Understanding the Weather Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 2 Free PDF
| Table of contents |

|
| Weather and Its Elements |

|
| Weather Instruments |

|
| Weather Stations |

|
| Predicting the Weather |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Weather and Its Elements
Weather affects our daily lives in many ways, such as deciding what clothes to wear. For example:
- Winter calls for warm clothes.
- Summer calls for cool clothes.
 Weather and Seasons
Weather and Seasons
This chapter explains how we measure and monitor weather and why weather predictions are important. Weather predictions help us prepare for events like:
- Heavy rain
- Storms
- Droughts
- Heat waves
Understanding weather also helps people like farmers, pilots, sailors, and governments plan and stay safe.
What is Weather?
Weather refers to the state of the Earth’s atmosphere at a specific time and place. We describe weather using words like hot, cold, rainy, cloudy, humid, snowy, or windy.
- Atmosphere: The atmosphere is a layer of gases or air surrounding the Earth. One can think of the Earth's atmosphere like a cake with different layers.
- Troposphere: The layer closest to the Earth's surface is known as the troposphere. It is where all land-based plants and animals, including humans, live and breathe. Almost all weather events happen here. The troposphere stretches from 6 to 18 kilometres above the ground; it is thinner at the poles, where cold air contracts, and thicker in the tropics, where warm air expands.
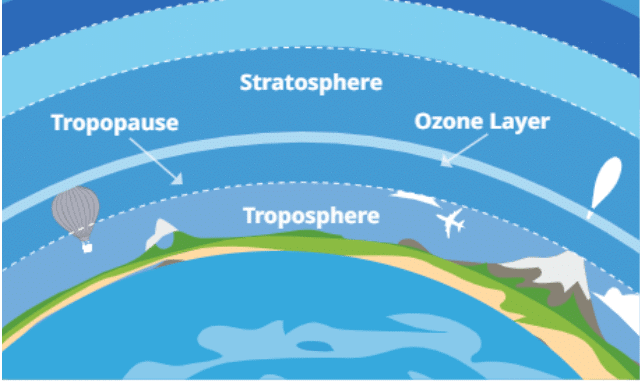 Troposphere
Troposphere
- The five main elements of weather are:
i) Temperature: How hot or cold the air is.
ii) Precipitation: Water falling from the sky, like rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
iii) Atmospheric Pressure: The weight of the air pressing down on the Earth’s surface.
iv) Wind: The movement of air, including its speed and direction.
v) Humidity: The amount of water vapour (gaseous water) in the air. - Since people experience weather differently (e.g., cold in Chennai may feel pleasant in Kashmir), standard methods to measure these elements are essential.
- Since ancient times, humans have observed nature to forecast the weather. For example, watching birds fly low, ants carry eggs, squirrels gather nuts, frogs croak loudly, or pine cones open and close has provided clues about upcoming rain or storms. This knowledge has been passed down through generations.
- In India, traditional methods are still used to predict the monsoon.
Let's Revise
Q: What is the troposphere, and why is it important?
 View Answer
View Answer 
 View Answer
View Answer 
Weather Instruments
Scientists use special instruments to measure these elements of weather accurately.
- Measured using a thermometer, which shows how hot or cold it is.
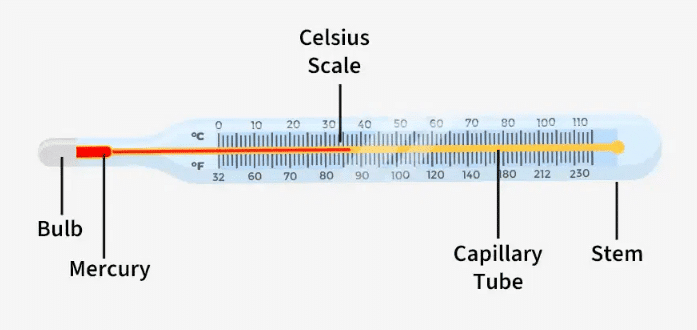 Clinical Thermometer
Clinical Thermometer
- Thermometers can be clinical or laboratory types, using Celsius and Fahrenheit scales (e.g., 15°C = 59°F).
- Some thermometers measure ambient temperature, while others record maximum and minimum temperatures of the day.
- Digital thermometers are more precise and store more data.
Useful statistics include: - Range: Maximum temperature minus minimum temperature in 24 hours.
- Mean daily temperature: (Maximum + Minimum) ÷ 2.
- Measured using a rain gauge, which collects rainwater in a cylinder through a funnel.
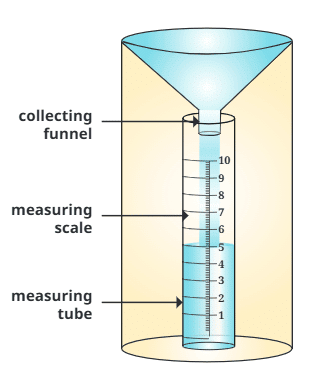 Rain Gauge
Rain Gauge - A scale measures the depth of water (e.g., 5 mm of water means 5 mm of rainfall).
- For snow, it is melted before measurements.
- We know about temperature and rain, but sometimes the weather feels 'heavy' before a storm. This relates to atmospheric pressure.
- Atmospheric Pressure is higher near sea coasts and lower in mountains, where air is thinner with less oxygen, causing breathlessness at high altitudes.
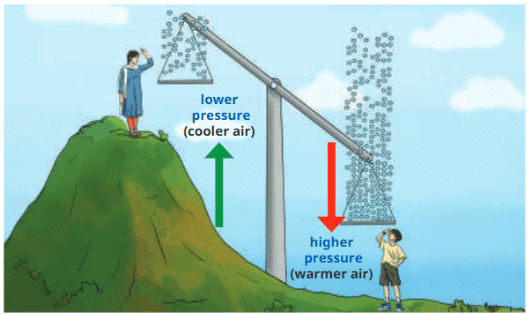 Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric Pressure
- Low pressure can form a depression or low-pressure system, leading to storms or cyclones.
- Measured using a barometer in millibars (mb). Normal pressure at sea level is about 1013 mb; pressure 1000 mb indicates a depression.
- This is crucial for individuals like mountaineers or soldiers at high altitudes (e.g., Khardung La in Ladakh at 5600 m has about 650 mb).
Let's Revise
 View Answer
View Answer 
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Wind is the movement of air from high-pressure to low-pressure areas, with speed and direction.
- Important for pilots, sailors, farmers, and weather forecasting, as it affects rain, soil drying, and seed dispersal.
- Wind vane (or weather vane) shows wind direction with a pointer and tail that turns when wind blows.
- Wind sock is a type of wind vane used at airports or industries.
- Anemometer measures wind speed with rotating cups; faster rotation means stronger wind, measured in km/h.
 Anemometer
Anemometer
- The amount of water vapour in the air, affected by temperature, wind, pressure, and location.
- High humidity (e.g., in coastal Kochi) slows evapouration, while low humidity (e.g., in dry Jaipur) speeds it up.
- Measured as relative humidity: 0% (no water vapour, impossible naturally) to 100% (air saturated with water vapour).
- Dry weather is 20–40% humidity; humid weather is 60–80%.
- Measured using a hygrometer, important for food processing and museums to keep items dry.
 Hygrometer
Hygrometer - High humidity (e.g., 84% in Kochi) makes clothes dry slower and causes more sweating than lower humidity (e.g., 52% in Delhi).
Weather Stations
A weather station combines instruments like thermometers, rain gauges, barometers, anemometers, and hygrometers to measure weather at one place. Readings are taken regularly to track and forecast weather.
 Weather Station
Weather Station
Automated Weather Station (AWS)
- An Automated Weather Station (AWS) uses sensors to measure temperature, humidity, wind, precipitation, and pressure without human help.
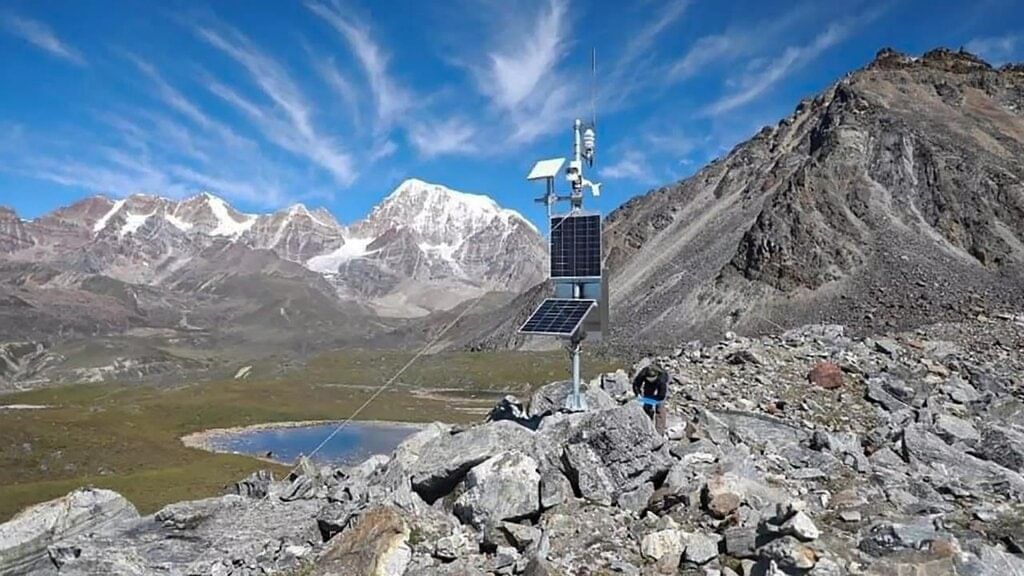 AWS at a glacial lake of Sikkim
AWS at a glacial lake of Sikkim
- AWS is used in agriculture, aviation, navigation, and environmental monitoring for accurate, timely data.
- In 2023, the National Disaster Management Authority established an AWS at a glacial lake in Sikkim, at an altitude of over 4800 metres above sea level, offering early warnings about upcoming weather conditions.
Predicting the Weather
Meteorologists gather data from weather tools over time to forecast weather using scientific methods. These forecasts are crucial now, as climate change increases the occurrence of extreme weather like droughts, floods, and cyclones. Accurate predictions help us prepare for these events and enable local authorities to allocate resources and plan for potential disasters.
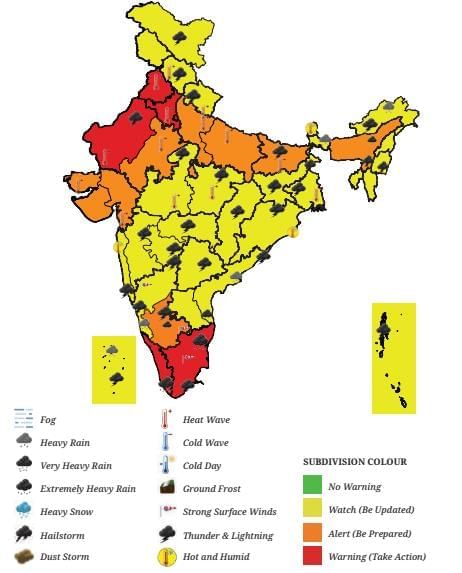 Weather Warning for India on 19 May 2024
Weather Warning for India on 19 May 2024
Accurate predictions help:
- Warn fishermen about stormy seas.
- Evacuate coastal areas before cyclones.
- Allow governments to prepare resources for disasters.
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) was established in 1875. Its motto is ādityāt jāyate vriṣhti, which means “Rain is produced by the sun.” This line comes from the ancient text Manusmṛiti. The full verse says, “Rain comes from the sun, food comes from rain, and all living beings come from food.”
 IMD
IMD
Points to Remember
- Weather is described by five main elements: temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, and atmospheric pressure.
- Special instruments like thermometers, rain gauges, barometers, anemometers, and hygrometers are used to measure these elements accurately.
- Data from these instruments helps us monitor and predict the weather.
- Weather elements dominate at different times: rainfall in July, temperature in May or December, and wind during hot loo winds or forest fires.
- Weather stations, including Automated Weather Stations (AWS), provide accurate weather data and forecasts.
- Weather is linked to climate, which will be discussed in the next chapter.
Difficult Words
- Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place.
- Atmosphere: The layer of gases (air) surrounding the Earth.
- Troposphere: The lowest layer of the atmosphere where weather happens.
- Precipitation: Water falling from the sky, like rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Atmospheric Pressure: The weight of air pressing down on the Earth’s surface.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapour in the air.
- Acclimatise: It means to slowly get used to a new place, weather, or situation
- Thermometer: An instrument that measures temperature.
- Rain Gauge: A tool that measures the amount of rainfall.
- Barometer: An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.
- Wind Vane: A tool that shows the direction of the wind.
- Anemometer: An instrument that measures wind speed.
- Hygrometer: A tool that measures humidity.
- Weather Station: A setup with multiple instruments to measure weather elements.
- Meteorologists: Scientists who study and predict weather.
















