The Constitution of India - An Introduction Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 10 Free PDF
Introduction
The Constitution of India is a special document that sets the rules for running the country, adopted on 26 January 1950, celebrated as Republic Day.
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad, India’s first President, said following the Constitution can make India great, but it needs hard work, respect for others’ views, and moral values.
- A constitution is like a rulebook that guides how a country’s government works and protects citizens’ rights.
- The Indian Constitution was shaped by the freedom struggle and India’s cultural heritage.
- It remains important today because it supports democracy and ensures fairness and equality.
What Is a Constitution?
A constitution is a document that lists a country’s basic rules and laws.
- India’s Constitution is kept safe in a helium-filled glass case in Parliament, showing its importance.
- Important officials like the President, Prime Minister, and judges promise to follow it.
 Constitution of India in Helium filled Glass CaseIt explains:
Constitution of India in Helium filled Glass CaseIt explains:
- How the three parts of government (legislature, executive, judiciary) work and their responsibilities.
- Checks and balances to ensure the government is fair and accountable.
- The rights and duties of citizens.
- The country’s long-term goals and values, like equality and justice.
- It acts like a rulebook, similar to rules in a game (e.g., kabaddi), to settle disputes fairly.
- Without a rulebook, disagreements could cause chaos, as seen in a kabaddi match where players argued over a rule.
- Everyone must agree to follow the constitution to ensure order and fairness.Question for Chapter Notes: The Constitution of India — An IntroductionTry yourself:What is celebrated as Republic Day in India?View Solution
Writing the Constitution of India
While fighting for independence from British rule, India planned how to govern itself. Big questions included: What type of government? Who can vote? How to settle disputes?
 Constituent Assembly
Constituent Assembly
- A Constituent Assembly was formed in 1946 to answer these questions and write the Constitution.
- Dr. Sachidananda Sinha, the first President of the Assembly, wished for wisdom and fairness in the process.
How Was Our Constitution Developed?
- The Constituent Assembly started on 9 December 1946 with 389 members (later 299 after Partition), including 15 women, representing India’s diverse regions and groups.
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the Chairman of the Assembly.
- A Drafting Committee, led by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, prepared the initial text. Dr. Ambedkar was a social reformer and India’s first Law and Justice Minister.
- It took almost three years to complete, from 1946 to 26 November 1949, when the Constitution was adopted.
- It came into effect on 26 January 1950, now celebrated as Republic Day.
- Members were elected by provincial assemblies, which were chosen by the people, ensuring a democratic process.
What Shaped and Influenced the Indian Constitution?
The Constitution was influenced by three main sources: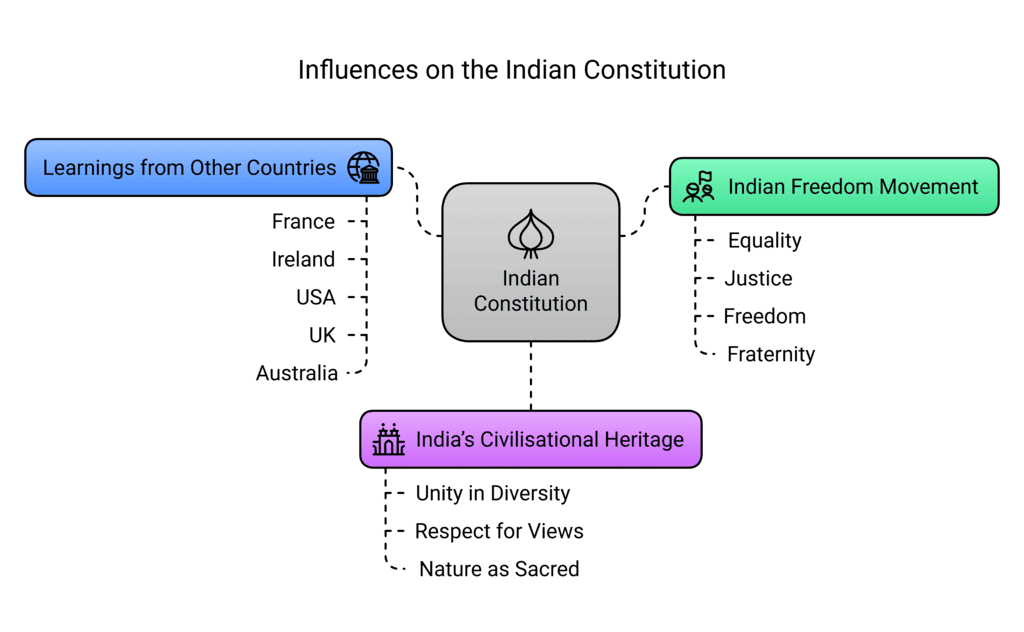 Indian Freedom Movement:
Indian Freedom Movement:- Values like equality, justice, freedom, and fraternity from the freedom struggle were included.
- Freedom movement leaders in the Constituent Assembly brought their experiences.
- It answered key questions, like ensuring universal adult franchise, separation of powers, and protecting fundamental rights.
- It set rules for amending the Constitution and the relationship between Central and State governments.
- India’s culture emphasizes unity in diversity, respect for different views, and nature as sacred.
- Ideas like vasudhaiva kutumbakam (world is one family) and sarve bhavantu sukhinah (well-being of all) are part of the Constitution.
- Historical governance systems (janapadas, sanghas, Kauṭilya’s saptanga, rajadharma) focused on people’s roles, influencing Fundamental Duties.
Following the Indian tradition of “Let noble thoughts come from every side,” the Assembly studied other constitutions.
- France: Inspired liberty, equality, and fraternity from the 1789 French Revolution.
- Ireland: Influenced Directive Principles of State Policy.
- USA: Shaped the idea of an independent judiciary.
- Other countries like the UK and Australia also provided ideas.
The Constitution includes illustrations of India’s heritage, like scenes from Mahabharata, Ramayana, Mohenjo-daro, and Mughal architecture, showing cultural pride.
Key Features of the Constitution of India
Before we get introduced to Main Features of Indian Constitution, Let's revise how the government works:
- Legislature: Makes laws.
- Executive: Implements laws, led by the Prime Minister.
- Judiciary: Ensures laws follow the Constitution and decides punishments.
- Separation of powers: Keeps the three parts independent for fairness.
- It has a three-tier system: Central, State, and local (Panchayati Raj) governments, with clear roles.
- The electoral system ensures every adult can vote.
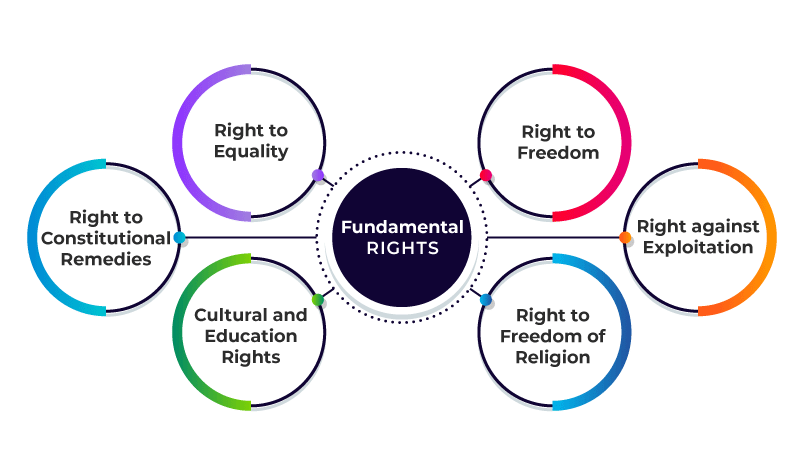
- Fundamental Rights: Promises like equality (Article 14), freedom (Article 21), education (Article 21-A), and protection from exploitation. Citizens can go to court if these are violated.
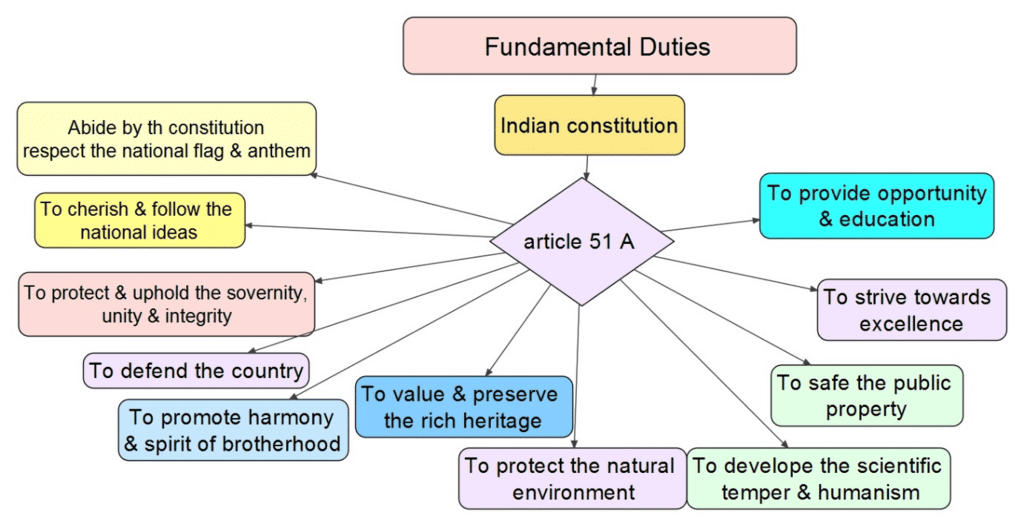
- Fundamental Duties: Responsibilities like respecting the Constitution, defending the country, preserving cultural heritage, protecting nature, and ensuring children’s education.
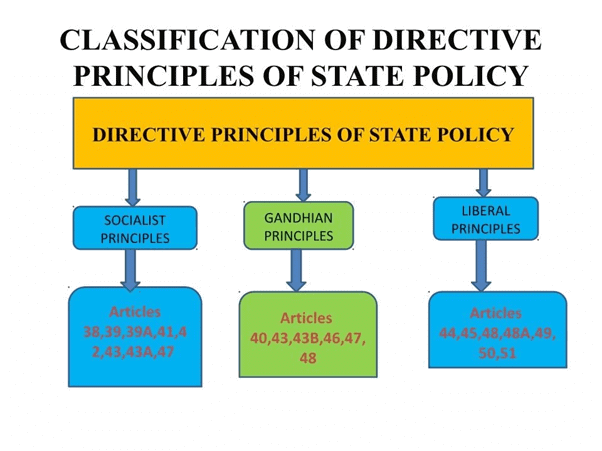
- Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP): Goals for the government, like improving living standards, ensuring justice (Article 38), protecting the environment (Article 48-A), and promoting health (Article 47). These are guidelines, not enforceable in court.
Begum Aizaz Rasul in 1949 said the Constitution’s equality for women (Article 14) reflects India’s ancient ideal, though social issues had weakened it.
The Constitution Is a Living Document
The Constitution can be changed through amendments to meet new needs, making it a living document.
 Illustration in Constitution of IndiaExamples of changes:
Illustration in Constitution of IndiaExamples of changes:
- Fundamental Duties were added in 1976 (Part IV-A).
- In 2004, the Supreme Court allowed citizens to fly the national flag at home, part of the Right to Freedom of Expression.
- The Panchayati Raj System was added in 1992 via the 73rd Amendment.
Amendments:
- Amendments are debated in Parliament and sometimes state assemblies, with public opinions often considered.
- Popular movements can also lead to changes.
- The Constitution’s text was handwritten by Prem Behari Narain Raizada, and Nandalal Bose illustrated it with scenes from India’s history, making it a work of art.Question for Chapter Notes: The Constitution of India — An IntroductionTry yourself:What does the executive branch of the government do?View Solution
Understanding the Preamble: The Guiding Values of the Constitution of India
The Preamble is the introduction to the Constitution, summarizing its core values that guide the government and citizens. It reflects the Constitution’s principles, like justice, liberty, and equality, used in policymaking.
 Preamble of Indian ConstitutionPreamble of the Indian Constitution explains the Constitution’s purpose and values:
Preamble of Indian ConstitutionPreamble of the Indian Constitution explains the Constitution’s purpose and values:
- WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA: The Constitution was made by the people through their representatives, not a king or foreign power.
- SOVEREIGN: India makes its own decisions, free from outside control.
- SOCIALIST: Wealth should be shared fairly, and the government reduces economic inequalities. (Added in 1976)
- SECULAR: No official religion; all religions are respected equally. (Added in 1976)
- DEMOCRATIC: People have equal political rights, elect leaders, and hold them accountable.
- REPUBLIC: The head of state is elected, not hereditary.
- JUSTICE: No discrimination based on caste, religion, or gender; the government works for everyone’s welfare.
- LIBERTY: Citizens can think, express, and act freely within reasonable limits.
- EQUALITY: All are equal before the law, with equal opportunities.
- FRATERNITY: Promotes unity and brotherhood among citizens.
- Secular: People can practice their religion freely without state interference.
- Equality: Jobs are open to all, regardless of gender, caste, or religion.
Points to Remember
- The Constitution of India is a rulebook protecting citizens’ rights and listing their duties.
- It was built on India’s civilizational heritage, the freedom struggle, and ideas from other countries’ constitutions.
- Key features include the structure of government, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, and Directive Principles.
- It is a living document, changeable through amendments to meet new needs.
Difficult Words
- Constitution: A document with a country’s basic rules and laws.
- Legislature: The government part that makes laws.
- Executive: The government part that implements laws.
- Judiciary: The government part that ensures laws are followed and settles disputes.
- Checks and balances: Systems to ensure the government is fair and accountable.
- Fundamental Rights: Basic rights like equality and freedom that citizens can demand in court.
- Fundamental Duties: Responsibilities of citizens, like respecting the Constitution.
- Directive Principles of State Policy: Guidelines for the government to improve the country, not enforceable in court.
- Constituent Assembly: The group that wrote the Indian Constitution.
- Republic Day: 26 January, when the Constitution came into effect in 1950.
- Universal adult franchise: The right of all adults to vote.
- Separation of powers: Keeping the legislature, executive, and judiciary independent.
- Amendment: A change made to the Constitution.
- Preamble: The introduction to the Constitution, stating its values.
- Sovereign: A country’s right to make its own decisions without outside control.
- Socialist: A system to share wealth fairly and reduce inequalities.
- Secular: Treating all religions equally with no official religion.
- Democratic: A government where people elect leaders and hold them accountable.
- Republic: A country with an elected head, not a king.
- Justice: Fair treatment for all, reducing discrimination.
- Liberty: Freedom to think, speak, and act within limits.
- Equality: Equal treatment and opportunities for all.
- Fraternity: Unity and brotherhood among citizens.
FAQs on The Constitution of India - An Introduction Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 10 Free PDF
| 1. What is the significance of the Preamble in the Constitution of India? |  |
| 2. How was the Constitution of India developed, and who were its key contributors? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of the Constitution of India that distinguish it from other constitutions? |  |
| 4. In what ways is the Constitution of India considered a living document? |  |
| 5. What were some of the influences on the drafting of the Indian Constitution? |  |

















