Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Heat Transfer in Nature
Short Questions and Answers
Q1: Define heat.
Ans: Heat is a form of energy which produces a sensation of warmth and flows when there is a temperature difference between two bodies. It is measured in joules or calories.
Q2: Define temperature. What is its unit?
Ans: A reliable measure of the hotness of an object is its temperature. Temperature is measured by a device called a thermometer. The unit of temperature is degree Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit, and Kelvin (SI unit).
Q3: What is the use of the maximum-minimum thermometer?
Ans: The maximum-minimum thermometer is used to measure the highest and lowest temperatures of a place in a day. It is commonly used in weather stations to track daily temperature variations. This thermometer helps in understanding temperature fluctuations, which is essential for weather forecasting and analysis.
 Max-min Thermometer
Max-min Thermometer
Q4: : What is conduction?
Ans: Heat flows from a hotter object to a colder object. The process by which heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object is known as conduction.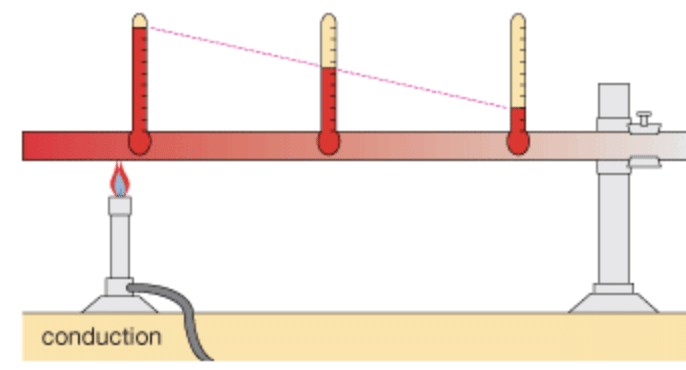
Q5: Why conduction is only possible in solids?
Ans: In solids, generally, the heat is transferred by the process of conduction because particles of solids are closely packed, and heat is transferred from the hotter end to the colder end of an object.
Q6: How does the heat from the sun reach us?
Ans: Heat from the sun reaches us by radiation, which does not require a medium to transfer heat. Unlike conduction (which occurs in solids) and convection (which occurs in liquids and gases), radiation can transfer heat even through the vacuum of space
Q7: Explain how water is heated by convection.
Ans: The water is a poor conductor of heat, so do not heat it by conduction. When water is heated, the water becomes lighter. Hot water rises up. The cold water from the sides moves down towards the source of heat. This water also gets hot and rises upward, and water from the sides moves down. This process continues till the whole water gets heated. This mode of heat transfer is known as convection.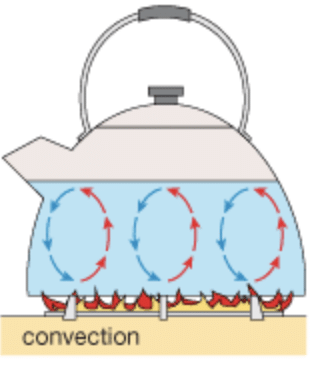
Q8: Differentiate between conductor and insulators?
Ans: The materials which allow heat to pass through them easily are conductors of heat. For example, aluminum, iron, and copper The materials that do not allow heat to pass through them easily are poor conductors of heat, known as insulators, such as plastic and wood.
Q9: Explain land breeze.
Ans: The water cools down more slowly at night than the land. So, the cool air from the land moves towards the sea. This is called the land breeze.
Q10: Explain sea breeze.
Ans: During the day, the land gets heated faster than the water. The air over the land becomes hotter and rises up. The sea's cooler air rushes towards the land to take its place. The warm air from the land moves towards the sea to complete the cycle. The air from the sea is called the sea breeze.
Long Questions and Answers
Q1: How does heat transfer take place in solids, liquids, and gases?
Ans: Heat can be transferred in three different ways depending on the medium:
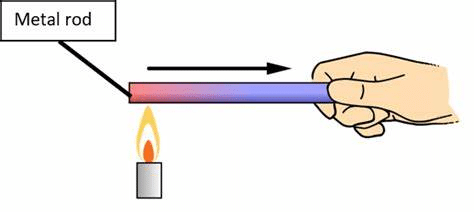
Conduction (Solids)
- In solids, heat travels from one particle to another without movement of the particles.
- Example: A metal spoon gets hot when placed in a cup of tea.
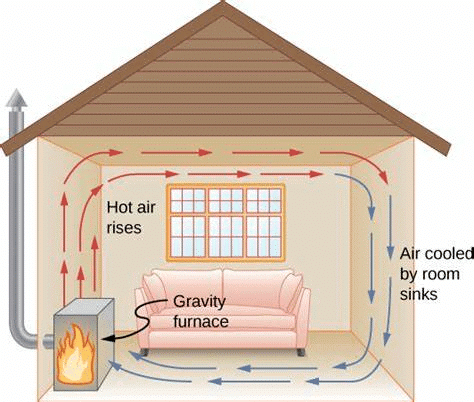
Convection (Liquids & Gases)
- In liquids and gases, heat moves through rising hot particles and falling cold particles.
- Example: Boiling water in a pan shows upward movement of hot water and downward movement of cold water.
Radiation (Without Medium)
- Heat can also be transferred without any medium in the form of rays.
- Example: Heat from the Sun reaches Earth through space by radiation.
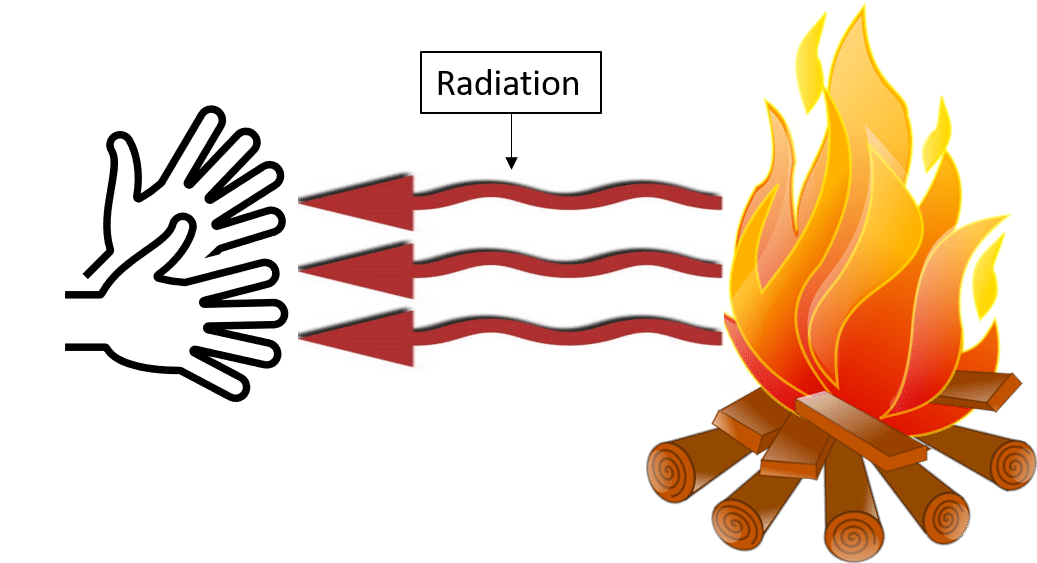 Thus, different materials transfer heat in different ways, and understanding these helps in designing better insulators and conductors.
Thus, different materials transfer heat in different ways, and understanding these helps in designing better insulators and conductors.
Q2: State similarities between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans: Similarities between laboratory thermometer and clinical thermometer are :
- Both are used to measure temperature.
- Both typically use mercury or digital technology to display readings.
- Both require careful handling to ensure accurate readings.
- Both thermometers have a scale marked in degrees Celsius.
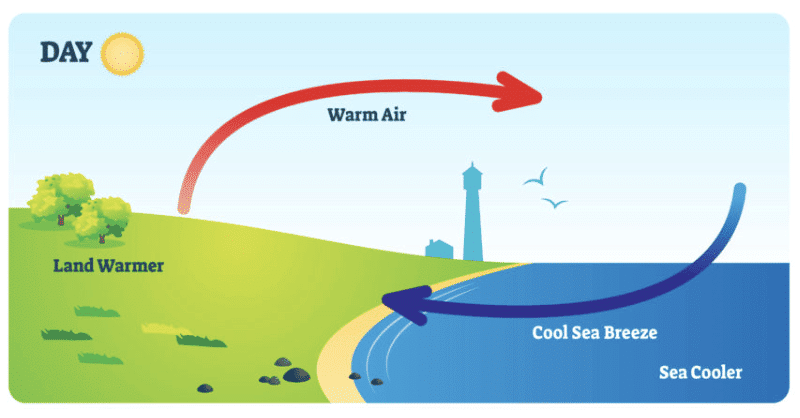
Q3: Why do coastal areas experience land breeze and sea breeze?
Ans: In coastal areas, the movement of air between land and sea causes land breeze and sea breeze.
Sea Breeze (Daytime)
- During the day, the land heats up faster than the sea.
- The air above the land becomes hot and rises, while cooler air from the sea moves in to take its place.
- This movement of air from the sea to the land is called sea breeze.
Land Breeze (Nighttime)
- At night, the land cools down faster than the sea.
- The air above the sea remains warmer and rises, and the cooler air from the land moves towards the sea.
- This movement of air from the land to the sea is called land breeze.
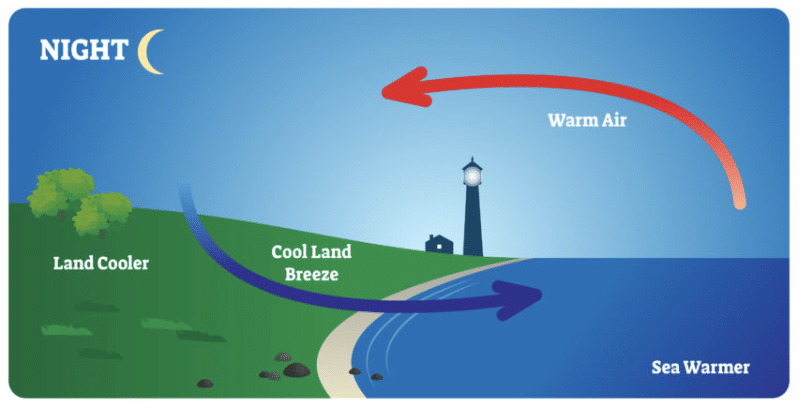
These breezes help moderate temperatures in coastal areas, making them more comfortable.
|
80 videos|322 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Heat Transfer in Nature
| 1. What are the main methods of heat transfer in nature? |  |
| 2. How does conduction work in everyday life? |  |
| 3. What is convection and where can we observe it in nature? |  |
| 4. How does radiation differ from conduction and convection? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding heat transfer important in our daily lives? |  |





















