Class 7 Social Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Questions - New Beginnings: Cities and States
Q1: What was India’s First Urbanisation?
Ans: India’s First Urbanisation refers to the Harappan Civilisation that ended around 2000 BCE.
Q2: When did India’s Second Urbanisation begin?
Ans: India’s Second Urbanisation began in the 1st millennium BCE.
Q3: What are janapadas?
Ans: Janapadas were early settlements or territories formed by clans in north India.
Q4: What does the word "janapada" literally mean?
Ans: "Janapada" means "where people set foot".
Q5: Who ruled over a janapada?
Ans: A janapada was ruled by a raja.
Q6: What are mahajanapadas?
Ans: Mahajanapadas were larger states formed by merging janapadas.
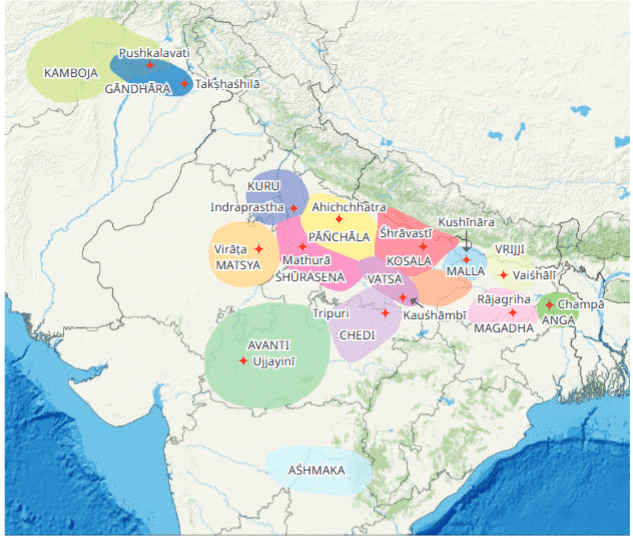 Map of 16 Mahajanpadas
Map of 16 Mahajanpadas
Q7: How many mahajanapadas are mentioned in ancient texts?
Ans: Ancient texts mention 16 mahajanapadas.
Q8: Name two powerful mahajanapadas.
Ans: Magadha and Kosala were two powerful mahajanapadas.
Q9: What was the capital of Vatsa?
Ans: The capital of Vatsa was Kauśhāmbī.
Q10: What were the capitals of mahajanapadas known for?
Ans: They were large, fortified cities with moats and narrow gateways.
Q11: What geographical region did many mahajanapadas develop in?
Ans: Many mahajanapadas developed in the Ganga plains.
Q12: Why was the Ganga plain suitable for settlements?
Ans: It had fertile land ideal for agriculture.
 Fertile Ganga Plains heped Mahajanpadas to grow
Fertile Ganga Plains heped Mahajanpadas to grow
Q13: What natural resource helped make tools and weapons during this period?
Ans: Iron ore from nearby mountains helped make tools and weapons.
Q14: What is a sabhā or samiti?
Ans: Sabhā or samiti was a council of elders advising the raja.
Q15: What kind of rule did monarchies follow?
Ans: Monarchies were hereditary and ruled by a single raja.
Q16: Name one mahajanapada that followed the gana or sangha system.
Ans: Vajji followed the gana or sangha system.
Q17: What is an early example of a democratic system in India?
Ans: The gana-sangha system is an early example of democracy.
Q18: Which texts give us information about this period?
Ans: Late Vedic, Buddhist, and Jain texts give us information about this period.
Q19: What did punch-marked coins look like?
Ans: They were silver coins stamped with symbols.
 Punch Marked Coins
Punch Marked Coins
Q20: What role did coins play during this time?
Ans: Coins were used for trade within and between regions.
Q21: What is the meaning of jāti?
Ans: Jāti is a group of people with a specific job passed down in families.
Q22: What were the four varnas in Vedic society?
Ans: The four varnas were Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras.
Q23: What is the English word “caste” derived from?
Ans: The word “caste” comes from the Portuguese word “casta”.
Q24: What is iron metallurgy?
Ans: Iron metallurgy is the use of iron to make tools and weapons.
Q25: What are the Dakshinapatha and Uttarapatha?
Ans: They were ancient trade routes linking different parts of India.
|
23 videos|276 docs|12 tests
|

















