Worksheet with Solutions: Morphology of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Section A. Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The thimble-like structure protecting the root apex is called the ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Root cap
Q2: The arrangement of leaves on a stem or branch is termed as ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Phyllotaxy
Q3: The outermost whorl of a flower, composed of sepals, is called the ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Calyx
Q4: A fruit formed without fertilization of the ovary is known as a ________ fruit.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Parthenocarpic
Q5: The scar on the seed coat through which the seed was attached to the fruit is called the ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Hilum
Section B. Match the Column
Column A (Feature) | Column B (Example/Description) |
|---|---|
a) Reticulate venation | i) Monocotyledons (Maize) |
b) Parallel venation | ii) Dicotyledons (Mustard) |
c) Hypogynous flower | iii) Superior ovary (Brinjal) |
d) Syncarpous ovary | iv) Fused carpels (Tomato) |
e) Pinnately compound leaf | v) Leaflets on a common axis (Neem) |
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: a-ii, b-i, c-iii, d-iv, e-v
Section C. Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is a characteristic of a tap root system?
(a) Found in monocotyledons
(b) Direct elongation of the radicle
(c) Fibrous and branched
(d) Develops from the stem
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Direct elongation of the radicle
Q2: What is the primary function of the petiole in a leaf?
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Holding the leaf blade to light
(c) Protecting the leaf bud
(d) Storing food
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Holding the leaf blade to light
Q3: Which type of inflorescence has flowers arranged in a basipetal order?
(a) Racemose
(b) Cymose
(c) Solitary
(d) Axillary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Cymose
Q4: Which type of aestivation is observed in pea flowers?
(a) Valvate
(b) Twisted
(c) Imbricate
(d) Vexillary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Vexillary
Q5: In which type of placentation is a single ovule attached at the base of the ovary?
(a) Marginal
(b) Axile
(c) Basal
(d) Parietal
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Basal
Section D. Assertion Reasoning Questions
Q1: Assertion: Dicotyledonous plants generally have reticulate venation.
Reason: The veinlets in their leaves form a network pattern.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
The assertion is true, as dicotyledonous plants do indeed have reticulate venation. The reason is also true, as the veinlets in dicot leaves form a network pattern. The reason directly explains the assertion, as the network pattern is what defines reticulate venation in dicots. Thus, the correct answer is (a): "Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion."
Q2: Assertion: Monocotyledonous seeds are generally endospermic.
Reason: The endosperm is absent in mature seeds of cereals like maize.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
The assertion is true because monocots generally have endospermic seeds. However, the reason is false because the endosperm is present in mature seeds of cereals like maize. Therefore, the correct answer is (c): "Assertion is true, but the reason is false."
Section E. Case-Based Questions
Case 1: Root System
The root system of flowering plants is crucial for anchorage, absorption, and sometimes storage. Discuss the types of root systems and their modifications with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:The root system in flowering plants is classified into:
Tap Root System: Formed by the elongation of the radicle, with secondary and tertiary roots (e.g., mustard). Common in dicotyledons.
Fibrous Root System: Numerous thin, thread-like roots of equal size, replacing the primary root (e.g., maize). Typical in monocotyledons.
Adventitious Root System: Roots arising from parts other than the radicle, such as stems or leaves (e.g., banyan for support).
Modifications:Storage: Swollen roots for food storage (e.g., carrot in tap roots).
Support: Prop roots in banyan or stilt roots in maize for mechanical support.
Respiration: Pneumatophores in mangroves for gaseous exchange.
Case 2: Flower Structure
Flowers are the reproductive units of angiosperms, exhibiting diverse structures. Explain the symmetry and ovary position in flowers with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Flowers vary in symmetry and ovary position:
Symmetry:
Actinomorphic: Can be divided into equal radial halves in any plane (e.g., mustard, datura). Exhibits radial symmetry.
Zygomorphic: Divisible into two similar halves in one vertical plane (e.g., pea, bean). Shows bilateral symmetry.
Asymmetric: Cannot be divided into similar halves by any plane (e.g., canna).
Ovary Position:
Hypogynous: Ovary superior, other parts below (e.g., china rose).
Perigynous: Ovary half inferior, other parts at the same level (e.g., rose).
Epigynous: Ovary inferior, other parts above (e.g., sunflower ray florets).
These variations aid in pollination and adaptation to different environments.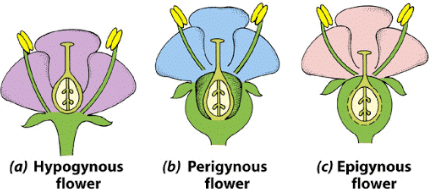
Section F. Short Answer Type
Q1: Explain the role of the region of elongation in root growth.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The region of elongation, located just above the meristematic region in the root, is where cells undergo rapid elongation and enlargement. This process drives the growth of the root in length, allowing it to penetrate deeper into the soil for better anchorage and absorption of water and minerals (e.g., in mustard roots).
Q2: Differentiate between nodes and internodes in a stem.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Nodes: Regions on the stem where leaves, branches, or buds arise (e.g., in china rose). They are points of attachment.
Internodes: Portions of the stem between two consecutive nodes. They determine the length and spacing of the stem (e.g., elongated in sunflower).
Q3: Describe the function of stipules in leaves.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Stipules are small, leaf-like structures at the leaf base (e.g., in pea). They protect the young leaf or bud, may aid in photosynthesis if green, and in some cases, become modified for defense (spines) or support (tendrils).
Q4: What is the significance of floral diagrams in plant description?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Floral diagrams illustrate the number, arrangement, and relationships of floral parts (calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium) in a flower. They provide a visual summary of floral structure, aiding in classification and identification (e.g., mustard in Brassicaceae).
Q5: Explain the structure of a drupe fruit with an example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A drupe is a fleshy fruit with a single seed, developed from a monocarpellary superior ovary. It has a thin epicarp (skin), a fleshy mesocarp (edible part), and a hard endocarp (stone) enclosing the seed. Example: Mango.
Q6: What is the role of the coleoptile in monocotyledonous seeds?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The coleoptile is a sheath enclosing the plumule in monocotyledonous seeds (e.g., maize). It protects the emerging shoot during germination and helps it break through the soil surface.
Q7: Define a bracteate flower and give an example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A bracteate flower has a reduced leaf-like structure called a bract at the base of the pedicel, which may protect the flower or attract pollinators. Example: Mustard.
Q8: Comment on the economic importance of the Solanaceae family.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Solanaceae family provides food (e.g., potato, tomato), spices (e.g., chilli), medicines (e.g., belladonna), fumigants (e.g., tobacco), and ornamentals (e.g., petunia), contributing significantly to agriculture and industry.
Section G. Long Answer Type
Q1: Discuss the significance of venation in leaves and its types with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Venation, the arrangement of veins and veinlets in a leaf lamina, is crucial for:
Structural Support: Veins provide rigidity to the leaf blade (e.g., in mustard).
Transport: They act as channels for water, minerals, and photosynthates between the leaf and other plant parts.
Classification: Venation patterns help distinguish monocotyledons from dicotyledons.
Types:Reticulate Venation: Veinlets form a network, typical in dicotyledons (e.g., china rose, brinjal). It supports efficient nutrient distribution.
Parallel Venation: Veins run parallel to each other, characteristic of monocotyledons (e.g., maize, wheat). It suits elongated, narrow leaves. These patterns reflect adaptations to photosynthetic and mechanical needs.
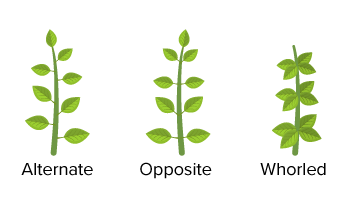
Q2: Explain the types of phyllotaxy and their role in optimizing leaf function with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves on a stem or branch, optimizing light capture and space utilization:
Alternate: A single leaf arises at each node in an alternate manner, maximizing light exposure (e.g., china rose, sunflower).
Opposite: A pair of leaves arises at each node, opposite each other, ensuring balanced light capture (e.g., guava, Calotropis).
Whorled: More than two leaves form a whorl at a node, crowding leaves for efficient photosynthesis in dense canopies (e.g., Alstonia).
These arrangements reduce shading among leaves, enhance photosynthesis, and support plant growth by optimizing resource use.
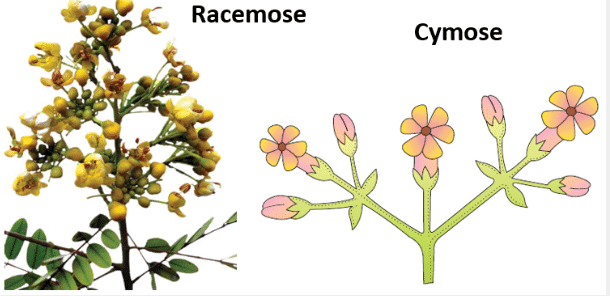
Q3: Describe the structure and types of inflorescences in flowering plants with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Inflorescence is the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis, influencing pollination and seed dispersal:
Racemose: The main axis continues to grow, with flowers borne laterally in acropetal succession (e.g., mustard). It allows continuous flowering.
Cymose: The main axis terminates in a flower, with flowers in basipetal order (e.g., jasmine). It limits growth but ensures early seed production.
Solitary: A single flower at the shoot tip or axil (e.g., Solanum).
These types reflect adaptations to pollinator attraction and reproductive strategies, with racemose suited for prolonged flowering and cymose for rapid reproduction.
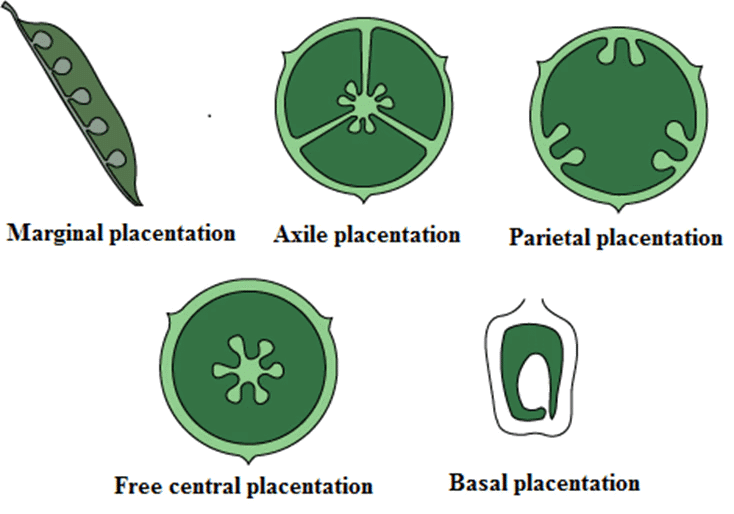
Q4: Discuss the variations in placentation and their significance in flowering plants with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Placentation is the arrangement of ovules within the ovary, impacting seed development and dispersal:
Marginal: Ovules form two rows along the ventral suture in a unilocular ovary (e.g., pea). Maximizes ovule number in simple ovaries.
Axile: Ovules attach to a central axis in a multilocular ovary (e.g., tomato, china rose). Supports multiple ovules per locule.
Parietal: Ovules develop on the inner ovary wall, often with a false septum (e.g., mustard). Increases ovule capacity in unilocular ovaries.
Free Central: Ovules on a central axis without septa (e.g., Dianthus). Efficient in small ovaries.
Basal: A single ovule at the ovary base (e.g., sunflower). Suits single-seeded fruits. These variations optimize ovule protection and seed production, aiding reproductive success.
Q5: Point out differences between the structure of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous seeds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Dicotyledonous Seeds:
Cotyledons: Two, often fleshy, storing reserve food (e.g., gram, pea).
Endosperm: Usually absent in mature seeds (non-endospermic, e.g., bean).
Seed Coat: Has two layers (testa and tegmen) with a hilum and micropyle (e.g., castor).
Embryo: Large, with distinct radicle and plumule.
Monocotyledonous Seeds:
Cotyledons: One, often shield-shaped (scutellum, e.g., maize).
Endosperm: Bulky, food-storing, present in mature seeds (endospermic, e.g., wheat).
Seed Coat: Membranous, often fused with the fruit wall, with an aleurone layer.
Embryo: Small, with coleoptile (plumule sheath) and coleorhiza (radicle sheath).
Key Difference: Dicot seeds rely on cotyledons for food storage, while monocot seeds depend on endosperm, reflecting distinct germination strategies.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet with Solutions: Morphology of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main parts of a flowering plant? |  |
| 2. How do the morphology of flowering plants vary among different species? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of studying the morphology of flowering plants? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of inflorescences in flowering plants? |  |
| 5. How does the structure of roots contribute to the overall health of a flowering plant? |  |
















