Mnemonics: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
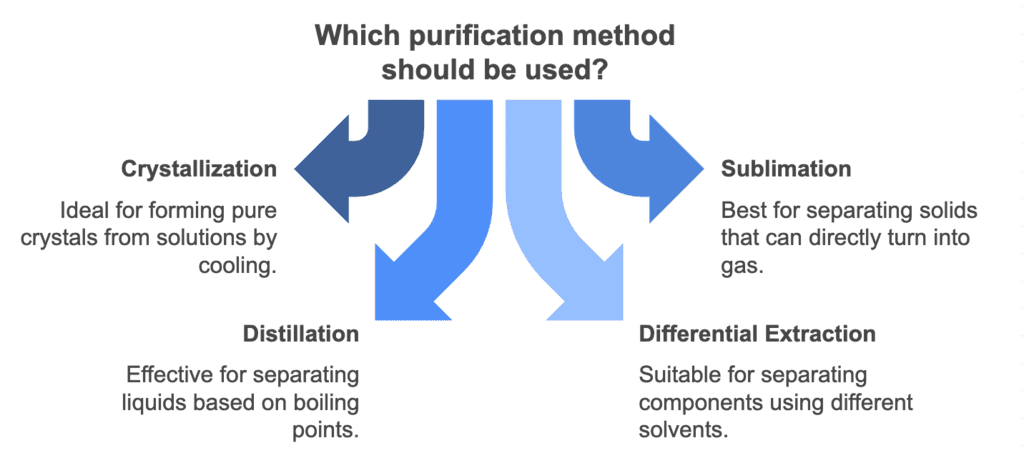
Purification Methods
Crystallization
Mnemonic: "Cool Crystals Climb Slowly."
Explanation: Crystallization occurs when a solution cools and forms crystals, slowly allowing pure crystals to climb or form.
Sublimation
Mnemonic: "Sublime Solids Skip Liquids."
Explanation: Sublimation is when solids skip the liquid phase and directly turn into gas, a "sublime" and efficient separation process.
Distillation
Mnemonic: "Distillation Divides By Boiling."
Explanation: Distillation separates liquids by their boiling points, making it effective in purifying volatile substances.
Differential Extraction
Mnemonic: "Different Solvents Divide."
Explanation: In differential extraction, different solvents help separate components of a mixture based on their solubility.
Chromatography
Mnemonic: "Chromatography Cuts Components."
Explanation: Chromatography separates a mixture into individual components, often resulting in distinct bands or "cuts."
Qualitative Analysis
Detection of Extra Elements
Mnemonic: "Nasty Sulfur Puts Halogens on Trial."
Explanation: Lassaigne’s test is used to detect Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Halogens. The phrase helps remember the four elements tested in the analysis: Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Halogens.
Detection of Functional Groups
Hydroxyl Group (Alcoholic & Phenolic)
Mnemonic: "Hydroxyl Hides in Alcohols and Phenols."
Explanation: The Hydroxyl group (-OH) is found in both Alcoholic and Phenolic compounds. This mnemonic emphasizes that the hydroxyl group "hides" in both types of compounds.
Carbonyl Group (Aldehyde & Ketones)
Mnemonic: "Carbonyl Catches Aldehydes and Ketones."
Explanation: The Carbonyl group (-C=O) is present in both Aldehydes and Ketones. The mnemonic helps you remember that this group “catches” or identifies both.
Carboxyl Group
Mnemonic: "Carboxyl Creates Organic Acids."
Explanation: The Carboxyl group (-COOH) is characteristic of organic acids like acetic acid. This mnemonic links carboxyl with its role in forming acids.
Amino Group
Mnemonic: "Amino Adds Nitrogen."
Explanation: The Amino group (-NH2) contains Nitrogen and is found in amines. This mnemonic helps emphasize the key element Nitrogen in the amino group.
Identification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
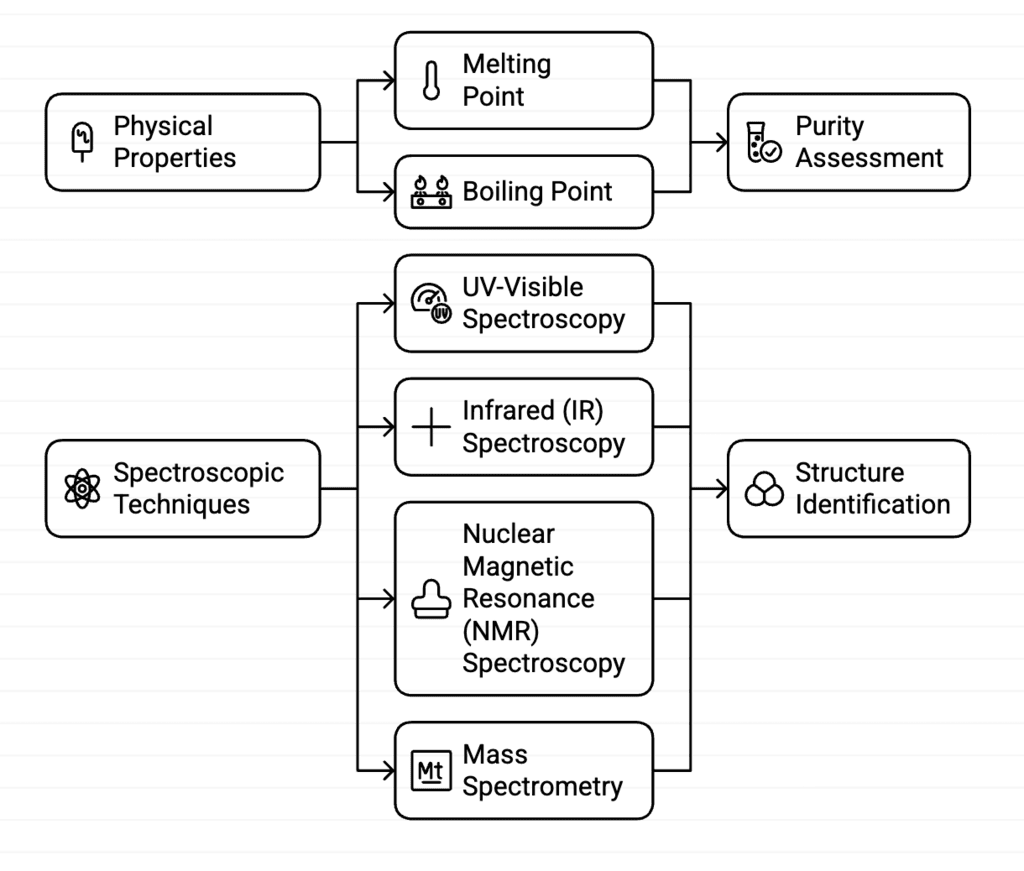
Physical Properties
Mnemonic: "Melting Boiling Points Reveal Purity."
Explanation: Melting point and boiling point are key physical properties used to identify and characterize organic compounds by assessing their purity.
Spectroscopic Techniques
UV-Visible Spectroscopy
Mnemonic: "UV-Visible Detects Absorption."
Explanation: UV-Visible spectroscopy detects the absorption of ultraviolet and visible light by compounds, helping identify their structure.
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
Mnemonic: "Infrared Identifies Bonds."
Explanation: IR spectroscopy identifies vibrations in chemical bonds, helping determine functional groups and molecular structure.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Mnemonic: "NMR Notes Nuclear Spins."
Explanation: NMR spectroscopy detects the nuclear spins of atoms, revealing detailed information about the structure of organic compounds.
Mass Spectrometry
Mnemonic: "Mass Spectrometry Measures Fragments."
Explanation: Mass spectrometry breaks down a compound into smaller ions and measures their mass, revealing the structure of the compound.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the common purification methods used for organic compounds ? |  |
| 2. How can qualitative analysis help in the identification of organic compounds ? |  |
| 3. What role does spectroscopy play in the characterization of organic compounds ? |  |
| 4. What are some mnemonics to remember purification methods and characterization techniques ? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to purify organic compounds before characterization ? |  |
















