Q1: Calculate the speed of a car that travels 150 meters in 10 seconds. Express your answer in km/h.
Answer:
Speed = Distance / Time
Given:
Distance = 150 meters
Time = 10 seconds
Convert meters to kilometers and seconds to hours:
150 meters = 0.15 km
10 seconds = 10/3600 hours = 1/360 hours
Now calculate speed:
Speed = 0.15 km / (1/360 hour) = 0.15 x 360 = 54 km/h
Q2: A runner completes 400 meters in 50 seconds. Another runner completes the same distance in 45 seconds. Who has a greater speed and by how much?
Answer:
Speed = Distance / Time
Runner 1:
Distance = 400 meters
Time = 50 seconds
Speed = 400 / 50 = 8 m/s
Runner 2:
Distance = 400 meters
Time = 45 seconds
Speed = 400 / 45 ≈ 8.89 m/s
Conclusion:
Runner 2 has a greater speed by:
8.89 m/s - 8 m/s = 0.89 m/s
Q3: A train travels at a speed of 25 m/s and covers a distance of 360 km. How much time does it take?
Answer:
Time = Distance / Speed
Convert 360 km to meters:
360 km = 360,000 meters
Now calculate the time:
Time = 360,000 meters / 25 m/s = 14,400 seconds
Convert seconds to hours:
14,400 / 3600 = 4 hours
Q4: A train travels 180 km in 3 hours. Find its speed in:
(i) km/h
(ii) m/s
(iii) What distance will it travel in 4 hours if it maintains the same speed throughout the journey?
Answer:
(i) Speed in km/h:
Speed = Distance / Time = 180 km / 3 hours = 60 km/h
(ii) Speed in m/s:
Convert 180 km to meters:
180 km = 180,000 meters
Now calculate speed in m/s:
Speed = 180,000 meters / (3 hours x 3600 seconds) = 16.67 m/s
(iii) Distance in 4 hours:
Distance = Speed x Time = 60 km/h x 4 hours = 240 km
Q5: The fastest galloping horse can reach the speed of approximately 18 m/s. How does this compare to the speed of a train moving at 72 km/h?
Answer:
Convert the speed of the train to m/s:
72 km/h = 72 x 1000 meters / 3600 seconds = 20 m/s
Comparison:
The horse moves at 18 m/s.
The train moves at 20 m/s.
Conclusion:
The train is faster than the galloping horse by:
20 m/s - 18 m/s = 2 m/s
Q6: Distinguish between uniform and non-uniform motion using the example of a car moving on a straight highway with no traffic and a car moving in city traffic.
Answer: Uniform motion
When a car moves on a straight highway with no traffic, it maintains a constant speed. This is uniform motion, where the distance covered in equal time intervals is the same.
Non-uniform motion
In city traffic, the car's speed changes due to stops, slowdowns, and accelerations. This is non-uniform motion, where the distance covered in equal intervals of time is not constant.
Q7: Data for an object covering distances in different intervals of time are given in the following table. If the object is in uniform motion, fill in the gaps in the table.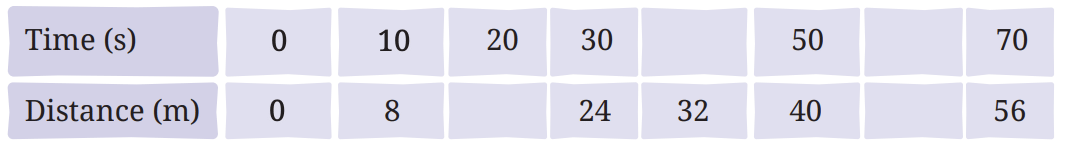
Answer: Check for uniform motion:
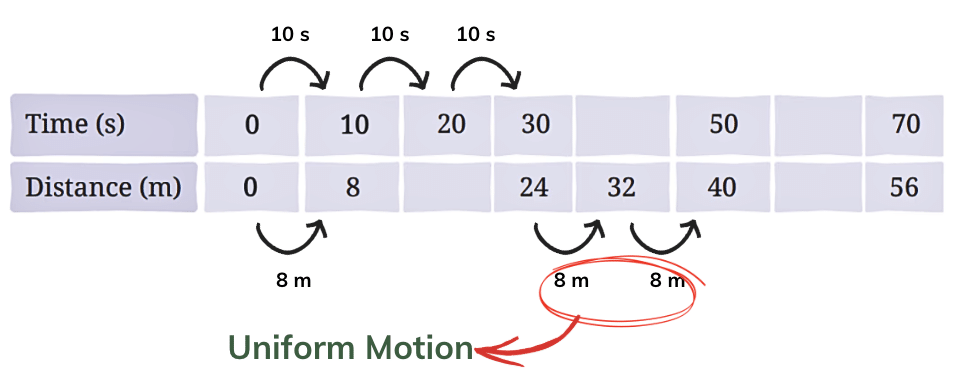
Keeping in mind , this is an uniform motion, the object must cover equal distances in equal time intervals.
Therefore, 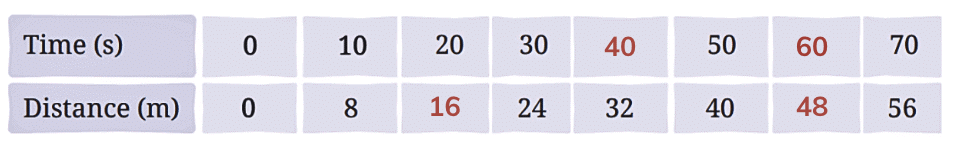
Q8: A car covers 60 km in the first hour, 70 km in the second hour, and 50 km in the third hour. Is the motion uniform? Justify your answer. Find the average speed of the car.
Answer:
Since the car covers different distances in each hour (60 km, 70 km, and 50 km), the motion is non-uniform.
To find the average speed:
Total distance = 60 km + 70 km + 50 km = 180 km
Total time = 3 hours
Average speed = Total distance / Total time = 180 km / 3 hours = 60 km/h
Q9: Which type of motion is more common in daily life—uniform or non-uniform? Provide three examples from your experience to support your answer.
Answer:
Non-uniform motion is more common in daily life. Examples:
A car in city traffic: The car's speed changes due to stops and accelerations.
A bicycle in a park: The rider's speed changes while turning or stopping.
People walking: Walking speed varies due to obstacles or fatigue.
Q10: Data for the motion of an object are given in the following table. State whether the speed of the object is uniform or non-uniform. Find the average speed.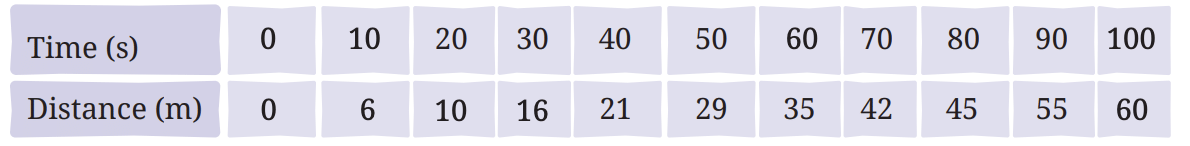
Answer: Check the distance traveled in each time interval: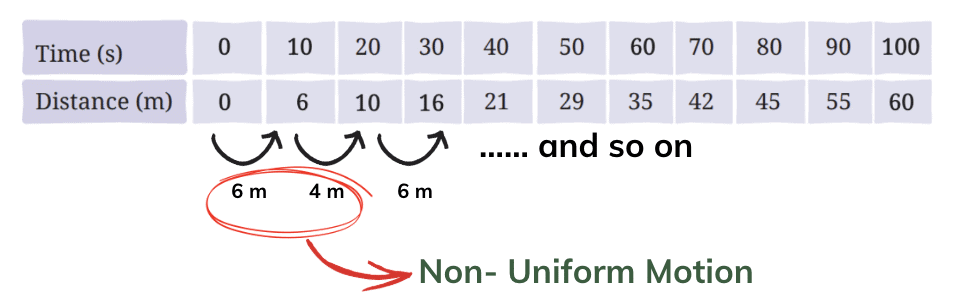
As the distances covered in each interval are not equal, the motion is non-uniform.
Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time
Total distance = 60 m (final distance)
Total time = 100 s (final time)
Average Speed = 60 m / 100 s = 0.6 m/s

















