Class 7 Social Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How do governments ensure the safety and welfare of people?
Ans: Governments ensure safety by maintaining law and order, protecting the country from external threats, and providing essential services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure. They also create policies for economic stability and social welfare.
Q2: What is the difference between a monarchy and a democracy in terms of power?
Ans: In a monarchy, power is typically inherited by a king or queen, while in a democracy, power is derived from the people through elections, and leaders are chosen by the citizens.

Q3: Why is democracy considered important for people?
Ans: Democracy is important because it gives people the power to choose their leaders, ensuring that their voices are heard and their rights are protected. It promotes equality, freedom, and accountability in governance.
Q4: How does the process of electing representatives work in a democracy?
Ans: In a democracy, citizens vote in regular elections to choose representatives who will make decisions on their behalf. These elections are held at different levels, such as local, state, and national.
Q5: What is a theocracy, and how does it differ from a democracy?
Ans: A theocracy is a form of government where religious leaders rule based on religious laws. Unlike democracy, where people elect their leaders, in a theocracy, power is vested in religious authorities.
Q6: How is the separation of powers important in a democracy?
Ans: The separation of powers ensures that no single branch of government (legislative, executive, judiciary) has unchecked authority. It maintains a system of checks and balances, ensuring fairness and preventing abuse of power.
Q7: What is the role of a legislature in a democracy?
Ans: The legislature’s role is to make laws that govern the country. In democracies, the legislature is often elected by the people and is responsible for representing their interests and ensuring justice through laws.
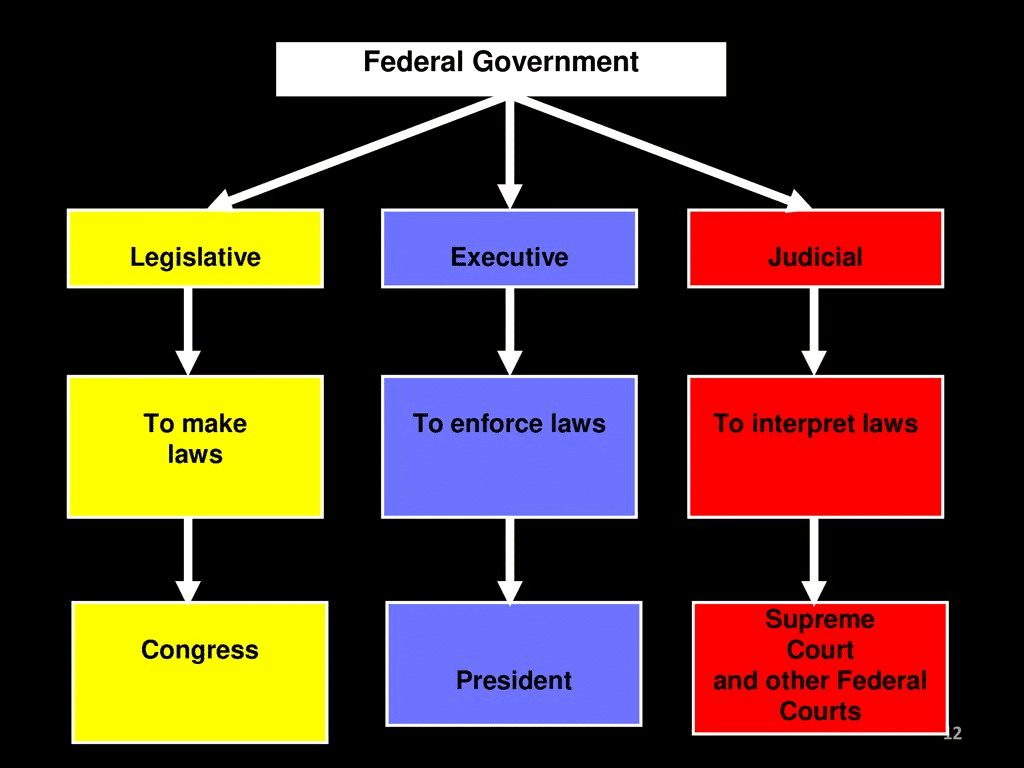
Q8: What is the role of an executive in a democracy?
Ans: The executive implements the laws made by the legislature and manages the country's day-to-day affairs. It includes leaders like the president, prime minister, and ministers, who are responsible for governance.
Q9: How does a judicial system contribute to a democracy?
Ans: The judicial system ensures that laws are followed and resolves disputes between citizens or between the government and the people. It protects citizens' rights and ensures justice, upholding the rule of law.
Q10: What challenges does democracy face in the modern world?
Ans: Democracy faces challenges such as corruption, unequal access to resources, and the concentration of power in the hands of a few people or groups. Additionally, misinformation and the influence of money in politics can undermine democratic processes.
Q11: What is the significance of universal adult franchise in a democracy?
Ans: Universal adult franchise allows all adult citizens, regardless of gender, caste, or wealth, the right to vote. This ensures that every citizen has an equal say in choosing their leaders and shaping the government.
Q12: How do monarchies today differ from those in ancient times?
Ans: Today’s monarchies are mostly constitutional, where the king or queen has limited power, and the government is run by elected officials. In ancient times, monarchies were absolute, with kings having full control over the state and its people.
 Monarchy
Monarchy
Long Answer Questions
Q1: How does democracy give people a voice in governance?
Ans:
- In a democracy, the people are the source of power. They have the right to vote in elections, choosing representatives who will make decisions on their behalf.
- This gives citizens a direct role in shaping the laws and policies of their country.
- Additionally, democratic governments are accountable to the people, meaning that they must listen to their concerns and act in their best interests.
Q2: Explain how the separation of powers works in a democracy.
Ans:
- The separation of powers divides the government into three branches: the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary. Each branch has its distinct functions and is independent of the others.
- The legislature makes laws, the executive implements them, and the judiciary ensures that laws are followed and resolves disputes.
- This system prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful and ensures that decisions are fair and just.
Q3: How is the concept of accountability significant in a democracy?
Ans:
- Accountability means that government officials must answer to the people for their actions.
- In a democracy, elected representatives are held accountable through regular elections, where citizens can choose to re-elect or replace them.
- This ensures that leaders work in the best interests of the people and are not above the law. It also promotes transparency and reduces the chances of corruption.
Q4: What is the role of a constitution in a democratic government?
Ans:
- A constitution outlines the basic laws and principles that govern a country. It sets up the structure of government, defines the roles of the branches, and protects the rights of citizens.
- In a democracy, the constitution ensures that the government operates fairly and transparently.
- It also serves as a guiding document for resolving conflicts and ensuring that the rights and freedoms of individuals are safeguarded.
 Constitution of India
Constitution of India
Q5: How do different forms of government affect people's rights and freedoms?
Ans:
- In democracies, people enjoy greater rights and freedoms, such as the freedom of speech, equality before the law, and the right to vote.
- However, in other forms of government like dictatorship or monarchy, these rights may be restricted.
- Dictatorships often suppress opposition and control media, while monarchies might limit people’s participation in decision-making.
- The form of government significantly influences how individuals can express their opinions and live their lives.
Q6: What is the significance of universal adult franchise in the democratic system?
Ans:
- Universal adult franchise means that every adult citizen has the right to vote, regardless of gender, caste, or social status.
- This is important in a democracy because it ensures equal representation for all segments of society.
- It helps to ensure that the government reflects the will of the entire population, not just a select few, and prevents discrimination based on social or economic background.
Q7: Explain the difference between direct and representative democracy.
Ans:
- In direct democracy, all citizens directly participate in making decisions and laws, which is possible in small communities.
- However, in representative democracy, citizens elect representatives who then make decisions on their behalf.
- Most modern democracies, like India and the USA, follow representative democracy, where elections are held periodically to choose lawmakers and leaders.
Q8: How does a dictatorship differ from a democracy in terms of decision-making?
Ans:
- In a dictatorship, decision-making is centralized in the hands of one individual or a small group, with little to no input from the general public. Leaders in dictatorships have unchecked power and are not held accountable to the people.
- In contrast, democracies allow citizens to participate in decision-making through elections and other democratic processes.
- In a democracy, leaders are accountable to the people and must act in their interests.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - From the Rulers to the Ruled: Types of Governments
| 1. What are the different types of governments discussed in "From the Rulers to the Ruled"? |  |
| 2. How does a democracy differ from a monarchy? |  |
| 3. What role do citizens play in a democracy? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a dictatorship? |  |
| 5. Can you explain how an oligarchy functions? |  |

















