Class 7 Social Science Chapter 8 Worksheet Solutions - How the Land Becomes Sacred
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What does 'sacredness' mean in religious or spiritual contexts?
a) Something holy or deeply respected
b) A journey to a distant land
c) A place for ordinary activities
d) Something that belongs to a specific religion
Ans: a) Something holy or deeply respected
Sacredness refers to something that is considered holy or highly respected in religious or spiritual contexts.
Q2: Which of the following is a sacred site for Sikhs?
a) Takht Sri Patna Sahib
b) Mahabodhi Stūpa
c) Dargah Sharif
d) Velankanni Church
Ans: a) Takht Sri Patna Sahib
Takht Sri Patna Sahib is one of the holiest places for Sikhs, linked to Guru Nanak.
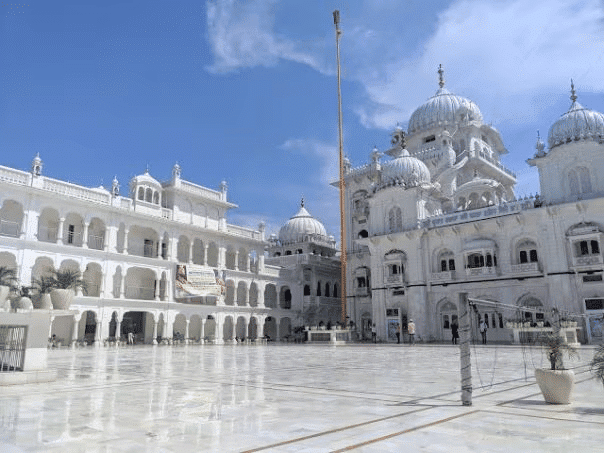 Takht Sri Patna Sahib
Takht Sri Patna Sahib
Q3:What is a pilgrimage in Indian culture known as?
a) Yātrā
b) Tīrthayātrā
c) Kumbh Mela
d) Dham
Ans: b) Tīrthayātrā
A pilgrimage in India is called a tīrthayātrā, meaning a journey to a sacred site.
Q4: Which river is considered a goddess in Hinduism?
a) Ganga
b) Nile
c) Thames
d) Amazon
Ans: a) Ganga
In Hinduism, the Ganga (Ganges) is worshipped as a goddess, symbolizing purity and divinity.
Q5: What is the significance of Sangams in Indian sacred geography?
a) Where rivers meet, considered sacred
b) Places for religious rituals
c) Ancient trade routes
d) Monasteries for monks
Ans: a) Where rivers meet, considered sacred
Sangams, or confluences of rivers, are considered especially holy in Hindu tradition, such as at Prayagraj.
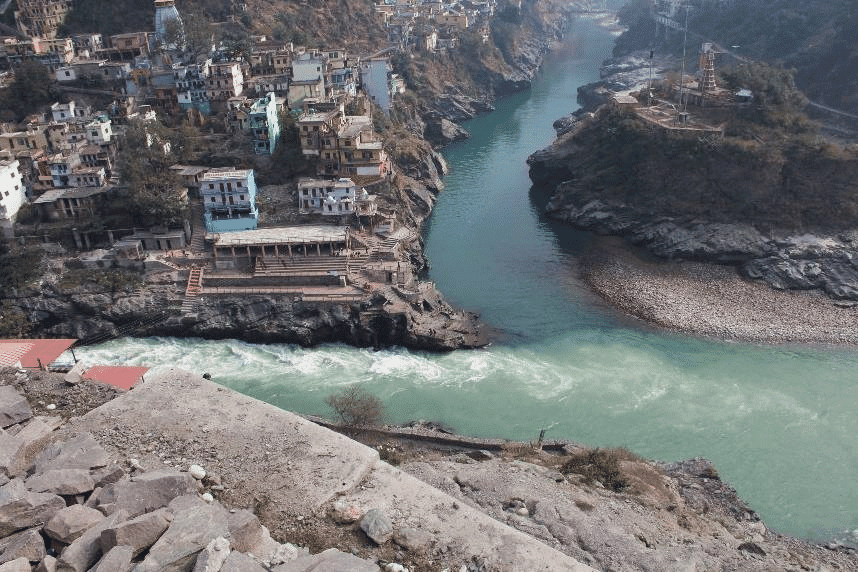 Sangam of Rivers
Sangam of Rivers
Q6: What does the Char Dhām Yātrā include?
a) Four sacred temples in the Himalayas
b) Pilgrimage to four sacred sites in north, south, east, and west India
c) A journey to the famous monasteries of India
d) Visits to the 12 Jyotirlingas
Ans: b) Pilgrimage to four sacred sites in north, south, east, and west India
The Char Dhām Yātrā is a pilgrimage that includes four sacred sites: Badrinath, Dwarka, Puri, and Rameswaram.
Q7: Which tree is considered sacred in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism?
a) Banyan tree
b) Peepul tree
c) Mango tree
d) Neem tree
Ans: b) Peepul tree
The Peepul tree, especially the one under which Buddha attained enlightenment, is considered sacred in multiple religions.
Q8: Which tribe holds the Niyam Dongar hill sacred?
a) Bhils
b) Dongria Khond
c) Gonds
d) Konds
Ans: b) Dongria Khond
The Dongria Khond tribe in Jharkhand considers Niyam Dongar hill sacred, as it is home to their deity, Niyam Raja.
Q9: Which sacred site is related to the myth of the body parts of Sati?
a) Char Dhām
b) Jyotirlingas
c) Shakti Pithas
d) Kumbh Mela
Ans: c) Shakti Pithas
The Shakti Pithas are sacred sites where parts of the goddess Sati’s body are believed to have fallen, marking them as holy.
Q10: What is the significance of the Kumbh Mela?
a) A major Hindu festival celebrating the harvest
b) A pilgrimage marking the meeting of rivers
c) A festival held every six years in four locations
d) A tribute to ancient kings
Ans: c) A festival held every six years in four locations
The Kumbh Mela is a major pilgrimage that takes place every six years at four locations, attracting millions of devotees.
 Jyotirlingas
Jyotirlingas
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Sacredness in India is linked to places like temples, rivers, mountains, and __________.
Ans: Pilgrimages
Pilgrimages are journeys to sacred places that are part of India’s cultural and spiritual heritage.
Q2: The Char Dhām Yātrā connects __________ sacred sites in India.
Ans: Four
The Char Dhām Yātrā connects four sacred sites in India: Badrinath, Dwarka, Puri, and Rameswaram.
Q3: The __________ River is considered a goddess in Hinduism.
Ans: Ganga
The Ganga River is worshipped as a goddess and is central to many religious rituals in Hinduism.
Q4: __________ is an important pilgrimage site for followers of Jainism in Gujarat.
Ans: Shatruñjaya hill
Shatruñjaya hill in Gujarat is a significant sacred site in Jainism, associated with Tirthankaras.
Q5: __________ is the sacred site in Bodh Gaya where Buddha attained enlightenment.
Ans: Mahabodhi Stūpa
The Mahabodhi Stūpa in Bodh Gaya marks the place where Buddha attained enlightenment.
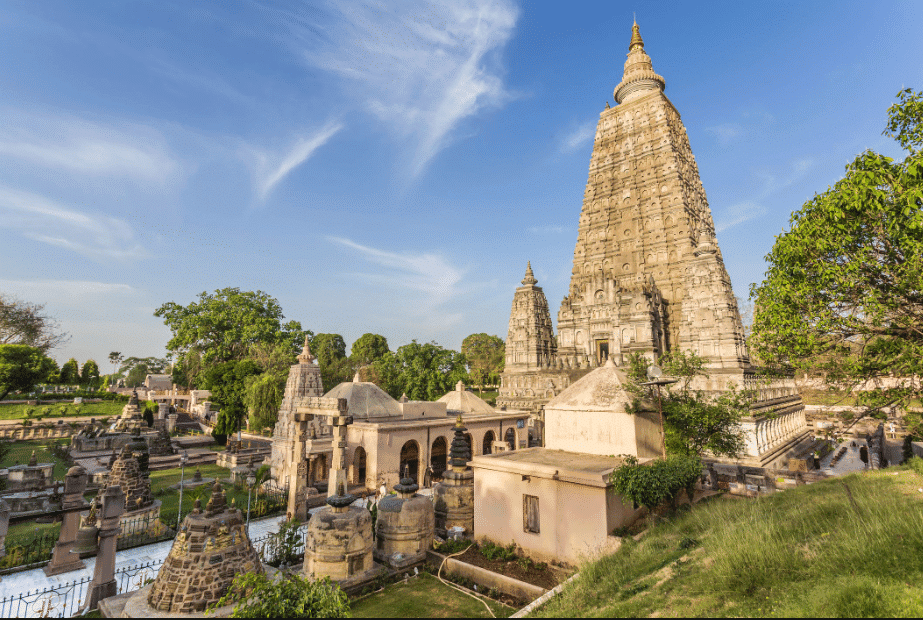 Mahabodhi Stupa
Mahabodhi Stupa
Q6: In India, the confluence of rivers is called a __________.
Ans: Sangam
Sangams, or confluences of rivers, are considered sacred in Hinduism, like the one in Prayagraj.
Q7: __________ was the major pilgrimage site for Sikhs, connected to Guru Nanak.
Ans: Takht Sri Patna Sahib
Takht Sri Patna Sahib is an important sacred site for Sikhs, associated with Guru Nanak.
Q8: __________ are sacred sites linked to the goddess Shakti in India.
Ans: Shakti Pithas
Shakti Pithas are sacred sites where parts of the goddess Sati’s body are believed to have fallen.
Q9: __________ is the sacred tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
Ans: Peepul tree
The Peepul tree at Bodh Gaya is sacred because it is believed to be the tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
Q10: The Kumbh Mela is held every __________ years at four sacred river sites.
Ans: Six
The Kumbh Mela is a major pilgrimage that occurs every six years at four sacred river sites in India.
 Tirth Yatra
Tirth Yatra
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is a tīrthayātrā?
Ans: A tīrthayātrā is a pilgrimage to a sacred site in India.
Q2: Which river is known as "Ganga ji" by many Indians?
Ans: The Ganga (Ganges) River.
Q3: What is a Sangam in Indian sacred geography?
Ans: A Sangam is the confluence of rivers, considered holy.
Q4: Who is associated with the Takht Sri Patna Sahib?
Ans: Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism.
Q5: Which tribe considers Niyam Dongar hill sacred?
Ans: The Dongria Khond tribe.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How does sacred geography help unite India?
Ans: Sacred geography unites India by connecting diverse regions through shared pilgrimage routes and sacred sites, fostering cultural exchange and unity.
Q2: What is the significance of the Kumbh Mela in Indian culture?
Ans: The Kumbh Mela is a major pilgrimage that brings millions of people together every six years, symbolizing the unity of diverse communities and the importance of sacred rituals.
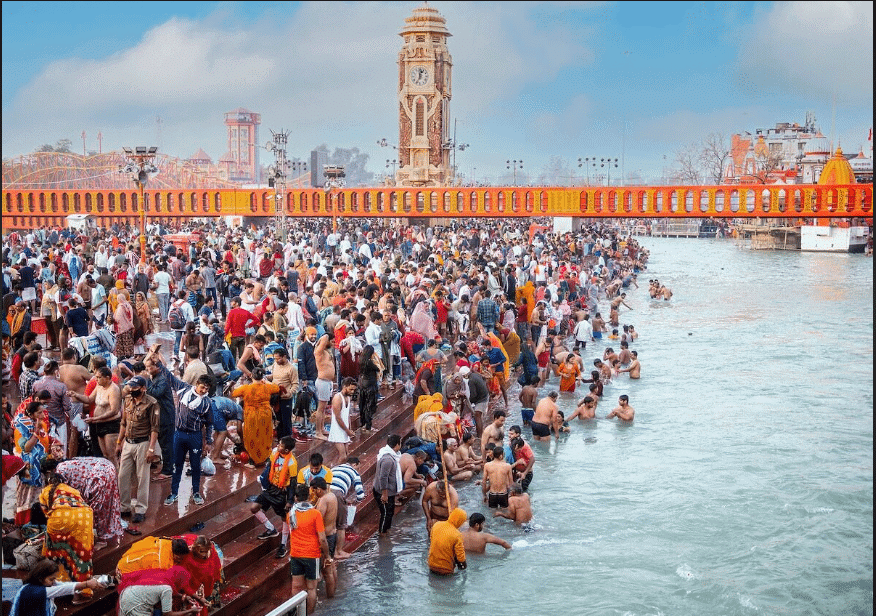 Kumbh Mela
Kumbh Mela
Q3: How does sacred ecology contribute to environmental protection?
Ans: Sacred ecology promotes the protection of nature by treating rivers, mountains, and forests as sacred spaces, encouraging people to protect them from pollution and exploitation.
Q4: Why are rivers considered sacred in India?
Ans: Rivers like the Ganga and Yamuna are worshipped as goddesses and considered sacred in Hinduism due to their life-giving properties and spiritual significance.
Q5: How does sacred geography influence trade in India?
Ans: Pilgrimage routes often overlap with trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, thereby enriching both spiritual and economic life.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
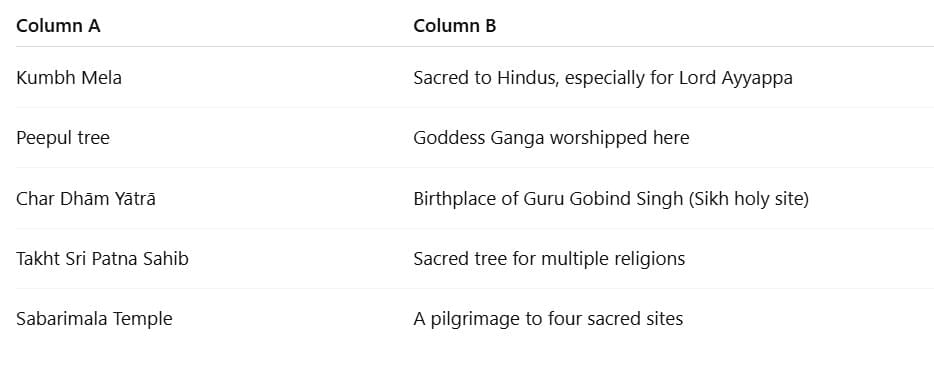
Ans: 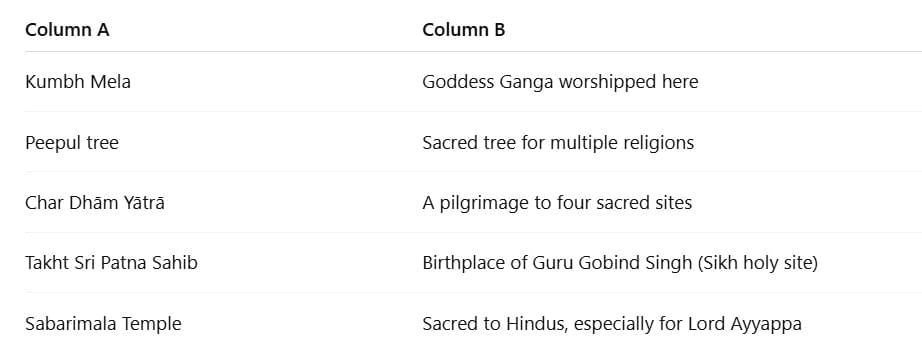
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 8 Worksheet Solutions - How the Land Becomes Sacred
| 1. What is the main theme of "How the Land Becomes Sacred"? |  |
| 2. How do different cultures perceive sacred land? |  |
| 3. What role do rituals play in making land sacred? |  |
| 4. Can land lose its sacred status, and if so, how? |  |
| 5. How can communities protect their sacred land? |  |















