Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How did Samudragupta expand the Gupta Empire?
Ans: Samudragupta expanded the Gupta Empire through military conquests. He defeated neighboring kings, including those in the north and central India, and brought them under Gupta control, either as tributaries or allies.
Q2: What role did Faxian’s travelogue play in understanding Gupta society?
Ans: Faxian’s travelogue, A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms, provides valuable insights into Gupta society. It describes the peaceful and prosperous conditions, the welfare of people, and the treatment of different social groups during that time.
Q3: What does the Iron Pillar in Delhi signify?
Ans: The Iron Pillar in Delhi signifies the advanced metallurgy of the Gupta period. Its rust-resistant quality showcases the Gupta’s skill in metalworking, especially in iron, and their contribution to early science.
 Iron Pillar, Mehraulli, Delhi
Iron Pillar, Mehraulli, Delhi
Q4: How did the Gupta rulers contribute to Sanskrit literature?
Ans: The Gupta rulers patronized Sanskrit literature, leading to the creation of important works like Kālidāsa’s Meghadūtam and the Purāṇas. This period is known for the flourishing of classical Sanskrit poetry and drama.
Q5: Why was the Gupta period considered the "Classical Age" of India?
Ans: The Gupta period is called the "Classical Age" because it saw remarkable achievements in art, literature, science, and governance. These accomplishments laid the foundation for much of India’s cultural legacy.
Q6: How did the Gupta rulers support Buddhism and other religions?
Ans: Gupta rulers supported Buddhism by funding Buddhist vihāras (monasteries) and promoting religious tolerance. They also supported other religions like Brahmanism and Jainism, ensuring a peaceful coexistence of beliefs.
Q7: What was the significance of the Gupta Empire's coinage system?
Ans: The Gupta Empire’s coinage system was highly advanced, with coins made of gold, silver, and copper. The coins featured images of rulers and deities, reflecting the empire’s wealth, artistic achievements, and political power.
Q8: How did Gupta art influence Indian architecture?
Ans: Gupta art influenced Indian architecture through its detailed sculptures, carvings, and temple designs. Examples include the Ajanta Caves, which feature intricate murals and statues of Buddha, showcasing the era's artistic skill.
 Ajanta Caves
Ajanta Caves
Q9: What role did Varāhamihira play in the development of Indian science?
Ans: Varāhamihira was a pioneer in Indian science, particularly in astronomy and astrology. His book Brihat Samhita combined observations of the natural world with traditional knowledge, making it an important work in ancient scientific studies.
Q10: How did Kālidāsa contribute to Indian literature?
Ans: Kālidāsa contributed significantly to Sanskrit literature, particularly through his poetry and plays. His famous work Meghadūtam is known for its poetic beauty and vivid descriptions of nature, love, and landscapes.
Q11: How did the Gupta administration support trade and economy?
Ans: The Gupta administration supported trade and the economy through a structured taxation system. This system funded military campaigns, infrastructure, and religious activities while facilitating trade within India and with other regions.
Q12: What led to the decline of the Gupta Empire?
Ans: The decline of the Gupta Empire was caused by external invasions, particularly by the Huna tribe, and internal conflicts. The weakening central authority led to the fragmentation of the empire into smaller regional powers.
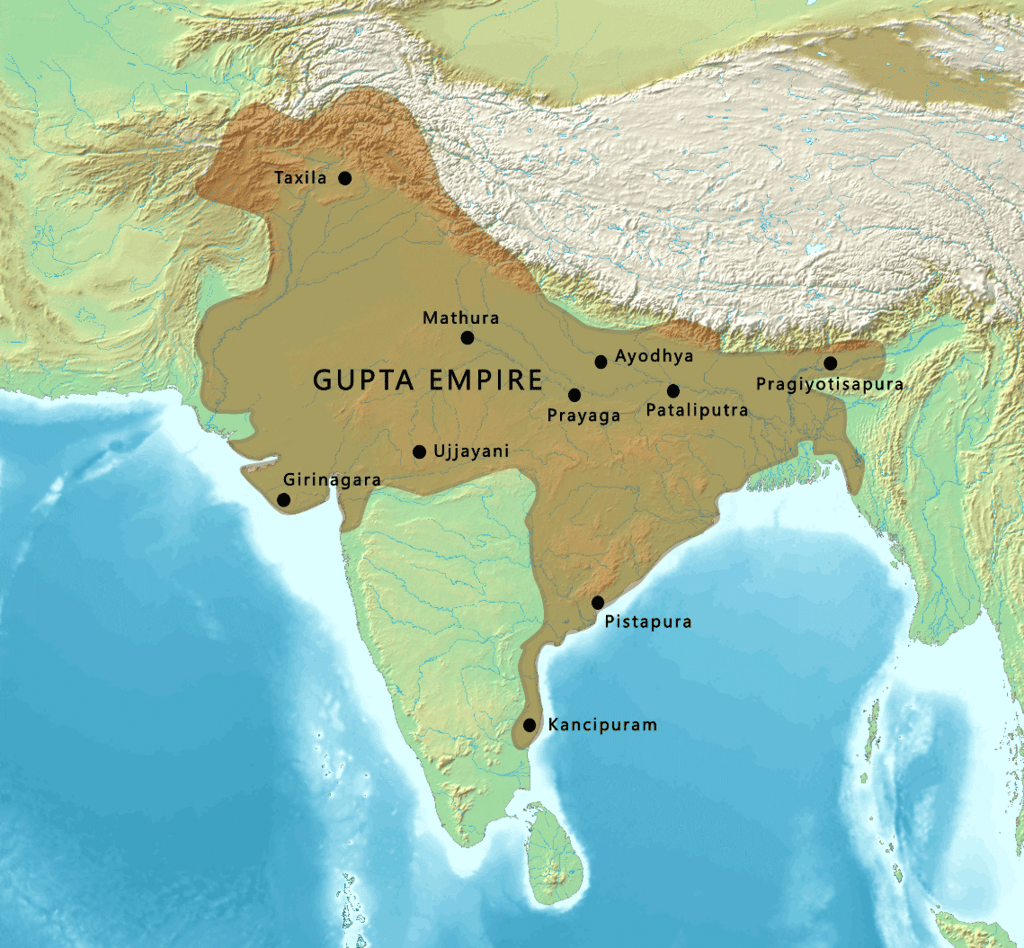 Gupta Empire
Gupta Empire
Long Answer Questions
Q1: How did Samudragupta contribute to the expansion of the Gupta Empire?
Ans: Samudragupta was a skilled military leader who expanded the Gupta Empire through conquests. He defeated numerous smaller kingdoms, including those in the north, east, and central India. He incorporated these regions into the Gupta Empire either through direct control or as tributaries, ensuring a large and prosperous kingdom. His expansion helped solidify the foundation for the Gupta Golden Age.
Q2: How did the Gupta period contribute to the development of science and mathematics?
Ans: The Gupta period witnessed significant progress in science and mathematics. Āryabhaṭa, a renowned mathematician and astronomer, calculated the Earth’s size and explained the rotation of the Earth on its axis. He also made accurate calculations for eclipses and formulated methods for solving algebraic equations. His work in mathematics and astronomy laid the groundwork for later developments in these fields.
Q3: Discuss the role of art and architecture during the Gupta period.
Ans: Art and architecture flourished under the Gupta rulers. The Gupta period saw the construction of iconic structures like the Ajanta Caves, with their detailed paintings and sculptures. The architecture of temples and vihāras (monasteries) reached new heights, with the use of intricate carvings and sculptures depicting Hindu and Buddhist deities. This era's art focused on beauty, religious symbolism, and mastery in stonework.
 Aspects of Gupta Art
Aspects of Gupta Art
Q4: How did the Gupta rulers encourage religious tolerance?
Ans: Gupta rulers were known for promoting religious tolerance. They supported a variety of religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. The rulers funded Buddhist vihāras and temples, while also supporting Hindu religious practices and institutions. This inclusive approach created an environment where different religious traditions coexisted peacefully, allowing cultural and intellectual exchange to thrive.
Q5: How did trade contribute to the Gupta Empire's prosperity?
Ans: Trade played a crucial role in the Gupta Empire's prosperity. The empire's strategic location along trade routes facilitated commerce with regions in Southeast Asia, the Mediterranean, and Central Asia. The Gupta rulers levied taxes on trade, which funded their administration, military, and public works. The empire was known for trading textiles, spices, gems, and other goods, making it economically strong and culturally rich.
Q6: What is the significance of Faxian's travelogue in understanding Gupta society?
Ans: Faxian's travelogue, A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms, offers valuable insights into Gupta society. It describes the peaceful and prosperous conditions of the empire, where people were content and lived with relative freedom. Faxian’s observations about the treatment of merchants, the welfare of the poor, and the presence of Buddhist institutions highlight the cultural and social harmony of the time, though his account also shows some inequalities, such as the harsh treatment of outcastes.
Q7: Explain the contributions of Kālidāsa to Sanskrit literature.
Ans: Kālidāsa is one of the most celebrated poets of the Gupta period. His work, especially the poem Meghadūtam (The Cloud Messenger), is known for its lyrical beauty, vivid descriptions, and deep emotional expression. His plays and poems, which explore themes of love, nature, and human relationships, are considered masterpieces of Sanskrit literature and continue to be revered for their artistic merit and cultural impact.
 Kalidas
Kalidas
Q8: How did the decline of the Gupta Empire impact India?
Ans: The decline of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century CE marked the end of the Classical Age. This decline was caused by a combination of external invasions, particularly from the Huna tribe, and internal political instability. The weakening of the central authority led to the rise of regional powers, which fragmented India into smaller kingdoms. Despite the collapse of the Gupta Empire, its cultural and intellectual achievements left a lasting legacy in Indian history.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
| 1. What were the major contributions of the Gupta Empire in the field of science and mathematics? |  |
| 2. How did the Gupta period influence art and culture in India? |  |
| 3. What role did trade play in the Gupta Empire's economy? |  |
| 4. Who were some prominent rulers of the Gupta Empire, and what were their achievements? |  |
| 5. What were the religious developments during the Gupta period? |  |
















