Plea Bargaining | Criminal Law - CLAT PG PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Plea Bargaining under CrPC |

|
| Key Provisions and Their Applicatio |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Plea bargaining is a mechanism in the criminal justice system that allows an accused to negotiate with the prosecution to plead guilty in exchange for a lesser sentence or reduced charges. Introduced in India through the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining is governed by Sections 265A to 265L of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC). It aims to reduce judicial backlog, expedite case disposal, and provide relief to undertrials. The Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 (BNSS) has further refined these provisions to enhance accessibility and fairness. These notes provide a comprehensive guide to plea bargaining, covering its scope, procedure, case laws, and preparation strategies for the CLAT PG 2025 examination, equipping aspirants to tackle application-based questions effectively.
Plea Bargaining under CrPC
Plea bargaining is a consensual process where the accused pleads guilty to a lesser offense or agrees to a reduced sentence in exchange for concessions from the prosecution. It is regulated by Sections 265A to 265L CrPC, introduced to address delays in criminal trials and reduce the burden on courts.
Scope and Applicability (Section 265A CrPC)
Eligible Cases:- Offenses punishable with imprisonment up to 7 years.
- Offenses that do not affect socio-economic conditions of the country (e.g., offenses under the Essential Commodities Act are excluded).
- Offenses not committed against women or children below 14 years.
- Offenses punishable with death, life imprisonment, or imprisonment exceeding 7 years.
- Offenses under laws like the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act or NDPS Act.
- Cases involving heinous crimes or public interest.
- Plea bargaining can be initiated by the accused through an application to the court.
- It is not applicable to cases where the accused denies the charges or opts for a full trial.
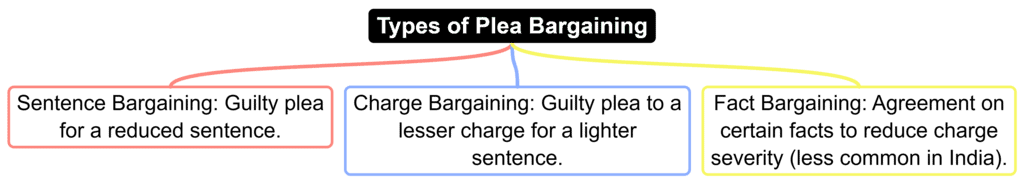
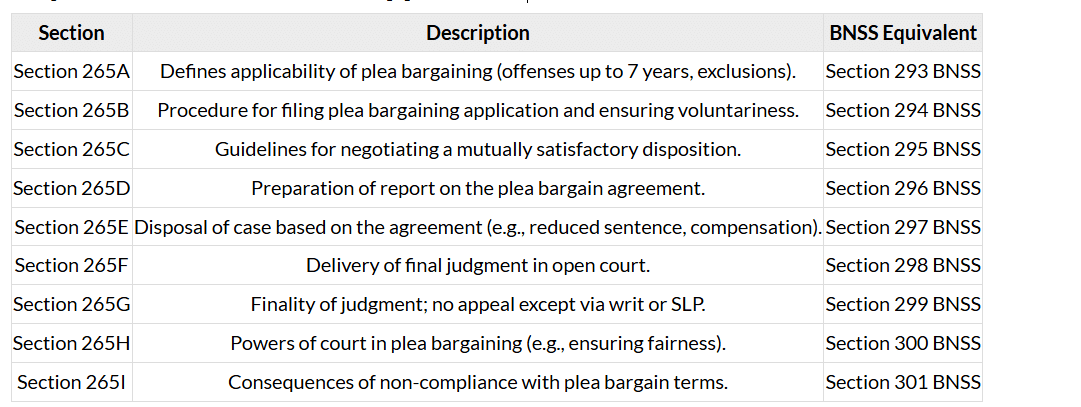
Procedure for Plea Bargaining (Sections 265B–265I CrPC)
- Application by Accused(Section 265B):
- The accused files a written application in the court where the trial is pending, expressing willingness to plead guilty and seek plea bargaining.
- The application must include a brief description of the case and be accompanied by an affidavit affirming the plea is voluntary.
- Examination by Court(Section 265B):
- The court examines the accused in camera (private session) to ensure the plea is voluntary and not coerced.
- If the plea is found involuntary, the court rejects the application and proceeds with the trial.
- Mutual Agreement(Section 265C):
- The court issues notice to the public prosecutor, the investigating officer, the accused, and the victim to participate in a meeting.
- Parties negotiate a mutually satisfactory disposition, which may include:
- Reduced sentence.
- Pleading guilty to a lesser charge.
- Compensation to the victim.
- Report Submission(Section 265D):
- If an agreement is reached, the court prepares a report of the mutually satisfactory disposition, signed by all parties.
- If no agreement is reached, the court proceeds with the trial.
- Disposal of Case(Section 265E):
- The court disposes of the case based on the agreement, which may involve:
- Releasing the accused on probation under the Probation of Offenders Act.
- Imposing a sentence of one-fourth of the prescribed punishment for the offense.
- Ordering compensation to the victim alongside the sentence.
- The court disposes of the case based on the agreement, which may involve:
- Judgment(Section 265F):
- The court delivers the judgment in open court, incorporating the terms of the plea bargain.
- The judgment is final and cannot be appealed, except via a writ petition under Articles 226 or 227 of the Constitution or a special leave petition under Article 136.
- Non-Compliance(Section 265I):
- If the accused violates the terms of the plea bargain (e.g., fails to pay compensation), the court may initiate proceedings for breach.
Safeguards and Conditions
- Voluntariness: The plea must be made voluntarily, without coercion or undue influence (Section 265B).
- Victim’s Role: The victim has a right to participate in negotiations and receive compensation (Section 265C).
- Judicial Oversight: The court ensures fairness and compliance with legal principles.
- No Coercion: Plea bargaining cannot be used if the accused is pressured or lacks legal representation.
Benefits of Plea Bargaining
- Reduces judicial backlog by expediting case disposal.
- Provides relief to undertrials languishing in jails.
- Ensures victim compensation, promoting restorative justice.
- Saves time and resources for courts, prosecution, and defense.
Limitations
- Limited to offenses with imprisonment up to 7 years.
- Not applicable to serious or socio-economic offenses.
- Requires victim consent, which may delay or derail negotiations.
- Potential for misuse if voluntariness is not strictly ensured.
BNSS Updates
- Section 293 BNSS: Replaces Section 265A CrPC, expanding plea bargaining to certain compoundable offenses under special laws.
- Section 294 BNSS: Replaces Section 265B CrPC, mandating legal aid for accused to ensure informed decision-making.
- Digital Processes: BNSS allows plea bargaining applications and negotiations via electronic means.
Key Case Laws
State of Gujarat v. Natwar Harchandji Thakor (2005)
- Holding: Plea bargaining is a valid mechanism to reduce judicial backlog, provided it is voluntary and fair.
Murlidhar Meghraj Loya v. State of Maharashtra (1976)
- Holding: Emphasized the need for judicial oversight to prevent coercion in plea negotiations (pre-amendment, but relevant).
Thippaswamy v. State of Karnataka (1983)
- Holding: Plea bargaining must ensure the accused is fully aware of consequences, reinforcing the need for legal representation.
Note: For CLAT PG, focus on the eligibility criteria, procedural steps, and safeguards under Sections 265A–265L. Practice questions on the applicability of plea bargaining and victim’s role.
Key Provisions and Their Applicatio
Conclusion
Plea bargaining, as outlined in Sections 265A to 265L CrPC, represents a progressive approach to criminal justice, offering an alternative to protracted trials while ensuring fairness and victim compensation. Its structured procedure, coupled with safeguards like voluntariness and judicial oversight, makes it a vital tool for reducing judicial backlog and supporting undertrials. The BNSS enhancements, such as digital processes and expanded scope, reflect its growing relevance. For CLAT PG 2025, mastering plea bargaining’s eligibility, procedural nuances, and case laws like State of Gujarat v. Natwar Harchandji Thakor is essential. By focusing on key provisions, practicing application-based questions, and leveraging recommended resources, aspirants can excel in the Criminal Law section and contribute to a more efficient justice system.
|
75 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Plea Bargaining - Criminal Law - CLAT PG
| 1. What is plea bargaining under the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key provisions related to plea bargaining in the CrPC? |  |
| 3. Who is eligible for plea bargaining under the CrPC? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of plea bargaining for the accused? |  |
| 5. How does the court ensure fairness in the plea bargaining process? |  |




















