Solids, Liquids and Gases Chapter Notes | Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Arrangement of Particles |

|
| Changing States of Matter |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
| Summary |

|
Arrangement of Particles
All matter exists in three states—solids, liquids, and gases—each with unique properties determined by the arrangement and behavior of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. These particles are far too small to see, even with a strong microscope, but scientists have confirmed their existence using special instruments. Understanding how these particles are arranged and move helps explain why solids, liquids, and gases behave differently.
Properties of the Three States
- Solids: Maintain a fixed shape and cannot be compressed. Examples include bones in the body or a bar of soap.
- Liquids: Flow and take the shape of their container, filling it from the bottom up to a certain level with a fixed volume. Examples include water in blood or a cup of tea.
- Gases: Flow and fill the entire space of their container, escaping if the container is open. They can be compressed. Examples include air in the lungs or gas in a balloon.
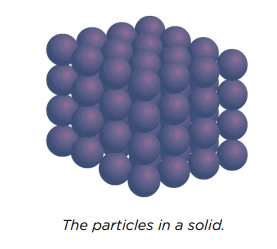
Particle Arrangement in Solids
In solids, particles are:
- Tightly Packed: Particles are very close together, leaving little space between them.
- Fixed Positions: Particles vibrate in place but cannot move to new positions, explaining why solids keep their shape and cannot be squeezed into a smaller volume.
Particle Arrangement in Liquids
In liquids, particles are:
- Closely Packed: Particles are still close together, similar to solids, so liquids cannot be compressed.
- Mobile: Particles can move around each other, allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of their container. Even when a liquid appears still, its particles are constantly moving.

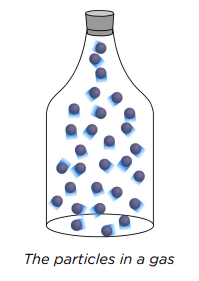
Particle Arrangement in Gases
In gases, particles are:
- Far Apart: Large empty spaces, called vacuums, exist between particles, allowing gases to be compressed by reducing these spaces.
- Freely Moving: Particles move quickly and spread out to fill the entire container. In an open container, gas particles disperse, escaping into the surrounding space.
Changing States of Matter
Matter can change from one state to another through processes driven by the addition or removal of energy, typically heat. These changes affect the behavior of particles but not the particles themselves. Water is a common example used to illustrate these state changes.
States of Water
Water exists in three states:
- Solid: Ice, where particles are tightly packed and fixed in position.
- Liquid: Water, where particles are close but can move around each other.
- Gas: Water vapor or steam, where particles are far apart and move freely.
Processes of State Change
The following processes describe how water changes between states:- Melting: Ice (solid) changes to liquid water when heat is added, causing particles to gain energy and move from fixed positions to sliding past each other.
- Freezing: Liquid water changes to ice when heat is removed, causing particles to lose energy and return to fixed positions.
- Evaporation: Liquid water changes to water vapor (gas) when heat is added, giving particles enough energy to move far apart and spread out.
- Condensation: Water vapor changes to liquid water when heat is removed, causing particles to slow down and come closer together.
Particle Behavior During State Changes
When matter changes state, the particles themselves do not change; only their arrangement and movement do.For example:
- In ice, water particles are fixed and vibrate in place.
- In liquid water, the same particles move freely around each other.
- In water vapor, the same particles are far apart and move rapidly. The addition or removal of heat energy alters how the particles behave, not their identity.
Points to Remember
- Even when water in a glass appears still, its particles are constantly moving, a characteristic of liquids.
- Matter exists in three states: solids (fixed shape), liquids (flow and take container shape), and gases (fill entire container and can escape).
- Solids have tightly packed particles in fixed positions, preventing compression.
- Liquids have closely packed particles that move around, allowing flow.
- Gases have widely spaced particles that move freely, enabling compression.
- Changing states (e.g., melting, freezing) involves adding or removing heat energy, which changes particle behavior, not the particles themselves.
Difficult Words
- Matter: Anything that takes up space and has mass, existing as solids, liquids, or gases.
- Particles: Tiny building blocks (atoms or molecules) that make up all matter, too small to see without special instruments.
- Solid: A state of matter with a fixed shape and volume, where particles are tightly packed and fixed in position.
- Liquid: A state of matter that flows and takes the shape of its container, with particles that are close but can move around.
- Gas: A state of matter that fills its container and can escape, with particles far apart and moving freely.
- Compress: To squeeze matter into a smaller volume, possible with gases but not solids or liquids.
- Vacuum: Empty space between particles in a gas, allowing compression.
- Disperse: To spread out over an area, as gas particles do when escaping an open container.
- Melting: The process of a solid turning into a liquid by adding heat.
- Freezing: The process of a liquid turning into a solid by removing heat.
- Evaporation: The process of a liquid turning into a gas by adding heat.
- Condensation: The process of a gas turning into a liquid by removing heat.
Summary
Matter exists in three states—solids, liquids, and gases—each defined by the arrangement and behavior of tiny particles. In solids, particles are tightly packed and fixed, maintaining shape. In liquids, particles are close but mobile, allowing flow. In gases, particles are far apart and move freely, filling containers and escaping if open. These states can change through processes like melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation, driven by adding or removing heat energy, which alters particle movement but not the particles themselves. Understanding particle behavior explains the unique properties of each state and how matter transitions between them.
FAQs on Solids, Liquids and Gases Chapter Notes - Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A)
| 1. What are the main differences between solids, liquids, and gases? |  |
| 2. How do particles behave in different states of matter? |  |
| 3. What causes a change in the state of matter? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of changes of state? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand the properties of solids, liquids, and gases? |  |




















