Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Worksheet Solutions - Life Processes in Plants
True/False
(i) The food synthesized by the plants is stored as starch.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Plants make food (glucose) during photosynthesis. They store this food in the form of starch for future use.
(ii) Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their leaves.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Plants have small openings called stomata on their leaves that allow them to take in carbon dioxide from the air.
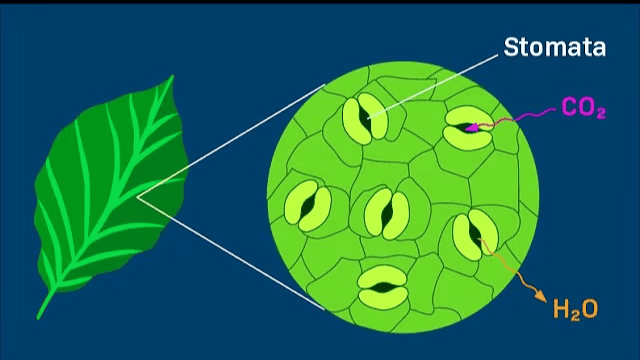 Stomata
Stomata
(iii) Only green leaves can perform photosynthesis.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Even red or violet leaves with hidden chlorophyll can perform photosynthesis.
(iv) Starch turns blue-black when tested with iodine.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
This is a standard test to detect starch in leaves.
(v) Phloem carries water and minerals from the soil.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Xylem carries water and minerals, not phloem.
Fill in the Blanks
(i) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ____.
Ans: Chlorophyll.
 View Answer
View Answer 
- The green pigment in plants that captures sunlight for photosynthesis is called chlorophyll.
- Chlorophyll is found primarily in the leaves, where it plays a critical role in converting solar energy into chemical energy.
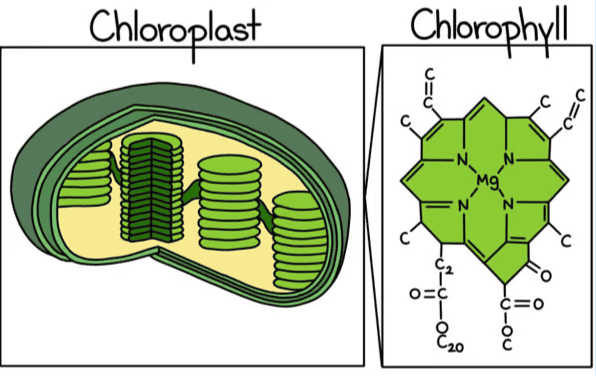 Chlorophyll & Chloroplast
Chlorophyll & Chloroplast
(ii) During photosynthesis plants take in ____ and release ____ .
Ans: Carbon dioxide, oxygen
 View Answer
View Answer 
- In the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and use it, along with water, to produce glucose.
- As a by-product of this reaction, they release oxygen, which is essential for most life forms on Earth.
(iii) ____ in plant take in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.
Ans: Stomata
 View Answer
View Answer 
- Stomata are tiny pores located on the surfaces of leaves.
- These stomata open and close to regulate gas exchange.
- During photosynthesis, stomata allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit, facilitating the photosynthetic process.
(iv) ____ are the products of photosynthesis.
Ans: Glucose and oxygen
 View Answer
View Answer 
The main products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen. During this process, plants use carbon dioxide and water, along with sunlight, to produce glucose (a simple sugar) as an energy source, while oxygen is released as a by-product into the atmosphere. This is represented by the equation: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose) + 6O₂.
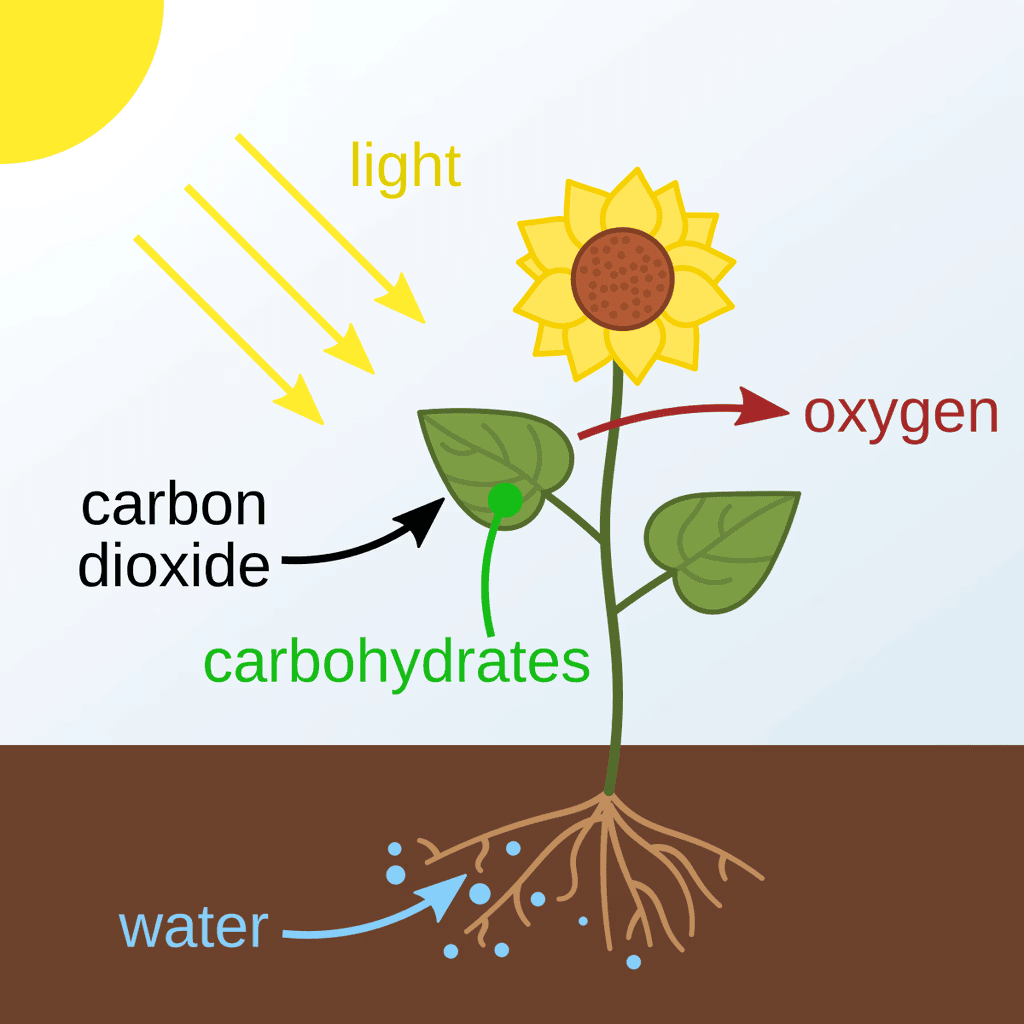 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
(v) Food made by leaves is transported by the __________.
Answer: Phloem
 View Answer
View Answer 
Phloem distributes glucose and starch to other parts of the plant.
(vi) During respiration, plants use __________ to break down glucose.
Answer: Oxygen
 View Answer
View Answer 
Oxygen is used in respiration to release energy
Answer the Following Questions
Q.1. From where do plants get raw materials to prepare their food?
Plants get raw materials to prepare their food from their surroundings.
- Carbon Dioxide: Absorbed from the air through stomata in the leaves.
- Water: Taken up from the soil through the roots.
- Sunlight: Captured by chlorophyll in the leaves. The energy from sunlight is crucial for converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Q.2. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms?
Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
- It provides the necessary light energy that plants use to perform photosynthesis, which is the foundation of most food chains.
- Plants convert this solar energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, which is then consumed by herbivores and further by carnivores, making the sun essential for life on Earth.
Q.3. What are the other parts of plant where photosynthesis occurs except leaves?
While leaves are the primary site for photosynthesis, other green parts of the plant can also perform this process. These include:
- Green Stems: Some plants, like cacti and young stems of other plants, can carry out photosynthesis due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- Green Branches: Similar to stems, branches that have green tissues can also contribute to photosynthesis.
Q.4. What are stomata?
Stomata are tiny pores found primarily on the underside of leaves. They play a vital role in:
- Gas Exchange: Allowing carbon dioxide to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and oxygen to exit as a by-product.
- Transpiration: Enabling water vapor to leave the plant, helping to regulate temperature and maintain nutrient flow.
Q.5. What is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the leaves of all green plants. It plays an essential role in photosynthesis by capturing the energy from sunlight.
- This pigment absorbs light, especially sunlight, which is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) during photosynthesis.
- The presence of chlorophyll is also what gives plants their characteristic green color.
Q.6. What is plant respiration and how is it different from photosynthesis?
Respiration is the process where plants break down glucose using oxygen to release energy. It happens in all parts of the plant. The word equation is: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy. Unlike photosynthesis, which occurs only in green parts and in light, respiration happens all the time and in all parts of the plant.
Q.7. Why do we boil the leaf in alcohol when we are testing it for starch?
In a starch test, we boil the leaf in alcohol to remove its chlorophyll, the green pigment that masks the presence of starch.
- When testing for starch in leaves, we need to see a color change to confirm the presence of starch.
- After removing chlorophyll by boiling the leaf in alcohol, the leaf becomes pale.
- Once iodine solution is added, it reacts with the starch in the leaf, turning it blue-black.
- This confirms that starch is present, proving that photosynthesis has taken place.
Q.8. What is the role of leaves in food preparation? How is starch tested in a leaf?
Leaves act as the food factories of plants because they contain chlorophyll and capture sunlight. They use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food. The food is stored as starch. To test for starch, the leaf is boiled and treated with iodine solution. If starch is present, it turns blue-black in color.
Q.9. Describe how water and minerals are transported in plants.
Water and minerals are absorbed by the roots from the soil. These are transported upward to the stems, leaves, and flowers through xylem tissue. The xylem acts like a pipeline. This supply is necessary for photosynthesis and plant growth. Without water, plants can wilt or die.
Q.10. How do plants transport food to different parts of the body?
Food made in the leaves through photosynthesis is sent to all parts of the plant. The phloem tissue carries glucose and starch from the leaves to roots, stems, and fruits. This ensures that even non-green parts of the plant get the energy they need to grow and store food.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Worksheet Solutions - Life Processes in Plants
| 1. What are the main life processes in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is transpiration, and why is it important for plants? |  |
| 4. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 5. What role does respiration play in plants? |  |





















