Solutions as Special Mixtures Chapter Notes | Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Solutions |

|
| Soluble Substances |

|
| Saturated Solutions |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
| Summary |

|
Solutions
Solutions are a special type of mixture where one substance appears to disappear into another, creating a uniform mixture. Unlike regular mixtures where components remain visible (e.g., sand and sugar), solutions involve a solute that dissolves completely into a solvent, making it indistinguishable to the naked eye.
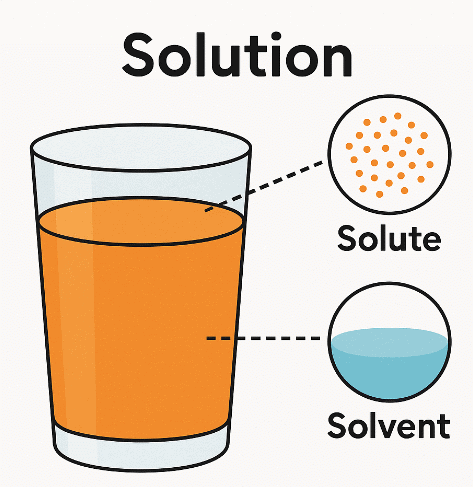
Defining a Solution
- Solute: The substance that seems to disappear when mixed, e.g., sugar in a sugar-water mixture.
- Solvent: The substance that remains visible and dissolves the solute, e.g., water in a sugar-water mixture.
- Solution: The combined mixture of solute and solvent, e.g., the sugar-water mixture itself.
A solution forms when the solute’s particles spread evenly among the solvent’s particles, creating a clear, uniform appearance, as seen in a copper sulfate solution where blue crystals dissolve to form a clear blue liquid.
Characteristics of Solutions
- Appearance: The solute cannot be seen in the solvent, giving the solution a uniform look (e.g., sugar dissolved in water looks like plain water).
- No Settling: The solute does not settle out over time, unlike sand in water.
- Non-Filterable: Solutions cannot be separated by filtration because the solute particles are too small and dispersed among the solvent particles.
Examples: Common solutions include sugar and water (solid solute, liquid solvent), vinegar and water (liquid solute, liquid solvent), and copper sulfate and water (solid solute, liquid solvent). Not all mixtures are solutions, e.g., oil and water or sand and water do not form solutions.
Soluble Substances
Not all substances form solutions when mixed with a solvent like water. The ability of a substance to dissolve determines whether it is soluble or insoluble, and this property affects how solutions behave and how they can be separated.
Soluble vs. Insoluble Substances
- Soluble Substances: These dissolve in a solvent to form a solution, e.g., sugar, salt, vinegar, and copper sulfate dissolve in water, appearing to disappear.
- Insoluble Substances: These do not dissolve in a solvent and remain visible, e.g., sand and oil do not form solutions with water.
- Some substances insoluble in water may dissolve in other solvents, e.g., nail polish is insoluble in water but soluble in acetone (nail polish remover).
Separating Solutions
Unlike regular mixtures, solutions cannot be separated by common methods like sieving, filtering, hand sorting, or decanting because the solute particles are too small and evenly mixed with the solvent. The primary method to separate a solution is:Evaporation: Heating the solution to evaporate the solvent (e.g., water), leaving the solute (e.g., sugar or salt) behind. This can be done by leaving the solution in a sunny spot or boiling it.
Saturated Solutions
There is a limit to how much solute can dissolve in a given amount of solvent. When this limit is reached, the solution becomes saturated, and no more solute can dissolve, leading to interesting applications like crystal formation.
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Solutions
- Saturated Solution: A solution where no more solute can dissolve in the solvent, e.g., when adding sugar to water until some sugar remains undissolved at the bottom.
- Unsaturated Solution: A solution where more solute can still dissolve, e.g., a cup of tea with only a few teaspoons of sugar that can still dissolve more.
The amount of solute that can dissolve depends on the solvent’s capacity, which can be tested by adding solute incrementally until no more dissolves.
Crystal Formation
When a saturated solution is prepared and allowed to cool or evaporate slowly, the solute can form crystals. For example:- A saturated sugar solution with food coloring can grow sugar crystals on a string over time.
- In nature, stalactites and stalagmites in limestone caves form as dissolved limestone crystallizes when water evaporates, creating structures over thousands of years.
Points to Remember
- Stalactites (hanging down) and stalagmites (growing up) in caves like Cango Caves in South Africa form as water dissolves limestone, which crystallizes upon evaporation, demonstrating natural solution processes.
- Solutions are mixtures where the solute appears to disappear into the solvent, forming a uniform mixture.
- Soluble substances (e.g., sugar, salt) dissolve in water, while insoluble substances (e.g., sand, oil) do not.
- Solutions cannot be separated by filtration, sieving, or decanting but can be separated by evaporating the solvent.
- A saturated solution cannot dissolve more solute, while an unsaturated solution can.
- Crystals, like sugar crystals or stalactites, form from saturated solutions when the solvent evaporates or cools.
Difficult Words
- Solution: A special mixture where the solute dissolves completely in the solvent, appearing uniform.
- Solute: The substance that dissolves in a solution, seeming to disappear, e.g., sugar in water.
- Solvent: The substance that dissolves the solute in a solution, e.g., water.
- Soluble: A substance that can dissolve in a solvent to form a solution, e.g., salt in water.
- Insoluble: A substance that does not dissolve in a solvent, e.g., sand in water.
- Saturated Solution: A solution where no more solute can dissolve, with excess solute remaining undissolved.
- Unsaturated Solution: A solution that can still dissolve more solute.
- Evaporation: The process of heating a solution to remove the solvent, leaving the solute behind.
- Crystals: Solid structures formed when a solute solidifies from a solution, e.g., sugar crystals or stalactites.
Summary
Solutions are unique mixtures where a solute dissolves completely in a solvent, creating a uniform appearance, unlike regular mixtures where components remain visible. Soluble substances, like sugar and salt, dissolve in water, while insoluble ones, like sand and oil, do not. Solutions cannot be separated by filtration or sieving but can be separated by evaporating the solvent, leaving the solute behind. A solution becomes saturated when no more solute can dissolve, and crystals can form from saturated solutions, as seen in sugar crystal experiments or natural formations like stalactites. Understanding solutions helps explain how substances interact and how they can be separated or crystallized.
FAQs on Solutions as Special Mixtures Chapter Notes - Natural Science and Technology (Grade 6-A)
| 1. What are solutions in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What is a saturated solution? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of soluble substances? |  |
| 4. How do temperature and pressure affect solubility? |  |
| 5. What are some key points to remember about solutions? |  |















