Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Worksheet Solutions - Exploring Substances: Acidic, Basic and Neutral
Q.1. True/False
(i) Nitric acid turns red litmus blue.
False
Nitric acid is an acid that has the ability to change the colour of litmus paper:
Therefore, the statement is false.
- It turns blue litmus paper red.
- It does not turn red litmus paper blue.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide turns blue litmus red.
False
Sodium hydroxide is a base and has the following effects on litmus paper:
Thus, the statement is false.
- Turns red litmus paper blue.
- Does not turn blue litmus paper red.
(iii) Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid neutralize each other and form salt and water.
True
When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, they neutralise each other. This reaction produces:
Thus, the statement is true.
- Salt (sodium chloride)
- Water
(iv) An indicator is a substance that shows different colors in acidic and basic solutions.
True
Indicators are substances that change colour based on the pH of a solution. They help identify whether a solution is:
Thus, the statement is True.
- Acidic - typically turns indicators red.
- Basic - usually turns indicators blue.
- Neutral - does not change the colour of indicators.
(v) Tooth decay is caused by the presence of a base.
False
Tooth decay occurs due to:
Thus, it is incorrect to say that tooth decay is caused by a base.
- Acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
- These acids attack the tooth enamel, leading to decay.
(vi) If an indicator changes color with a base, it does not change color with an acid.
False
- Many indicators can change colour in both acidic and basic solutions.
- The colour change depends on the specific properties of the indicator.
- Thus, an indicator that changes colour in a basic solution may also change in an acidic solution.
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) Change of color in an acid and a base depends on the type of the ____.
indicator
An indicator is a substance that changes color in response to the acidity or basicity of a solution, helping to identify its nature.
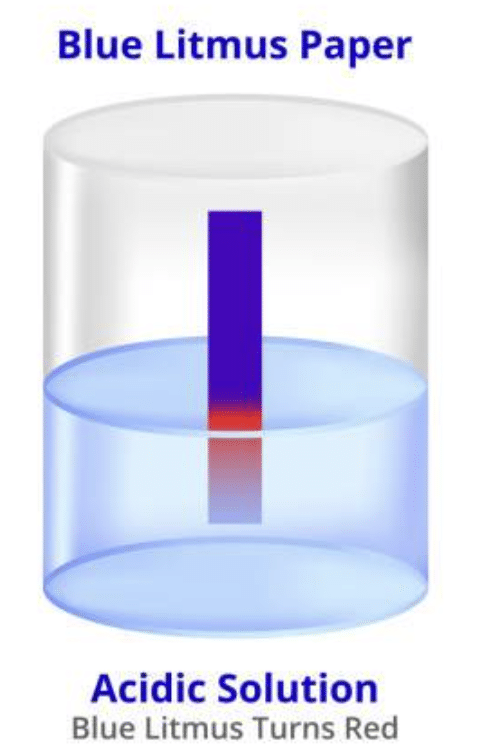
(ii) Acid turns ____ litmus red.
blue
Blue litmus paper turns red when it comes into contact with an acidic solution, indicating the presence of acid.
(iii) Bases turn ___ litmus blue.
red
Red litmus paper turns blue when it is exposed to a basic solution, indicating the presence of a base.
(iv) Litmus has a ____ color in distilled water.
mauve (purple)
In distilled water, litmus retains its natural color, which is mauve (purple), indicating a neutral pH.
(v) In the neutralization reaction a new substance is formed. This is called ____.
salt
- The new substance formed in a neutralisation reaction is called salt.
- Salt can be acidic, basic, or neutral in nature.
(vi) Lemon juice is ____ in nature.
acidic
Lemon juice contains citric acid, which gives it an acidic nature, making it sour in taste.
Answer the following Questions
Q.3. Why do curd, lemon juice, orange juice, and vinegar taste sour?
Curd, lemon juice, orange juice, and vinegar taste sour because they contain acids.
- These substances have a chemical nature that is acidic.
- The term acid comes from the Latin word acere, meaning sour.
- The acids present in these foods are natural acids.
Q.4. Tom rubs a solution between his fingers and feels soapy, what is the nature of that solution?
The solution that feels soapy when rubbed between fingers is basic. This characteristic indicates that it contains substances known as bases, which typically have a bitter taste and a slippery feel.
Q.5. What do you mean by neutral solution? Give examples.
Neutral solutions do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus paper. These solutions are neither acidic nor basic.
- Sugar solution
- Distilled water
These examples illustrate the characteristics of neutral solutions.
Q.6. State a few properties of acids.
Properties of acids
- Acids are sour in taste
- Acid turns blue litmus red.
- China rose indicator turns acidic solutions to dark pink (magenta).
- Turmeric indicator does not change its colour with acid
- Gives burning sensation.
- Acids are usually sticky.
- When the solution is acidic, phenolphthalein remains colourless.
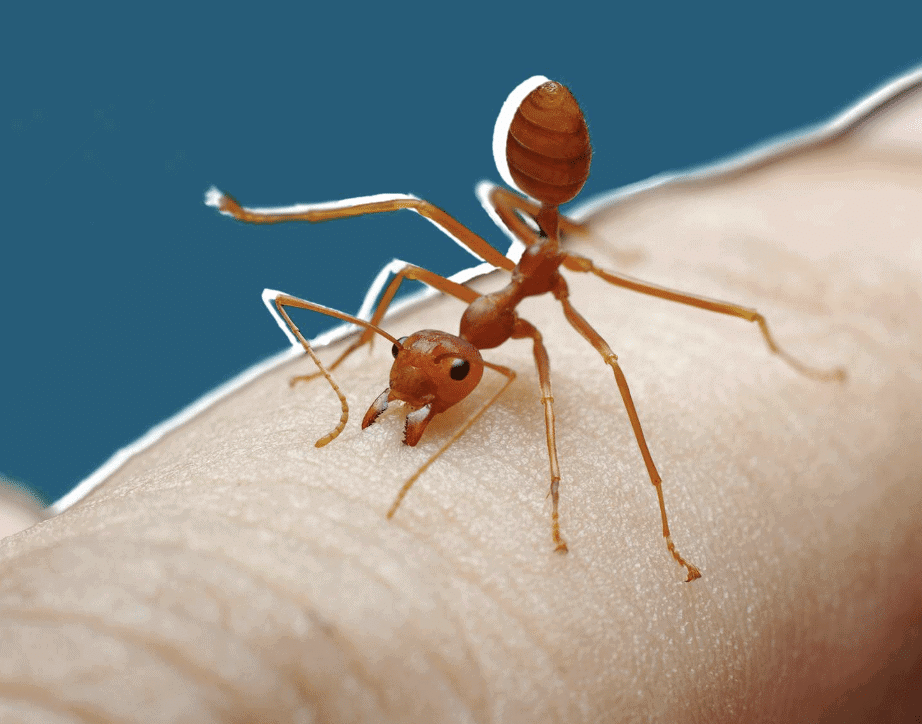
Q.7. Which acid is present in an ant sting?
Formic acid is present in an ant sting.
Q.8. What is the nature of distilled water?
The Distilled water is neutral.
Q.9. Which is the most commonly used natural indicator?
The most commonly used natural indicator is litmus. Key features of litmus include:
- Extracted from lichens.
- Appears mauve (purple) in distilled water.
- Turns red in acidic solutions.
- Turns blue in basic solutions.
- Available as a solution or as strips of paper, known as litmus paper.
- Typically found in red and blue varieties.
Q.10. Blue litmus paper is dipped in a solution. It remains blue. What is the nature of the solution? Explain.
The solution is either a base or neutral because blue litmus paper remains unchanged in both types of solutions. Here are the key points:
- If the litmus paper stays blue, it indicates that the solution does not contain acidic properties.
- Blue litmus paper will not change colour in a neutral solution.
- Thus, the solution is confirmed to be either basic or neutral.
Q.11. Why factory waste is neutralised before disposing it of in the water bodies?
The wastes from many factories often contain acids. If these acids enter water bodies, they can harm aquatic life, including fish and other organisms. To prevent this, factory wastes are neutralised by adding basic substances, which helps to make the water safe.
Q.12. Give some examples of acids and bases that we encounter in day-to-day life.
Acids - Curd, lemon juice, vinegar, orange juice etc.
Base - baking soda, lime water etc
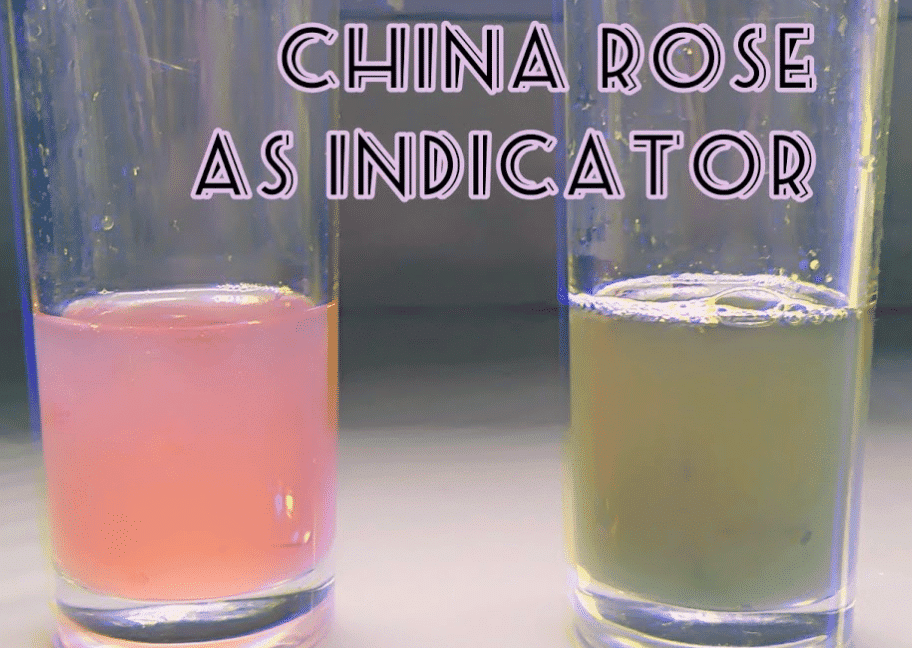
Q.13. What is the effect of the China rose indicator on acidic and basic solutions?
The China rose indicator has distinct effects on solutions:
- In acidic solutions, it turns a dark pink (magenta) colour.
- In basic solutions, it changes to green.
Q.14. Why a turmeric stain on my white shirt is turned to red when it is washed with soap.
A turmeric stain on a white shirt turns red when washed with soap due to the basic nature of the soap solution.
Here’s a brief explanation:
- Turmeric acts as a natural indicator.
- In a basic solution, turmeric changes from yellow to red.
- Soap solutions are typically basic, causing this colour change.
Q.15. Is the distilled water acidic/basic/neutral? How would you verify it?
Distilled water is considered neutral in nature. You can verify this by using litmus paper:
- Use red litmus paper and blue litmus paper.
- Place distilled water on both papers.
- No colour change will occur on either paper.
This indicates that distilled water is neutral.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Worksheet Solutions - Exploring Substances: Acidic, Basic and Neutral
| 1. What are acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 2. How can we identify acids and bases using indicators? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |
| 4. What is the pH scale, and why is it important? |  |
| 5. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |