covered with hair or fur. Most live on land, but some, like whales and dolphins, reside in the sea.
Animals without Bones
Animals without bones are called invertebrates, meaning without a backbone. Some invertebrates have an exoskeleton, a hard outer layer that protects and supports their bodies.
Examples of exoskeletons include:
- Insects, such as locusts and beetles, which have exoskeletons.
- Crabs, which also have exoskeletons.
- Other invertebrates, like worms and jellyfish, have soft bodies without an exoskeleton.
Identification Keys
- Identification keys are tools used to classify animals based on observable characteristics.
- They help identify whether an animal is a vertebrate or invertebrate and further categorise vertebrates into specific groups.
Medicines and infectious diseases

Medicines
Medicines are used to treat illnesses and help us feel better. Some medicines prevent illnesses, stopping us from getting sick.
Taking Medicines Safely
- Medicines must be taken safely and correctly to be effective and avoid harm. Only take medicines given by a doctor, nurse, or responsible adult.
- All medicines come with instructions detailing the dosage (how much to take) and frequency (how often to take it). Always follow the instructions that come with the medicine.
How We Take Medicines
Medicines can be given in various ways:
- Injections: Some injections, called vaccinations, prevent illnesses like measles or flu.
- Inhalers: Used for asthma and other breathing problems, medicines are breathed in.
- Creams and Ointments: Applied to the skin to treat insect bites, itching, or skin conditions.
- Drips: In hospitals, medicines are delivered directly into the blood for very sick patients.
Infectious Diseases
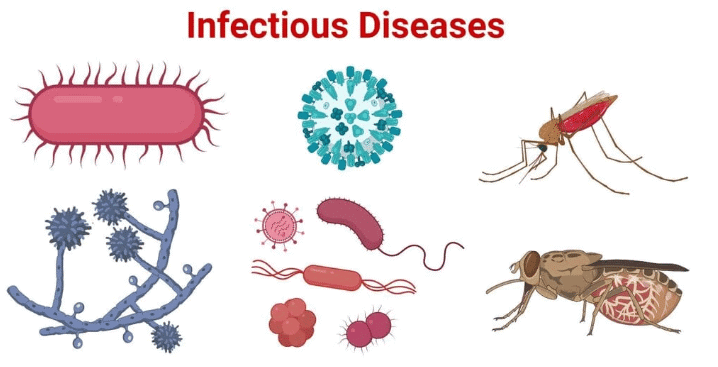
Infectious diseases are caused by tiny living organisms called germs, which infect the body and cause illness. Medicines are used to kill germs and treat infectious diseases.
Infectious diseases can affect:
- Humans: Examples include flu, measles, and malaria.
- Animals: For instance, bird flu is highly fatal to birds and can spread to humans and other animals.
- Plants: An example is leaf blast, which can kill young rice plants.
Vaccinations can prevent infectious diseases in both people and animals (e.g., farmers vaccinate chickens, geese, and ducks to prevent bird flu).
|
14 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Living Things Chapter Notes - Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 4
| 1. What is a skeleton and what is its primary function in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How does the human skeleton protect the body? |  |
| 3. In what ways do skeletons allow us to move? |  |
| 4. How do muscles work in conjunction with the skeleton? |  |
| 5. How do skeletons contribute to growth in living beings? |  |




















