Class 7 Science Chapter 5 NCERT Based Activity - Changes Around Us: Physical and Chemical
Activity 5.1: Let us think and reflect
You might have observed various changes happening around you. Some of them are listed in Table 5.1, you may notice that something is changing in each case. Take a moment to reflect on the changes in each case. Record your observations in Table 5.1.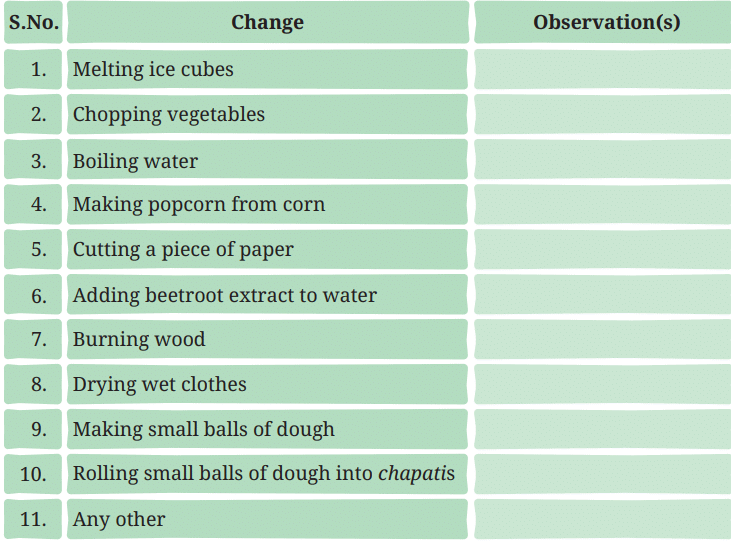 Table 5.1: Some changes observed around us
Table 5.1: Some changes observed around us
You might have noticed that these changes could be in the size, shape, smell, or other property of the substance or object. Can you think of some other changes that happen in your surroundings? Make a list of those changes too.
Ans: Record your observations in Table 5.1:
Q: Can you think of some other changes that happen in your surroundings? Make a list of those changes, too:
Ans: List as follows:
- Dissolving sugar in water (changes appearance, sugar disappears into water).
- Rusting of iron (forms brown rust, page 6).
- Curdling of milk (forms curd, page 14).
- Ripening of fruits (changes color, smell, and taste, page 14).
- Folding clothes (changes shape, page 14).
Explanation: Observations are based on changes in physical properties (size, shape, state, color) or formation of new substances.
Physical changes (e.g., melting, cutting) involve no new substances, while chemical changes (e.g., burning, popcorn) produce new substances. The additional change (freezing water) aligns with state changes discussed in the document.
Activity 5.2: Let us create and discuss
A. Creating some objects with paper
- Take a few sheets of paper and fold them to create new objects (Fig. 5.1).
- Do you get the same paper back when you unfold these objects?
 Fig. 5.1: Objects made from paper
Fig. 5.1: Objects made from paper
B. Playing with a balloon
- Take a balloon and inflate it. Now, loosen your grip and let the air escape out.
- Do you get the uninflated balloon back?
- Take another balloon; inflate it and grip the opening tightly. Now, prick it with a pin.
- Caution—Be careful while using a pin.
- What happens? Will you be able to get the uninflated balloon back?
C. Crushing a piece of chalk
- Crush a small piece of chalk into powder.
- Can you get the chalk piece back from the powder?
- Is there any similarity in the changes listed in A, B, and C?
Ans:
- Do you get the same paper back when you unfold these objects?
Yes, unfolding the paper returns it to its original flat state, with no change in its substance. - Do you get the uninflated balloon back (after letting air escape)?
Yes, the balloon returns to its uninflated state when air escapes, with no damage to the rubber. - What happens (after pricking the balloon)? Will you be able to get the uninflated balloon back?
The balloon bursts, creating a hole. You cannot get the uninflated balloon back in its original form due to the damage (implied by the action of pricking). - Can you get the chalk piece back from the powder?
No, the chalk powder cannot be reformed into the original solid piece, as the structure is permanently altered. - Is there any similarity in the changes listed in A, B, and C?
Similarity: In A (folding paper) and B (inflating/deflating balloon), the material (paper, rubber) remains the same, and the changes are reversible physical changes. In C (crushing chalk) and B (pricking balloon), the material remains the same, but the changes are often irreversible due to structural damage. All involve physical changes, as no new substances are formed.
Explanation: Folding paper and inflating/deflating a balloon are reversible physical changes. Pricking a balloon and crushing chalk are physical changes (no new substance), but typically irreversible due to damage or fragmentation.
Activity 5.3: Let us explore
- Take two glass tumblers or small transparent bottles. Mark them A and B.
- Fill one-fourth of glass tumbler A with tap water and one-fourth of glass tumbler B with lime water.
- Now, blow air (exhale) into each glass tumbler, one at a time, using separate straws (Fig. 5.2) and observe them.
- Caution—Do not suck the water or lime water while doing this.
- Do you notice any changes?
 Fig. 5.2: Blowing air in (a) tap water; (b) lime water
Fig. 5.2: Blowing air in (a) tap water; (b) lime water
Do you notice any changes?
Ans: In glass tumbler A (tap water), blowing air creates bubbles, but there is no change in the water’s appearance. In glass tumbler B (lime water), blowing air creates bubbles, and the lime water turns milky (cloudy). After some time, a white substance (calcium carbonate) settles at the bottom (page 4).
Explanation: Tumbler A shows no chemical change, as exhaled air (containing carbon dioxide) doesn’t react with water. Tumbler B undergoes a chemical change, as carbon dioxide reacts with lime water (calcium hydroxide) to form calcium carbonate (insoluble, milky) and water, a new substance (page 4: “Such changes… are called chemical changes”).
Activity 5.4: Let us experiment
- Take a teaspoonful of vinegar or lemon juice in a test tube.
- Add a pinch of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) to it.
- What do you observe?
- You would hear a fizzing bubbling sound and see the gas bubbles forming.
- Pass this gas through freshly prepared lime water kept in another test tube, as shown in Fig. 5.3a.
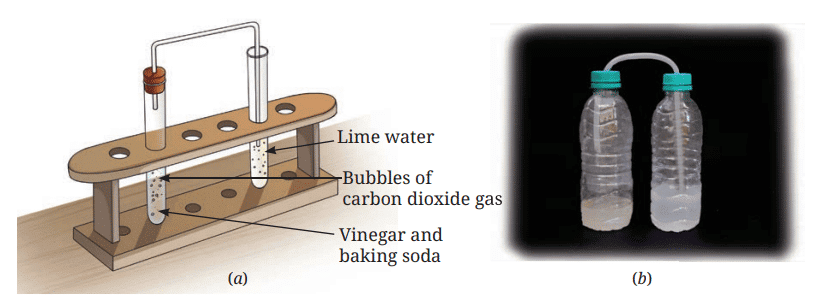 Fig. 5.3: Reaction of vinegar and baking soda
Fig. 5.3: Reaction of vinegar and baking soda - What do you observe?
- The lime water turns milky. What do you infer about the gas formed by mixing vinegar and baking soda?
- This indicates that the gas formed is carbon dioxide.
- This activity can also be performed using two small used bottles instead of test tubes and a flexible straw, as shown in Fig. 5.3b.
- Repeat the above activity using baking soda and water. Do you observe any bubble formation? Is this a physical or a chemical change?
Ans:
What do you observe (after adding baking soda to vinegar/lemon juice)?
A fizzing bubbling sound is heard, and gas bubbles form (page 5).What do you observe (after passing the gas through lime water)?
The lime water turns milky (page 5).What do you infer about the gas formed by mixing vinegar and baking soda?
The gas is carbon dioxide, as it turns lime water milky (page 5: “This indicates that the gas formed is carbon dioxide”).Repeat with baking soda and water. Do you observe any bubble formation? Is this a physical or a chemical change?
- Observation: No bubble formation occurs when mixing baking soda with water, as no reaction takes place (implied, as vinegar’s acidity causes the reaction, not water).
- Type of change: This is a physical change, as baking soda dissolves in water without forming new substances (page 12: “Physical change… no new substance is formed”).
Explanation:
- Vinegar (acetic acid) reacts with baking soda to produce carbon dioxide, water, and other substances, a chemical change (page 5). The carbon dioxide turns lime water milky, confirming its presence. Mixing baking soda with water only dissolves it, a physical change, as no new substances form.
Activity 5.5: Let us investigate
- Place two identical candles on two separate petri dishes and light them.
- Cover one of these with a glass tumbler, as shown in Fig. 5.6.
- What happens to the candle flames in the two cases?
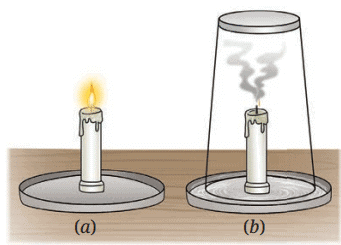 Fig. 5.6: Candle (a) burning (b) covered with a glass tumbler
Fig. 5.6: Candle (a) burning (b) covered with a glass tumbler
1. What happens to the candle flames in the two cases?
Ans: The candle not covered (Fig. 5.6a) continues to burn. The candle covered with a glass tumbler (Fig. 5.6b) stops burning after some time.
Explanation: The uncovered candle has a continuous oxygen supply, sustaining combustion. The covered candle consumes the limited oxygen inside the tumbler, extinguishing the flame (page 7: “The component of air that supports combustion is oxygen”). The carbon dioxide produced can be tested with lime water, which turns milky (page 7).
Activity 5.6: Let us investigate
- Caution—Perform this activity under the supervision of your teacher or an adult.
- Hold a piece of paper with a pair of tongs and bring a lighted matchstick to it. It quickly catches fire. Do we say that we need a fire to start the burning process?
- Take another piece of paper. Using a magnifying glass, focus the sunrays to make the smallest and brightest spot on the paper, as shown in the Fig. 5.7a. Hold it there for some time.
- What do you observe?

1. Do we say that we need a fire to start the burning process?
Ans: No, fire is not always needed. Heat sufficient to reach the substance’s ignition temperature can start burning (page 8).
2. What do you observe (when focusing sunrays on paper)?
Ans: The paper starts to emit smoke and then catches fire (page 8: “The paper starts to emit smoke, and then catches fire”).
Explanation: A matchstick’s flame exceeds paper’s ignition temperature, causing immediate burning. Focused sunrays heat the paper to its ignition temperature, initiating combustion without a flame, demonstrating that heat, oxygen, and fuel are required (page 8: “Fire triangle”).
Activity 5.7: Think, pair, and share
- Look at the Fig. 5.9. Analyse what students are discussing about the burning candle.
- What do you think?
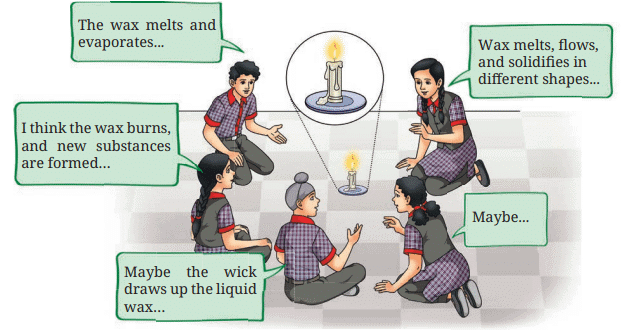
1. What do you think?
Ans: The burning of a candle involves both physical and chemical changes:
- Physical changes: The wax melts (solid to liquid), is carried up the wick, and evaporates (liquid to gas) due to the flame’s heat.
- Chemical change: The wax vapor burns, reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, heat, and light.
Explanation: Melting and evaporation are physical changes, as no new substances form. Burning is a chemical change, producing new substances.
Activity 5.8: Let us think
- Think again about all the changes that we have discussed or talked about so far. In which of these can we get back the object or substance in the form we started with? Record your observations in Table 5.2.
- Table 5.2: Can changes be reversed?
Ans: Record your observations in Table 5.2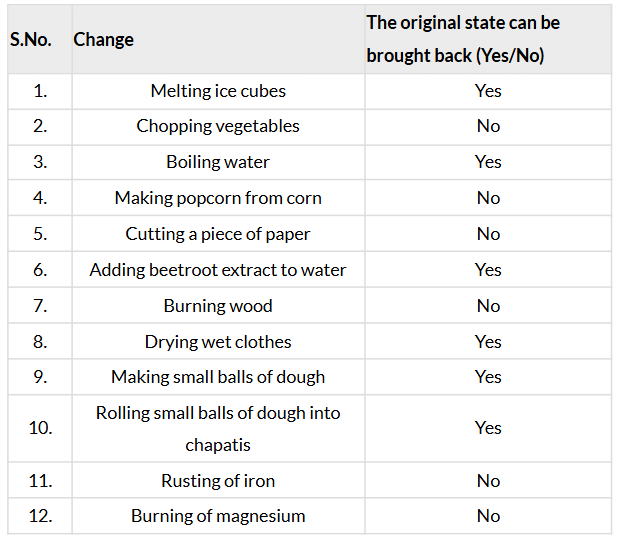
Explanation:
- Reversible changes (Yes): Melting ice (refreeze to ice), boiling water (condense to liquid), adding beetroot extract (can separate water by evaporation), drying clothes (rewet), shaping dough (reshape) are physical changes that can be reversed (page 10).
- Irreversible changes (No): Chopping vegetables, cutting paper, making popcorn, burning wood, rusting, and burning magnesium are mostly irreversible due to structural damage or new substances forming (page 10: “Some changes cannot be reversed”).
Exploratory Project: Yeast Experiment
- Yeast is added while baking bread to make it fluffy and soft. How does yeast work? Try and find out!
- Take a small bottle, some sugar, fresh yeast, water, and a balloon. Make a sugar solution in the bottle by mixing two teaspoons of sugar and a small amount of water. Now add a spoonful of yeast and cover the mouth of the bottle with a balloon. Leave it undisturbed for about an hour.
- What do you observe?
- Carefully take off the balloon, holding its mouth tightly closed and attach it to another small bottle containing freshly prepared lime water. Shake the bottle so that the contents of the balloon get mixed with lime water.
- What do you observe?
- What can you conclude from this experiment?
- Identify all the changes occurring in the experiment and state which of them are physical and chemical changes.
1. What do you observe (after leaving the yeast mixture for an hour)?
The balloon inflates, indicating gas production inside the bottle (implied by the setup, as yeast fermentation produces gas).
2. What do you observe (after mixing balloon contents with lime water)?
The lime water turns milky (based on page 5: lime water turns milky with carbon dioxide).
3. What can you conclude from this experiment?
Yeast ferments sugar, producing carbon dioxide gas, which inflates the balloon and turns lime water milky, confirming the gas’s identity.
4. Identify all the changes occurring in the experiment and state which of them are physical and chemical changes:
Physical changes:
- Dissolving sugar in water (no new substance, page 12).
- Balloon inflating (shape change due to gas pressure).
- Shaking lime water with gas (mixing, no new substance initially).
Chemical changes:
- Yeast fermenting sugar to produce carbon dioxide and other substances (new substances formed, similar to vinegar/baking soda reaction, page 5).
- Carbon dioxide reacting with lime water to form calcium carbonate (milky), a chemical change (page 4: “Formation of a new substance indicates a chemical change”).
Explanation: Yeast breaks down sugar into carbon dioxide and ethanol, a chemical change, inflating the balloon. The carbon dioxide reacts with lime water, forming calcium carbonate, another chemical change (page 4). Dissolving and mixing are physical changes, as no new substances form (page 12).
|
80 videos|319 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 5 NCERT Based Activity - Changes Around Us: Physical and Chemical
| 1. What are the physical and chemical changes discussed in the NCERT Class 7 chapter "Changes Around Us"? |  |
| 2. How can we identify a physical change from a chemical change? |  |
| 3. What is the role of yeast in the yeast experiment mentioned in the exploratory project? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to conduct experiments like the yeast experiment in understanding physical and chemical changes? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken during the yeast experiment? |  |
















