From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 9 Free PDF
Introduction
A government is a system that runs a country, making rules and ensuring people’s safety and welfare. Kauṭilya in his book Arthaśhāstra said a ruler’s duties are: protecting the country from enemies (raksha), keeping peace inside (pālana), and caring for people’s well-being.
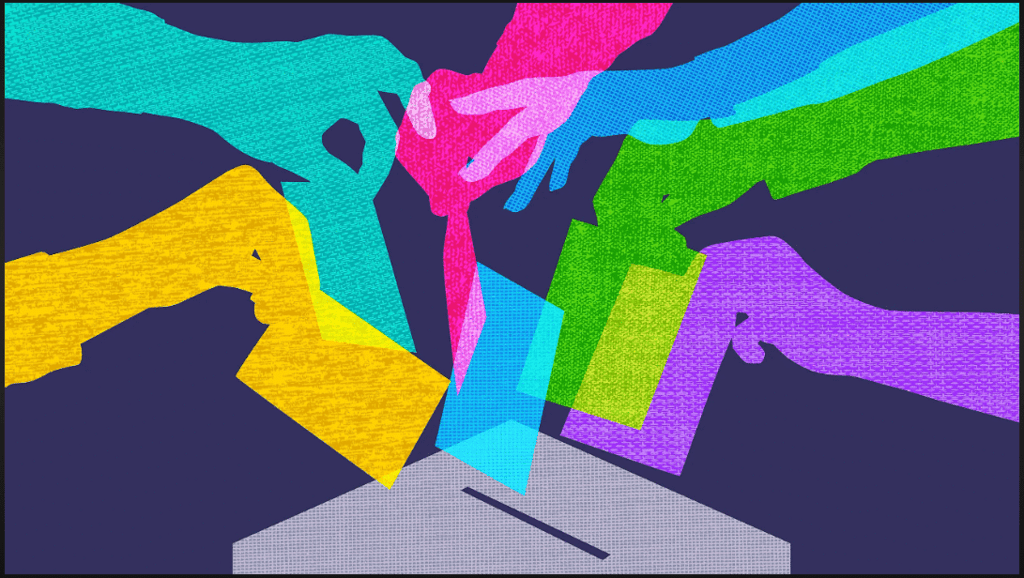

- There are different types of governments, like democracy, monarchy, and others, each working differently.
- Governments get their power from different sources, such as the people in a democracy or a king in a monarchy.
- Governments interact with people by making laws, providing services, and ensuring fairness.
- Democracy is important because it gives people a voice in how their country is run.
What is Government? What are its Functions?
A government is a group that manages a country, making sure it runs smoothly. India has a democratic government, but other countries have different types.
- Keeping law and order so society is safe.
- Ensuring peace, stability, and security for everyone.
- Managing relations with other countries.
- Protecting the country through national defence.
- Providing important services like education, healthcare, and roads.
- Managing the economy, like trade and money matters.
- Working for people’s welfare to improve their lives.
What is Democracy?
Democracy means “rule of the people,” where the people are the source of power.
 Voting in India to Elect Government
Voting in India to Elect Government
Example: In a school, students need to manage tasks like timetables, sports, and meals. A Student Committee can be formed to make and follow rules.
Three ways to form the committee were suggested:- Every student joins the committee (hard to manage).
- The Head Teacher picks students (not everyone’s voice is heard).
- Students vote for representatives from each grade (fairest way).
The third way, where students choose representatives, is like a democracy because it includes everyone’s voice. Abraham Lincoln, a US president, called democracy a “government of the people, by the people, for the people.”
Functions of Government
In a democracy, people choose representatives to do these jobs, but the process differs in each country. Like a school committee, a government has three main jobs:
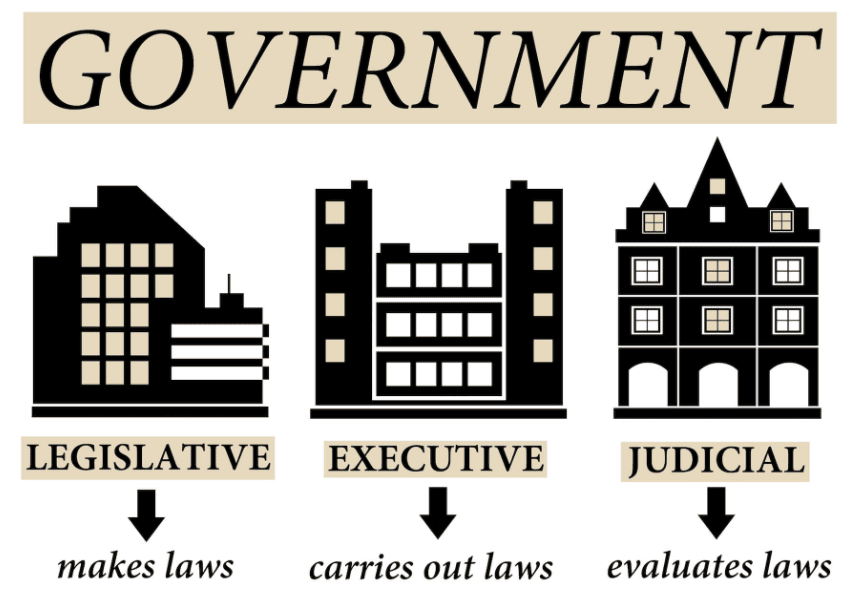
- Legislative function: Making rules (laws) to run the country.
- Executive function: Carrying out the rules and managing the country.
- Judicial function: Ensuring everyone follows the rules and settling disputes.Question for Chapter Notes: From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of GovernmentsTry yourself:What is the fairest way to form a student committee?View Solution
What Makes Governments Different?
Governments vary because each country has its own history, culture, and goals.
Key differences include:
- Who decides what the government is?
- How is the government formed?
- What are the parts of the government, and what do they do?
- What goals is the government working for?
Key Differences Between Governments
- Who decides “this is the government”?
In a democracy, the people decide through voting. In a theocracy, religious beliefs and leaders give power. - How is the government formed?
In a democracy, it’s through elections. In a monarchy, a king or queen from the family rules. - What are the parts of the government?
The legislative, executive, and judiciary parts may be separate or combined. In democracies, rules are often in a constitution. In monarchies, the king may decide. - What is the government working for?
Some governments, like India’s, aim for equality and prosperity for all. Others may focus on certain groups or families.
Democratic Governments Around the World
- Democracy is the most popular government type today, but democracies differ in how they work.
- Some countries adopted democracy long ago: USA (1787), Switzerland (1848), India (1947), Germany (1949), Kenya (1964), Nepal (2008).
Fundamental Principles of Democracy
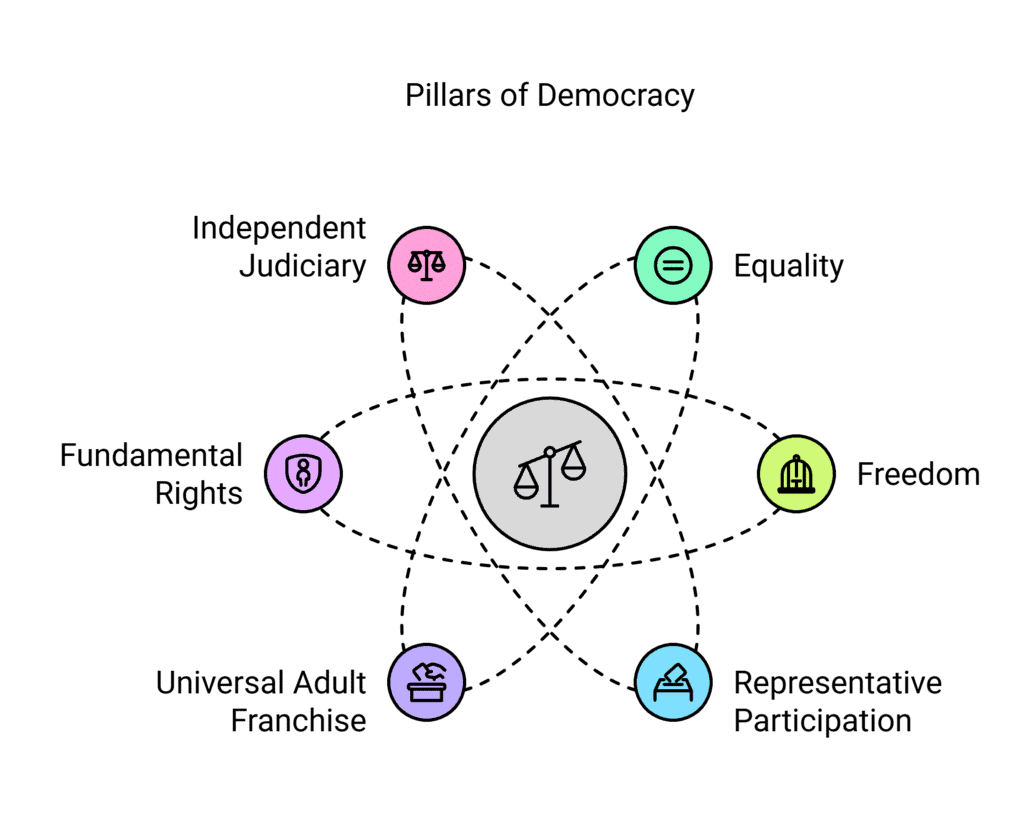
- Equality: Everyone is treated the same, with equal access to education, health, and laws.
- Freedom: People can make choices and express opinions freely.
- Representative participation: People choose representatives through elections.
- Universal adult franchise: Every adult can vote to choose representatives.
- Fundamental rights: Rights like equality, free speech, and protection from exploitation are guarded.
- Independent judiciary: Courts protect rights and ensure laws are followed by everyone, including the government.
These principles are ideals, not always fully achieved. For example, India gave all adults voting rights in 1950, but Switzerland gave women voting rights only in 1971.
Different Forms of Democratic Governments
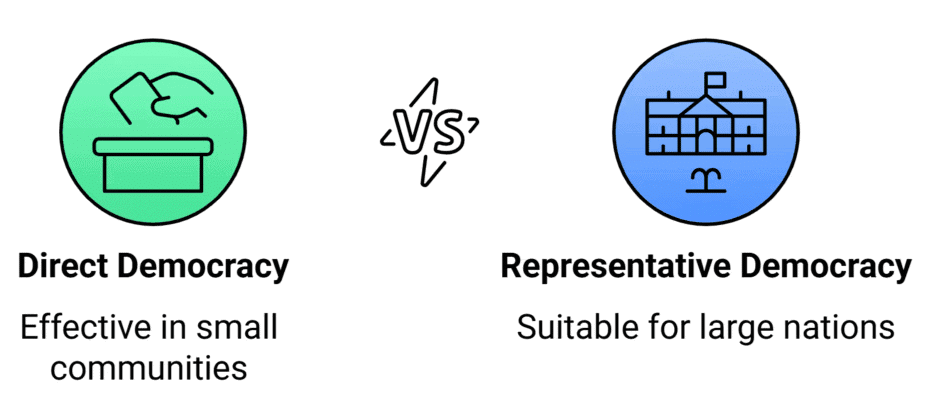
- Direct democracy: All citizens directly make rules and decisions. Used in small places like parts of Switzerland, but hard in big countries.
- Representative democracy: People elect representatives to govern, like in India. Elections happen regularly (every 5 years in India, 4 years in the USA).
Here are two Types of representative democracy:
1. Parliamentary democracy: The executive (prime minister and ministers) is part of the legislature (parliament). They need the legislature’s support (e.g., Lok Sabha in India). People elect the legislature, not the executive.
2. Presidential democracy: The president is elected separately and works independently of the legislature (e.g., USA). In India, states like Rajasthan have their own governments but are guided by the Union Government.Question for Chapter Notes: From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of GovernmentsTry yourself:How is a government formed in a democracy?View Solution
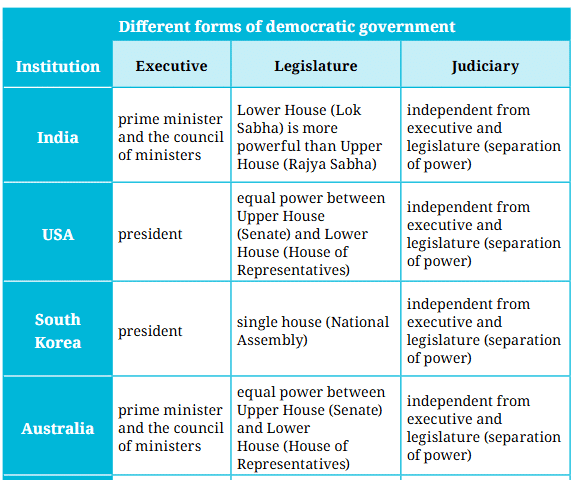
What Do These Terms Mean?
- Executive: The part of government that carries out laws. Its election process varies by country.
- Legislature: The group that makes laws, called Parliament in India and Congress in the USA. It often has two parts: Upper House (e.g., Rajya Sabha) and Lower House (e.g., Lok Sabha).
1. Lower House: Elected directly by people, usually more powerful (e.g., Lok Sabha in India).
2. Upper House: Elected or nominated, less powerful (e.g., Rajya Sabha in India). - Separation of Power: The legislature, executive, and judiciary work independently without interfering with each other.
A Peek into History
In ancient India, the Vajji mahajanapada (Lichchhavi clan) was an early republic. Leaders were chosen based on merit, and clans met to solve issues, ensuring people’s welfare.
- Republic: A government where the head is elected, not a hereditary king.
- Uttaramerur inscriptions from the 10th century CE in Tamil Nadu show how the Chola village sabha elected members using sealed ballot boxes. Rules included qualifications, duties, and removal for corruption.
 Chola Period Inscriptions
Chola Period Inscriptions - In ancient Greece and Rome (5th–4th century BCE), republics existed, but only free men could vote, excluding women and slaves.
Other Forms of Government
1. Monarchy: Ruled by a king or queen(monarch), usually hereditary.
- In ancient India, mahajanapadas had kings advised by sabhā or samiti. Empires gave kings more power, but they relied on ministers and scholars for dharma.
- Some kings claimed divine power, but in India, kings followed rājadharma, ruling fairly for people’s welfare.
- Example from Mahābhārata: Bhīshma taught Yudhiṣhṭhira that a king prioritizes people’s welfare, applies laws fairly, avoids ego, and seeks wise advice.
- Example from Rajatarangini (12th century CE): King Chandrapiḍa respected a cobbler’s hut, showing fairness and dharma.
- Absolute monarchy: The monarch has full power (e.g., Saudi Arabia, where the king rules by Islamic law but has advisors).
- Constitutional monarchy: The monarch has little power, and a parliament governs (e.g., United Kingdom, where the prime minister and parliament hold power).
 King Charles in a Ceremonial Coach
King Charles in a Ceremonial Coach
- Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran) combines theocracy and democracy. The Supreme Leader, chosen by clerics, has ultimate power, guided by Islamic principles. An elected president and parliament handle daily governance.
- Other theocracies: Afghanistan and Vatican City.
 Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler- Example: Adolf Hitler in Germany (1933–1945) became a dictator, caused the Holocaust (killing six million Jews), and started World War II.
- Example: Idi Amin in Uganda killed thousands and forced Indians to flee.
- Example: In North Korea, Shane’s life shows strict rules on haircuts, clothes, and internet access, with the government watching closely, unlike a democracy.
- In ancient Greece, aristocratic families ruled as oligarchies.
- Today, some democracies may act like oligarchies if a few rich or powerful people control decisions.Question for Chapter Notes: From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of GovernmentsTry yourself:What is the role of the executive branch in government?View Solution
Why Democracy Matters
Democracy is considered better than other governments because it gives people more rights and choices.
- In a democracy, people can choose how to live, speak, dress, and believe, as long as they don’t harm others.
- The government is accountable to the people, protecting their rights and providing basic needs.
- If the government fails, people can change it through elections.
- Democracy has challenges like corruption, wealth gaps, and control by a few, but citizens must stay alert to fix these.
- More than half the world’s countries are democracies because they value people’s freedom and well-being.
- Universal adult franchise: Only in democracy (Yes); not in dictatorship, absolute monarchy, or oligarchy (No).
- Equality: Democracy aims for equality (Yes); others often don’t (No).
- Freedom of speech: Allowed in democracy (Yes); limited or absent in others (No).
- Separation of powers: Present in democracy (Yes); often absent in others (No).
- Well-being of all: Democracy focuses on all citizens (Yes); others may prioritize certain groups (No).
Points to Remember
- Government runs a country, and different types answer: Who decides the government? What are its parts? What are its goals?
- Democracy is the most popular government type, with variations like direct and representative democracy.
- Representative democracy has two types: parliamentary (like India) and presidential.
- Other government types include monarchy, theocracy, dictatorship, and oligarchy.
- Democracy matters but faces challenges, and citizens must stay vigilant.
Difficult Words
- Government: The system that manages a country, making rules and providing services.
- Democracy: A government where people choose their leaders through voting.
- Representative: A person chosen to act or decide for others.
- Legislative: The job of making laws.
- Executive: The job of carrying out laws and managing the country.
- Judicial: The job of ensuring laws are followed and settling disputes.
- Constitution: A book of basic rules for running a country.
- Universal adult franchise: The right of all adults to vote.
- Fundamental rights: Basic rights like equality and free speech protected in a democracy.
- Independent judiciary: Courts that work separately from other government parts to protect rights.
- Republic: A government with an elected head, not a king.
- Monarchy: A government led by a king or queen.
- Theocracy: A government ruled by religious leaders and rules.
- Dictatorship: A government where one person or group has all power.
- Oligarchy: A government where a small, powerful group rules.
- Accountability: The government’s responsibility to answer to the people.
- Sovereign: A government’s independent power, free from outside control.
- Rājadharma: The duty of a king to rule fairly according to moral principles.
FAQs on From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 9 Free PDF
| 1. What is the primary role of government in society? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of a democratic government? |  |
| 3. How does democracy differ from other forms of government? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of democratic governments around the world? |  |
| 5. What are the fundamental principles of democracy? |  |

















