Back Questions (Page 207 & 208)
Q1: Write names of the various types of government that you have learnt in the chapter.
Ans: The types of government discussed in the chapter are:
Democracy
Monarchy
Theocracy
Dictatorship
Oligarchy
Q2: Which type of Government does India have? And why is that called that type?
Ans:
- India has a Democratic Government. It is called a democracy because the people have the power to choose their representatives through elections.
- In a democracy, the government is formed by the people and is accountable to them. This means the government works for the welfare of all the citizens, and people can change the government by voting during elections.
- India follows a Parliamentary Democracy, where the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers work together with the Parliament to make decisions.
 DemocracyQ3: You read that an independent judiciary is present in all types of democracies. State any three reasons why you think it is important for the judiciary to be independent.
DemocracyQ3: You read that an independent judiciary is present in all types of democracies. State any three reasons why you think it is important for the judiciary to be independent.
Ans: An independent judiciary means that the courts can make decisions without interference from the government or other powers. It is important for the judiciary to be independent for the following reasons:
- Ensures Justice: An independent judiciary ensures that laws are applied fairly and equally to everyone, without any influence from political parties or the government.
- Protects Fundamental Rights: The judiciary is responsible for protecting the fundamental rights of citizens, such as freedom of speech and equality before the law. If the judiciary were not independent, these rights could be easily violated.
- Checks and Balances: It acts as a check on the government’s power. If the government makes any unjust or unconstitutional decisions, the judiciary can challenge them and ensure that the laws of the country are followed correctly.
Q4: Do you think democratic government is better than other forms of government? Why?
Ans: Yes, a democratic government is better than other forms of government for several reasons:
- Equality: In a democracy, everyone is treated equally before the law. Every citizen, regardless of their background, has the right to vote and choose their leaders.
- Freedom of Expression: People in a democracy can express their opinions freely, without fear of punishment. They can criticize the government if it is not doing its job properly.
- Accountability: In a democracy, the government is accountable to the people. If the government fails to fulfill its responsibilities, people can elect new leaders during elections.
- Protection of Rights: Democracy protects the fundamental rights of citizens. It ensures that everyone has the right to freedom, equality, and a fair trial.
In contrast, other forms of government like monarchy or dictatorship often do not give people the same rights or the opportunity to participate in decision-making.
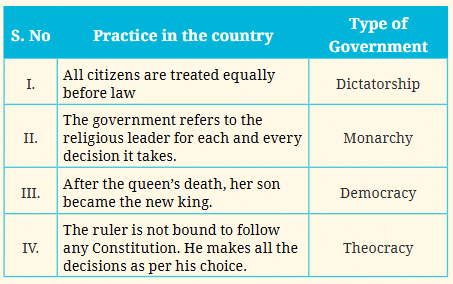
Q5: These are some practices in a few different countries. Can you match the practice with the type of government?
 Ans:
Ans: 
Explanation:
- Democracy: In a democracy, all citizens are treated equally before the law, meaning everyone has the same rights and is subject to the same rules. This is one of the key principles of democracy.
- Theocracy: In a theocracy, the government is guided by religious leaders, and decisions are made based on religious laws. This type of government places religious beliefs at the center of decision-making.
- Monarchy: A monarchy is a form of government where the position of the ruler is inherited, usually within a royal family. In this case, after the queen’s death, her son becomes the new king, following the hereditary system of monarchy.
- Dictatorship: In a dictatorship, one person holds all the power and makes all the decisions. The ruler is not bound by a constitution and can make decisions without the input of the people or any governing body.
Q6: Below is a list of countries. Find out the types of government these countries have: Ans:
Ans: 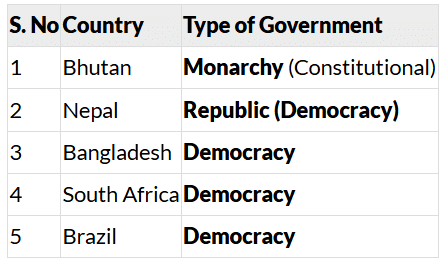
Explanation:
- Bhutan (Monarchy - Constitutional): Bhutan has a constitutional monarchy, meaning it has a king, but the king's powers are limited by a constitution. The country also has a democratic system in which elected representatives play a role in governance.
- Nepal (Republic - Democracy): Nepal has a republic, meaning it does not have a king. The country is governed by elected leaders, and the people have the power to choose their government, making it a democracy.
- Bangladesh (Democracy): Bangladesh follows a democratic government where citizens vote to elect their representatives. The government is accountable to the people, and it ensures equal rights for all.
- South Africa (Democracy): South Africa also has a democratic government where the people elect their representatives to make decisions on their behalf. The government is formed through regular elections.
- Brazil (Democracy): Brazil, like South Africa, has a democratic government. People elect their representatives, and the government is accountable to the citizens. It is based on the principle of representative democracy.
Q7: What are possible hurdles in a democracy in achieving its values and ideals? How can they be overcome?
Ans: Some possible hurdles in a democracy are:
Corruption: Corruption can prevent the government from fulfilling its duties properly and cause inequality. To overcome this, strong laws, transparency, and accountability should be in place.
Wealth Disparity: The gap between the rich and the poor can lead to unfair treatment. This can be overcome by promoting equal access to resources like education, healthcare, and employment for everyone.
Manipulation of Information: In some democracies, information can be manipulated to mislead people. Ensuring free press and media freedom will help to keep people informed and make the government more accountable.
Lack of Judicial Independence: If the judiciary is influenced by politics, people’s rights may not be protected. Strengthening the independence of the judiciary can help overcome this problem.
By ensuring equality, freedom, and accountability, we can address these challenges and make democracy more effective.
Q8: Democracy is different from monarchy and dictatorship. Explain.
Ans: Democracy is different from monarchy and dictatorship in the following ways:
Power Source:
In democracy, people are the source of power. They elect their representatives through voting.
In monarchy, the king or queen inherits power from their family, and their position is not elected by the people.
In dictatorship, one person or a small group holds all the power without the consent of the people.
Rights of Citizens:
In democracy, citizens have freedom of speech, equality before the law, and the right to choose their leaders.
In monarchy and dictatorship, the people have very limited rights and cannot freely express their opinions.
Decision-Making:
In democracy, the government is accountable to the people, and decisions are made with their participation.
In monarchy and dictatorship, decisions are made by the ruler, and the people have little say in the matters of governance.
In conclusion, democracy gives power to the people, ensuring that they have freedom and equal rights. Monarchies and dictatorships concentrate power in the hands of one individual or a few people, limiting citizens' rights and freedom.

























