Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) > Chapter Notes: Energy
Energy Chapter Notes | Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Energy Around Us |

|
| Energy Transfers |

|
| Energy Changes |

|
| Energy and Living Things |

|
Energy Around Us
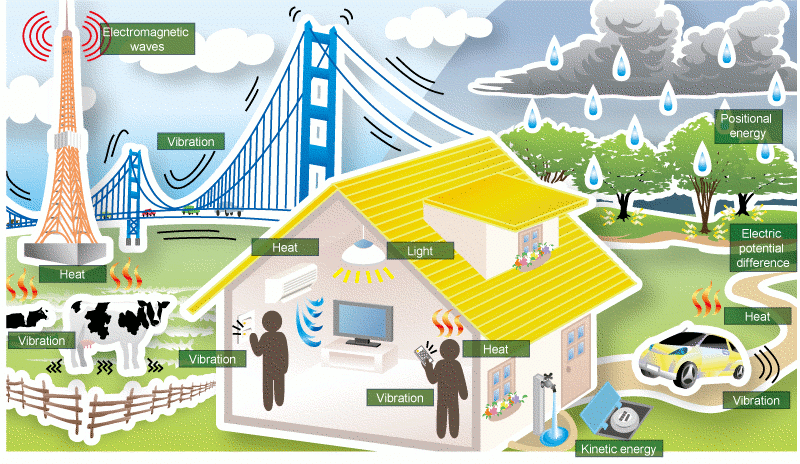
Energy is all around us
Energy is present everywhere, in all things, whether they are living or non-living.
Living Things
- Humans and other living organisms obtain energy from the food they consume.
- This energy is essential for vital life functions, including:
- Movement
- Growth
- Breathing
- Various other bodily activities
Non-Living Things
- Non-living things also possess energy.
- For instance, the energy in moving air can be harnessed to power wind turbines.
- Energy can manifest as:
- Light
- Heat
- Sound
Forms of Energy
- Energy can exist in various forms, such as light, heat, sound, and movement.
What is Energy?
- Energy might not always be visible, but its effects are apparent.
- It is the force behind movement; all moving objects possess energy.
- Energy has the ability to cause changes, like a moving ball shattering a window.
- It is fundamental for all activities in our daily lives.
Energy Transfers
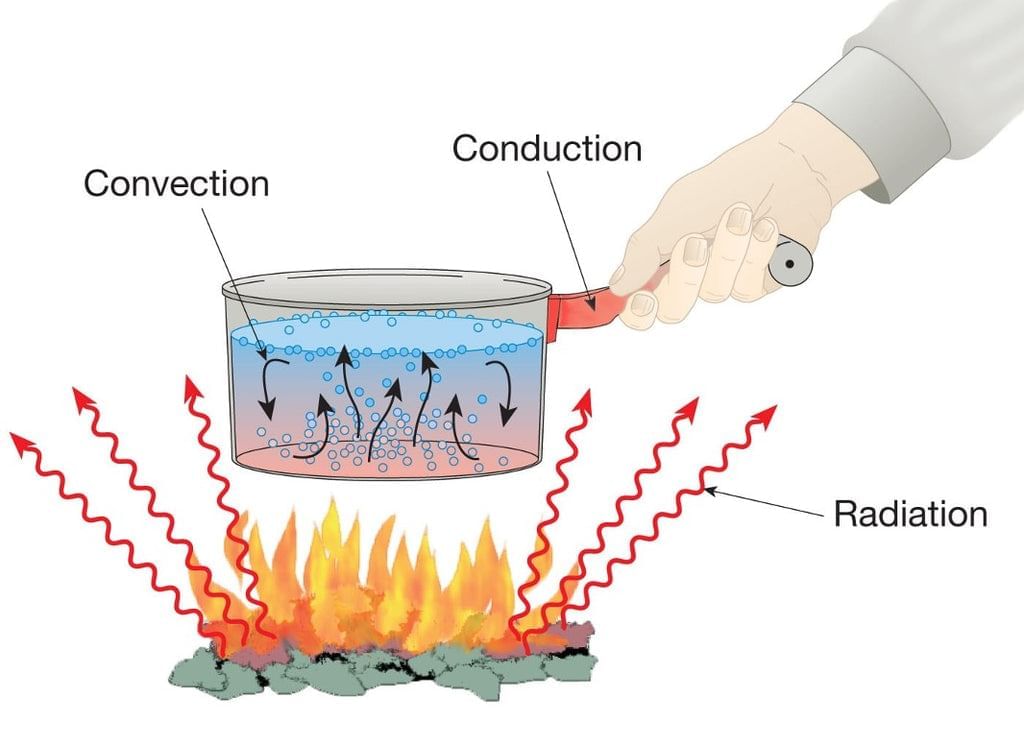
Energy can move
- Energy can transfer from one object to another, enabling various processes.
- During these transfers, energy is conserved; it does not vanish.
- When hot water is poured into a cup, heat energy transfers to the cup, warming it up.
- Over time, both the cup and water cool down as heat energy moves to the surrounding environment.
- This process can be represented as an energy chain: water → cup → surrounding environment.
- The Sun emits heat and light energy through space to Earth, providing us with warmth and light.
Energy Changes
Energy can change form
- Energy can transform from one form to another during a transfer.
- Some energy may dissipate into the surrounding environment.
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only transfers or changes form.
- When something appears to lose energy, like a cooling cup of tea, the energy is merely moving to the environment.
- Energy exists in various forms and is conserved during transformations.
- All energy has always existed and will continue to exist, constantly moving and changing.
- Energy can shift between objects and can transform during the process.
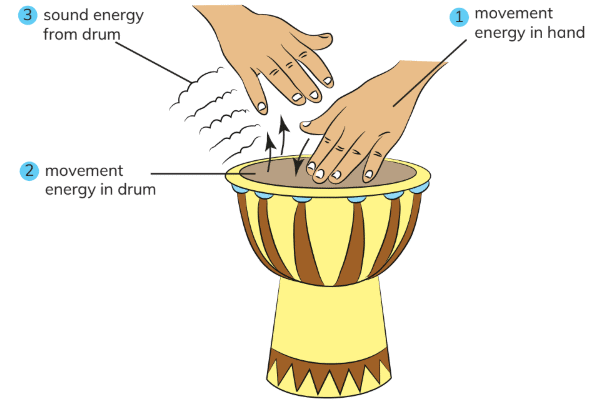
Example: Hitting a Drum
- When you hit a drum, the energy from your hand transfers to the drum, converting movement energy into sound energy.
- Energy transformation sequence: movement energy in hand → movement energy in drum → sound energy from drum.
Electrical Energy
- Electricity is a form of energy known as electrical energy.
- Electrical appliances, such as stoves and fans, convert electrical energy into other forms to function.
- For example, a fan transforms electrical energy into movement energy to spin its blades.
- Not all energy is utilized as intended; some is converted into other forms.
- In a fan, part of the movement energy is transformed into sound energy, which dissipates into the surroundings.
Conservation of Energy
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only transfers or transforms.
- When something appears to lose energy, like a hot cup of tea cooling, the energy is actually moving to the environment.
- For instance, heat energy in tea transfers to the cup and then to the air, cooling the tea.
- All energy is constant, always present, and continuously changing form.
Energy and Living Things
Living things need energy
- All living organisms require energy to survive and maintain their health.
- Energy is vital for life processes such as:
- Movement
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Other necessary functions
- Insufficient energy can lead to health problems in both plants and animals.
Animals need plants for energy
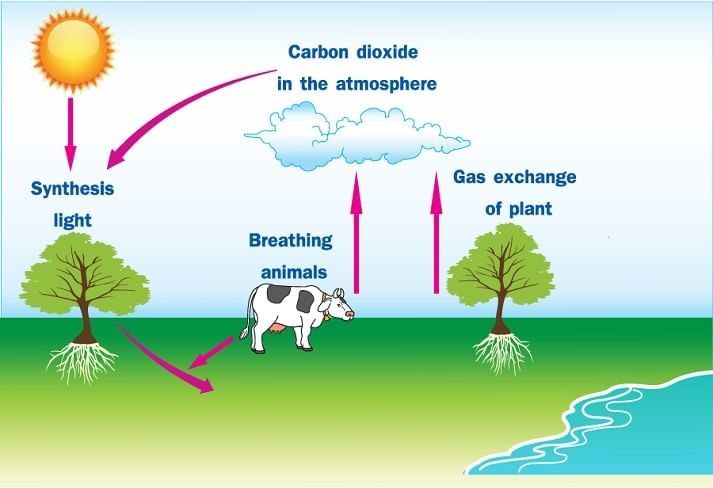
- Plants: Unlike animals, plants do not consume food for energy; they produce their own using sunlight through a process called photosynthesis. This ability makes plants producers.
- Animals: Animals, including humans, cannot make their own food. They obtain energy by eating plants or other animals, categorizing them as consumers. Energy transfers from the food into the animal's body, supporting various life processes.
Types of Consumers

- Herbivores: These animals eat only plants. Examples are zebras and snails.
- Carnivores: These animals eat other animals, typically herbivores or other carnivores. Examples include tigers and owls. Carnivores are often referred to as predators, while the animals they hunt are called prey (for example, an owl is a predator, and a mouse it catches is prey).
- Omnivores: These animals consume both plants and animals. For instance, monkeys eat leaves, fruits, seeds, insects, and small animals.
Food Chains
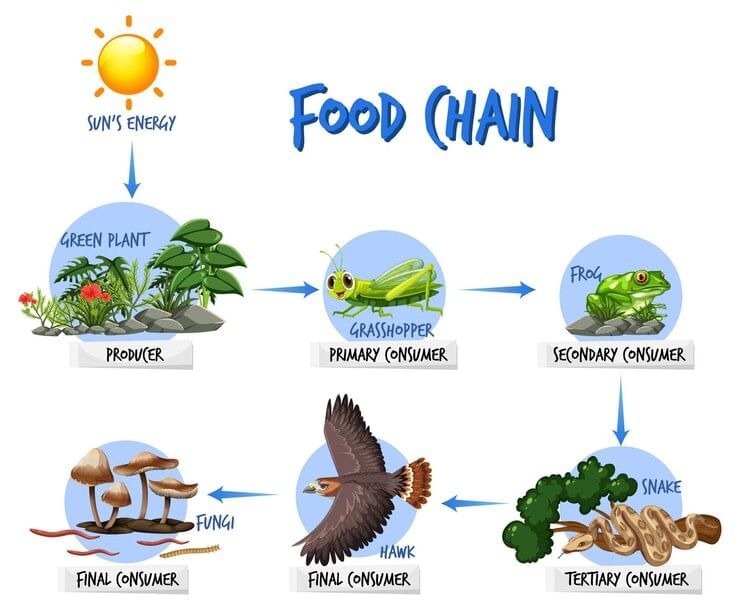
- A food chain illustrates how organisms obtain energy by consuming plants or other animals.
- Food chains always include at least one producer and one or more consumers.
- When a consumer eats a producer, energy transfers from the producer to the consumer.
- Example of a food chain: corn (producer) → hen (consumer). If a boy eats the hen, the food chain extends: corn → hen → boy.
- Food chains can also be visually represented to show the flow of energy between organisms.
- The basic structure of a food chain is always: producer → consumer.
- Arrows in a food chain indicate the direction of energy transfer from one organism to another.
The document Energy Chapter Notes | Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 4 is a part of the Class 4 Course Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 4 at this link: Class 4
|
14 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Energy Chapter Notes - Year 4 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 4
| 1. What is energy? |  |
Ans.Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. It exists in various forms, such as kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), thermal energy, and chemical energy, among others.
| 2. How does energy move? |  |
Ans.Energy moves in different ways. For example, it can be transferred through heat, work, or waves. In nature, energy flows from one place to another, such as from the sun to plants through photosynthesis or from plants to animals through food chains.
| 3. In what forms can energy change? |  |
Ans.Energy can change forms in various ways. For instance, when a plant uses sunlight to create chemical energy through photosynthesis, it transforms light energy into chemical energy. Other examples include the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy when an object falls, or the transformation of chemical energy in food into kinetic energy during movement.
| 4. Where does energy go after it is used? |  |
Ans.After energy is used, it often transforms into different forms. For example, when animals consume food, the chemical energy from the food is converted into kinetic energy for movement or thermal energy to maintain body temperature. Some energy is also lost as heat to the environment.
| 5. Why do living things need energy? |  |
Ans.Living things need energy to perform vital functions such as growth, reproduction, movement, and maintaining homeostasis. Energy is essential for carrying out metabolic processes that sustain life, and it is primarily obtained from food sources, which derive energy ultimately from the sun.
Related Searches




















