NCERT Based Activity: Structure of the Atom | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Activity 4.1: Charged Particles in Matter
Description:
- Part A: Comb dry hair. Does the comb then attract small pieces of paper?
- Part B: Rub a glass rod with a silk cloth and bring the rod near an inflated balloon. Observe what happens.
- From these activities, can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged?
- Where does this charge come from?
Ans:
- Part A: After combing dry hair, the comb attracts small pieces of paper. The comb becomes electrically charged due to the transfer of electrons between the comb and the hair, causing the comb to gain a charge (typically negative) that attracts the neutral or oppositely charged paper pieces.
- Part B: When the glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, the rod becomes charged (typically positive) and attracts the inflated balloon. The balloon, being neutral or slightly charged, is attracted to the charged rod due to electrostatic forces.
Q: Can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged?
Ans: Yes, rubbing two objects together can cause them to become electrically charged. This is due to the transfer of electrons between the surfaces of the objects, a phenomenon known as triboelectric charging.
Q: Where does this charge come from?
Ans: The charge comes from the movement of electrons between the two objects. For example, when hair is combed, electrons may transfer from the hair to the comb, making the comb negatively charged and the hair positively charged. Similarly, when a glass rod is rubbed with silk, electrons may transfer from the rod to the silk, leaving the rod positively charged.
Explanation: This activity demonstrates the existence of charged particles (electrons) within matter. The transfer of electrons during rubbing results in one object gaining a negative charge (extra electrons) and the other a positive charge (loss of electrons). This supports the idea that atoms are divisible and contain charged particles, as electrons can be removed or added, leading to the discovery of sub-atomic particles like electrons and protons.
Activity 4.2: Static Atomic Model
- Make a static atomic model displaying electronic configuration of the first eighteen elements.
- The composition of atoms of the first eighteen elements is given in Table 4.1.
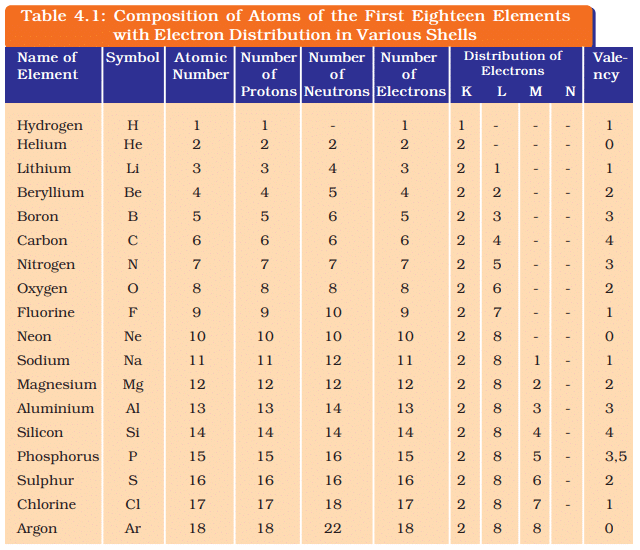
Ans:
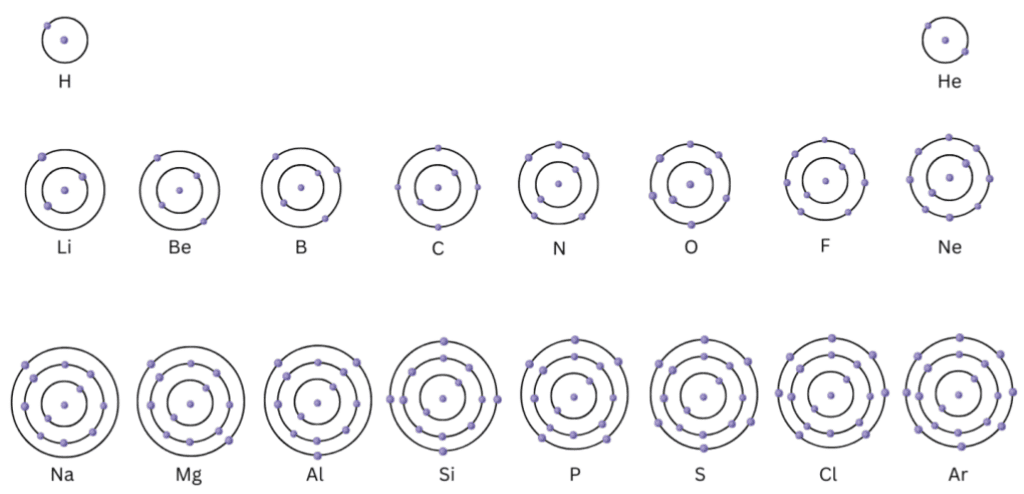
Summary of Key Concepts Demonstrated by the Activity
Charged Particles in Matter (Activity 4.1):
The activity illustrates that atoms contain charged particles, specifically electrons, which can be transferred between objects through friction, resulting in electrostatic charges. The attraction of paper to a charged comb and a balloon to a charged rod demonstrates the effects of these charges, supporting the concept that atoms are not indivisible but consist of charged sub-atomic particles (electrons and protons).
This activity provides hands-on evidence for the presence of charged particles within atoms, setting the stage for understanding atomic structure and the discoveries of electrons (by J.J. Thomson) and protons (via canal rays by E. Goldstein).
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Structure of the Atom - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the basic structure of an atom? |  |
| 2. How do protons, neutrons, and electrons differ in terms of charge and mass? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the atomic number? |  |
| 4. How do isotopes of an element differ from one another? |  |
| 5. What role do electrons play in chemical bonding? |  |
















