Worksheet with Solutions: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section A: Fill In The Blanks |

|
| Section B. Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Section C: Assertion and Reason |

|
| Section D: Answer the following Questions |

|
Section A: Fill In The Blanks
Q1. Ionization enthalpy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the __________ shell of an isolated gaseous atom to convert it into a cation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: outermost
Solution: Ionization enthalpy refers to the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom, which forms a cation.
Q2.The lower the ionization enthalpy, the __________ the chances of ionic bond formation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: greater
Solution: The lower the ionization enthalpy, the greater the chances of ionic bond formation because it’s easier to form a cation.
Q3. Electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an isolated gaseous atom takes up an electron to form an __________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: anion
Solution: Electron gain enthalpy is the energy released when an isolated gaseous atom takes up an electron to form an anion.
Q4. Halogens possess high electron affinity, so the formation of __________ is very common in halogens.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: anion
Solution: Halogens possess high electron affinity, which leads to the easy formation of an anion.
Q5. The Bond enthalpy unit is __________
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution: The bond enthalpy unit is kJ/mol.
Section B. Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. The correct bond order in the following species is ____________.
(a) O2+ < O2– < O22+
(b) O2– < O2+ < O22+
(c) O22+ < O2+ < O2–
(d) O22+ < O2– < O2+
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Solution: The correct one is O2– < O2+ < O22+ , bond order is 1.5 < 2.5 < 3.0 respectively.
Q2. The bond angle around atom which uses sp2 hybridization is ———–
(a) 1200
(b) 1800
(c) 1070
(d) 1090. 28’
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Solution: The bond angle around an atom which uses sp2 hybridization is 1200.
Q3. In the resonating structures of benzene, the number of sigma and pi bonds are
(a) 3π and 12σ
(b) 3σ and 3π
(c) 6σ and 6π
(d) 12σ and 12π
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Solution: In Benzene (C6H6) ring contain 3 alternative double bond = 3π bonds and (six C-C sigma bond + six C-H sigma bond) = 12 σ bonds
Q4. Which of the following substances has a dipole moment more than zero?
(a) Water
(b) Methane
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrogen
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Solutions: The dipole moment (μ) of H2O = 1.84 D
Q5. The ion which is iso-electronic with CO is —————
(a) CN–
(b) O2–
(c) N2+
(d) O2+
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Solution : Both CO (6 + 8=14) and CN– (6 + 7+1= 14) have the same electrons. so they are iso-electronic with each other.
Section C: Assertion and Reason
Q.1. Assertion : The bond order of helium is always zero.
Reason : The number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital and antibonding molecular orbital is equal.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (a)
Exaplanation: The bond order of helium is zero because it has equal electrons in bonding and antibonding orbitals, leading to no net bonding.
Q.2. Assertion : The lesser the lattice enthalpy more stable is the ionic compound.
Reason : The lattice enthalpy is greater, for ions of highest charge and smaller radii. H4
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d)
Exaplanation: Higher lattice enthalpy indicates more stability. The assertion is incorrect because lower lattice enthalpy means less stability, while the reason is correct.
Q.3. Assertion : Atoms can combine either by transfer of valence of electrons from one atom to another or by sharing of valence electrons.
Reason : Sharing and transfer of valence electrons is done by atoms to have an octet in their valence shell.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (a)
Exaplanation: Atoms combine by transferring or sharing electrons to achieve a stable octet, as described in the reason.
Q.4. Assertion : BF3 molecule has zero dipole moment.
Reason : F is electronegative and B–F bonds are polar in nature.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (b)
Exaplanation: BF₃ has zero dipole moment because of its symmetrical structure, even though individual B–F bonds are polar. The reason is incorrect because it overlooks the molecule's symmetry.
Q.5. Assertion : CH2Cl2 is non-polar and CCl4 is polar molecule.
Reason : Molecule with zero dipole moment is non-polar in nature.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d)
Exaplanation: CH₂Cl₂ is polar, and CCl₄ is non-polar. The assertion is incorrect, and the reason is wrong because zero dipole moment corresponds to non-polar molecules.
Section D: Answer the following Questions
Q1: Give the main features of VSEPR Theory.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The main postulates of VSEPR theory can be explained as follows:
1. The shape of any molecule generally depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs around the central atom.
2. Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repel each other, that’s why their electron clouds are negatively charged.
3. The pairs of electrons tend to occupy that position in space which minimize repulsion and maximize the distance between them.
4. The valence shell is considered as a sphere with the electron pairs localizing on the sphere at maximum distance from one another.
5. A multiple bond is treated as a single electron pair and two or three electron pairs of a multiple bond is treated as a super pair.
6. When two or more resonance structures can represent a molecule, the VSEPR nodal is applicable to any type of structure.
Q2: What's the difference between lone pair and bonded pair of electrons?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The main difference between lone pair and bond pair is that lone pair electrons do not take part in bond formation whereas bond pair electrons take part in bond formation.
Q3: CO₂ is linear whereas SO₂ is bent-shaped. Give a reason.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: CO₂ is said to be linear as in CO₂ the bond electrons are furthest away from each other, which further forms the angle of 180°.
SO₂ contains a bent shape as in the compound number of bonding pairs is 4 and it also contains one lone pair of electrons which does not participate in bond formation, due to which we can experience repulsive strain in the molecule. Shape of SO₂ can be shown as follows: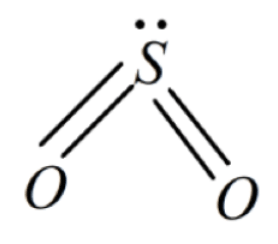
Q4: What are the different types of
 View Answer
View Answer 
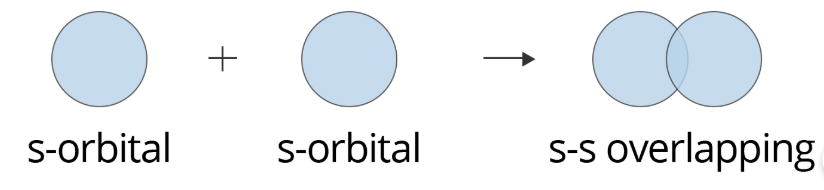
Ans: s-bond can be formed by any of the following types of combinations of atomic orbitals.
S–S overlapping: In this case, overlapping is between two half-filled s-orbitals along their internuclear axis, which can be shown as:
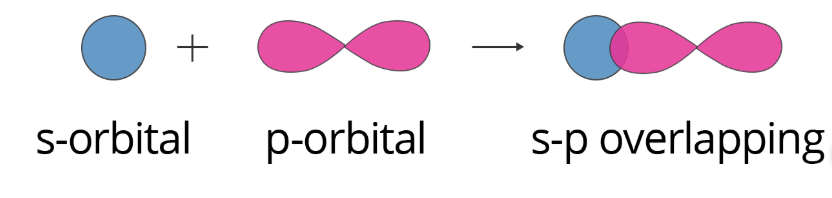
S–P overlapping: In this case, overlapping occurs between half-filled s-orbitals of one atom and half-filled p-orbitals of another atom. This can be shown as
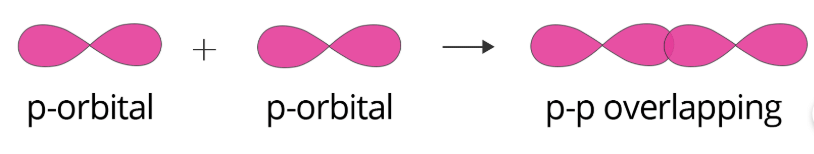
P–P overlapping: In this type of overlapping, the overlap takes place between half-filled p-orbitals of the two approaching atoms, which can be shown as:
Q5. Write the features of hybridization.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The main features of hybridization can be explained as follows:
1. The number of hybrid orbitals are always equal to the number of the atomic orbitals in which they get hybridized.
2. The hybridized orbitals are always equivalent in energy and shape.
3. The hybrid orbitals are said to be more effective in forming stable bonds as compared to pure atomic orbitals.
4. The hybrid orbitals revolve in such a manner that minimum repulsion will occur in any particular geometrical shape of the compound.
Q6. For the molecule, Why is structure (b) more stable than structure (a)? 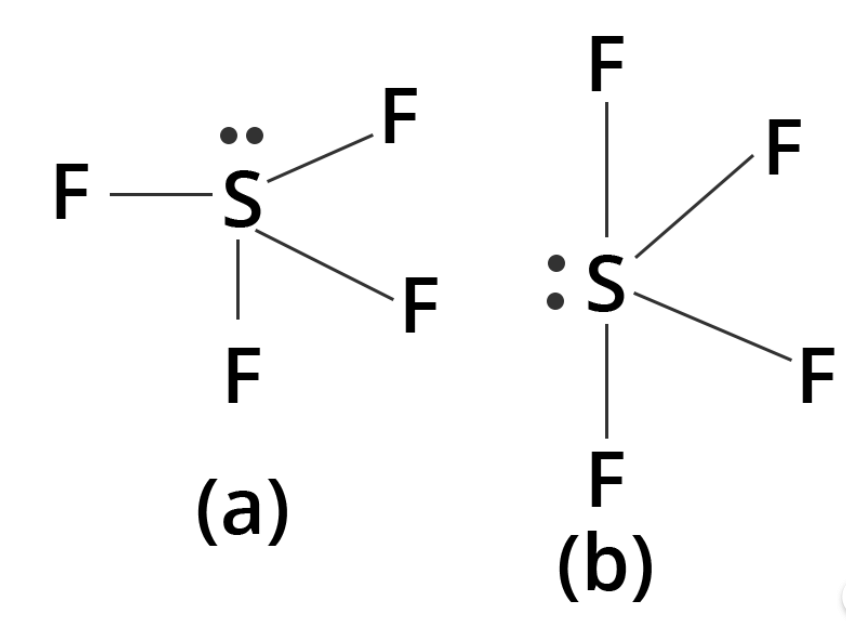
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In the case of structure:
(a) The lone pair is present at the axial position, which suggests that there are three lp-lp repulsions at 90°.
Whereas in the case of (b), the lone pair is present at an equatorial position, and there are two lp-lp repulsions. This represents that structure (b) is more stable as compared to structure (a).
Q6. How would you attribute the structure of the PH₃ molecule using the VSEPR model?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The outermost shell of the phosphorus atom contains 5 electrons. In this case, H⁻ atoms contribute one electron with each to make a total of 8 electrons around the phosphorus atom. In this way, 4 pairs of electrons are distributed in a tetrahedral manner around the central atom. Out of which, three pairs form three P-H bonds, while the fourth pair remains unused. Due to repulsion between the bond pair of these three and the lone pair of the remaining one, the shape is not of tetrahedral nature but becomes trigonal pyramidal.
12. Why does NH₃ have a higher dipole moment than NF₃ though both are pyramidal?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: NH₃ has a higher dipole moment than NF₃ because in the case of NH₃, the orbital dipole due to the lone pair is in the same direction as the resultant dipole moment of the N-H bonds. On the other hand, in NF₃, the orbital dipole is in the direction opposite to the resultant dipole moment of the three N-F bonds. Hence, the orbital dipole becoming a lone pair decreases, resulting in a lower dipole moment for NF₃.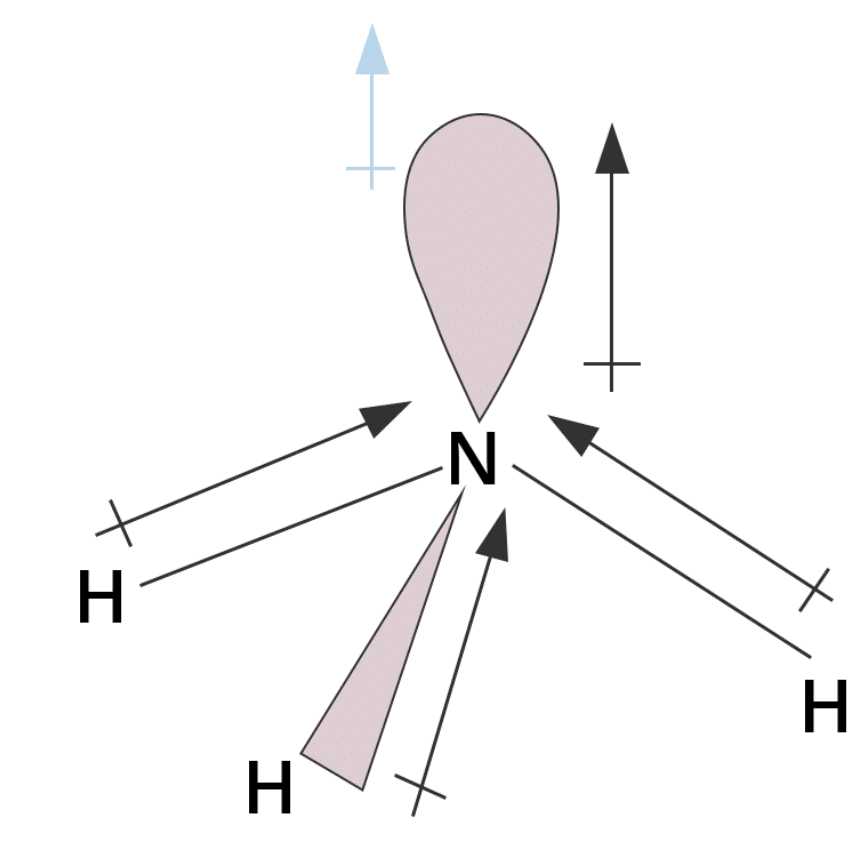
Q7. Draw the resonating structure of NO₃⁻.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The resonating structure generally involves the movement of electrons, and resonating structures of NO₃⁻ can be shown as: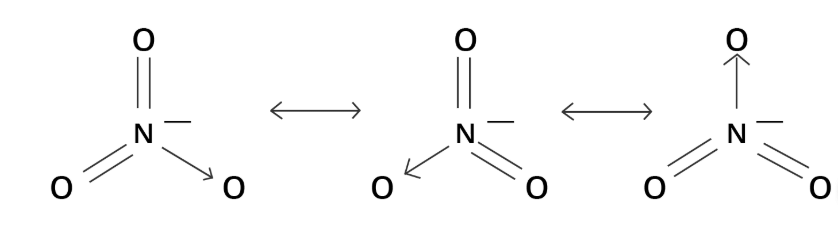
Q8. What is the ionic bond? With two suitable examples, explain the difference in between an ionic and the covalent bond?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond is that an ionic bond essentially donates the electron to the other atom participating in the bond. In contrast, electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms.
Q9. Arrange the following of the bonds in order to increase the ionic character, giving a reason
N—H, F—H, C—H and O—H
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The ionic character is greater in the molecules with the highest electronegativity difference because the electron pair shifts toward the more electronegative atom, increasing the ionic character.
Thus, the ionic character order will be:
C-H < N-H < O-H < F-H
Q10. Group the following as linear as well as non-linear molecules :
H2O, HOCl, BeCl2, Cl2O
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: BeCl2 has a linear structure
HOCl is also non-linear in structure.
H2O has a V-shaped structure.
Cl2O has a V-shaped structure.
|
119 videos|346 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet with Solutions: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of chemical bonds studied in chemical bonding? |  |
| 2. How does the VSEPR theory help in predicting molecular shapes? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of electronegativity in chemical bonding? |  |
| 4. How can you differentiate between polar and nonpolar molecules? |  |
| 5. What is hybridization, and why is it important in understanding molecular structure? |  |




















