6 Golden Rules for Odd Sentence Out | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding the Basics: What is an Odd Sentence Out Question? |

|
| The 6 Golden Rules for Identifying the Odd Sentence Out |

|
| Quick Checklist for Odd Sentence Out |

|
| Extra Tips for Success |

|
Odd Sentence Out is a regular in the CAT Verbal Ability. You get 5 sentences, 4 make sense together, 1 doesn’t. Sounds easy, but CAT makes it tricky. The good news? Once you know the patterns, these become one of the easiest scoring areas. Let us dive deeper to make this topic your strength.
Understanding the Basics: What is an Odd Sentence Out Question?
Think of it like a group chat: four people talk about cricket, and one suddenly talks about cooking. That’s your odd sentence. In CAT, the sentences look academic, but the principle is the same — spot the one that breaks the flow.
Excelling at this requires more than just a good vocabulary or general reading skills. It demands a keen eye for textual coherence, an understanding of how arguments and narratives are structured, and the ability to discern subtle shifts in topic or logic. It's also beneficial to be aware of how these questions are typically constructed, as this can provide clues to identifying the outlier.
Question setters often work with complicated texts, like academic articles or detailed explanations. The main challenge is to identify the specific theme and structure of a four-sentence paragraph. It's important to find the sentence that, even if it seems similar on the surface, does not fit with the overall unity of the paragraph.
The 6 Golden Rules for Identifying the Odd Sentence Out
Here are six fundamental rules to guide your approach to Odd Sentence Out questions:
Golden Rule 1: Identify the Central Theme and Scope
Read all five sentences quickly to get the general topic. Then, look for the specific idea that most sentences focus on. The odd sentence might be about the same topic, but go off in a different direction.
- Example:
(A) The history of wind energy dates back to ancient times.
(B) Wind turbines today generate clean energy efficiently.
(C) They help reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly.
(D) Many regions are adopting wind farms for power.
(E) Wind energy also supports sustainable development goals.
Odd Sentence: A.
Explanation: Sentences B, C, D, and E focus on the current benefits and adoption of wind energy (clean energy, emissions reduction, wind farms, sustainability). Sentence A shifts to the historical aspect of wind energy, which doesn’t align with the modern-focused theme. - Trap to Avoid: Don’t just focus on the general topic (e.g., solar energy). Look for the specific focus (e.g., benefits, not history).
- Time-Saving Tip: Skim the sentences in 10–15 seconds and write down the main idea in 2–3 words (e.g., "solar benefits").
Golden Rule 2: Look for Logical Flow and Transitions (Even When Hidden)
Sentences in a paragraph should connect logically. Look for words like "however," "therefore," or "also" that link ideas. Even if these words aren’t there, the sentences should flow naturally. The odd sentence will break this flow.
- Example:
(A) Planning a project starts with setting clear goals.
(B) The team then assigns tasks to members.
(C) Regular meetings ensure progress is on track.
(D) Milestones are set to monitor key achievements.
(E) I prefer using digital tools for planning.
Odd Sentence: E.
Explanation: Sentences A, B, C, and D describe a sequential project planning process (setting goals, assigning tasks, monitoring progress, setting milestones). Sentence E introduces a personal preference, disrupting the objective process-focused flow. - Trap to Avoid: Don’t focus only on grammar. A sentence can be grammatically correct but still not fit the logical flow.
- Time-Saving Tip: Look for connecting words first—they’re a quick clue to which sentences fit together.
Golden Rule 3: Trace Pronoun References and Keyword Chains
Pronouns like "it," "they," or "this" should refer to something clear in the other sentences. Also, look for repeated keywords that tie sentences together. The odd sentence might use a pronoun that doesn’t make sense or bring in new, unrelated words.
- Example:
(A) Deforestation destroys habitats for many species.
(B) It also contributes to climate change.
(C) Reforestation efforts are gaining momentum globally.
(D) It leads to soil erosion in affected areas.
(E) It increases carbon dioxide levels significantly.
Odd Sentence: C.
Explanation: Sentences A, B, D, and E focus on the negative effects of deforestation (habitat loss, climate change, soil erosion, CO2 increase), with "it" consistently referring to deforestation. Sentence C introduces reforestation, a solution-oriented topic that breaks the chain of negative impacts. - Trap to Avoid: Don’t assume a pronoun always fits. If "it" refers to something not mentioned in the other sentences, that sentence might be the odd one.
- Time-Saving Tip: Circle pronouns and keywords as you read. If a pronoun or keyword doesn’t match the others, flag that sentence.
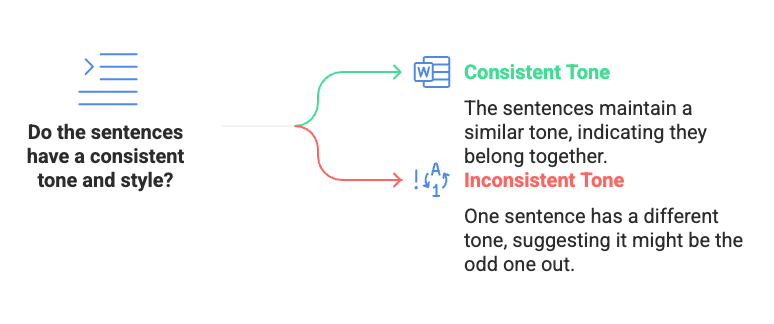
Golden Rule 4: Look for Same Tone and Style
The four sentences that fit together usually have a similar tone (e.g., serious or casual) and style (e.g., formal or simple). A sentence with a very different tone or style might be the odd one out.
- Example:
(A) The study was conducted with rigorous methodology.
(B) Honestly, I thought the study was kinda boring.
(C) Participants were selected based on strict criteria.
(D) Data analysis followed established protocols.
(E) Results were validated by independent experts.
Odd Sentence: B.
Explanation: Sentences A, C, D, and E maintain a formal, academic tone, focusing on the study’s process. Sentence B’s casual tone ("kinda boring") and subjective opinion contrast sharply with the formal narrative, making it the odd one out. - Trap to Avoid: Tone isn’t always the main clue. Use this rule only if the other rules don’t give a clear answer.
- Time-Saving Tip: Quickly note if one sentence feels very different (e.g., too funny or too serious) while reading.
While not always the primary determinant, a significant shift in tone (e.g., from formal to informal, objective to subjective) or style can sometimes indicate an odd sentence. The four sentences forming the paragraph will generally maintain a consistent voice and level of formality. An abrupt change might signal a sentence that doesn't belong.
Golden Rule 5: Test Paragraph Order
Try to make a paragraph with four of the sentences. If four sentences form a logical order, the leftover one is the odd one out. The odd sentence might be tricky—it could be the first or last one, so test different orders.
- Example:
(A) Birds migrate seasonally to find better climates.
(B) They often travel thousands of miles.
(C) During migration, they stop to rest in key areas.
(D) This journey ensures their survival in harsh conditions.
(E) My favorite bird species is the eagle.
Odd Sentence: E.
Explanation: Sentences A, B, C, and D form a coherent paragraph about bird migration (A introduces, B elaborates on distance, C on resting, D on purpose), with a logical order (A-B-C-D). Sentence E, discussing a personal favorite, doesn’t fit into this migration narrative. - Trap to Avoid: Don’t assume the first sentence is always part of the paragraph. Test all combinations.
- Time-Saving Tip: Use the sentence numbers (e.g., 1-2-3-4) to quickly test orders in your mind or on paper.
Golden Rule 6: The Odd One Out Often Disrupts Micro-Coherence
The four sentences that belong together will have a specific focus, like a small story or argument. The odd sentence might be about the same topic but add an unrelated detail, contradict the others, or go off-topic.
- Example:
(A) Governments should invest in renewable energy sources.
(B) Fossil fuels contribute to air pollution significantly.
(C) They also cause health issues in urban areas.
(D) Burning coal releases harmful greenhouse gases.
(E) This leads to long-term environmental damage.
Odd Sentence: A.
Explanation: Sentences B, C, D, and E focus on the negative impacts of fossil fuels (air pollution, health issues, greenhouse gases, environmental damage), forming a cohesive paragraph. Sentence A introduces a solution (investing in renewables), which doesn’t align with the impact-focused narrative, disrupting micro-coherence. - Trap to Avoid: Don’t pick a sentence just because it’s shorter or longer. Focus on whether it fits the main idea.
- Time-Saving Tip: After finding the main focus, check which sentence feels out of place in 5 seconds—it’s often obvious.
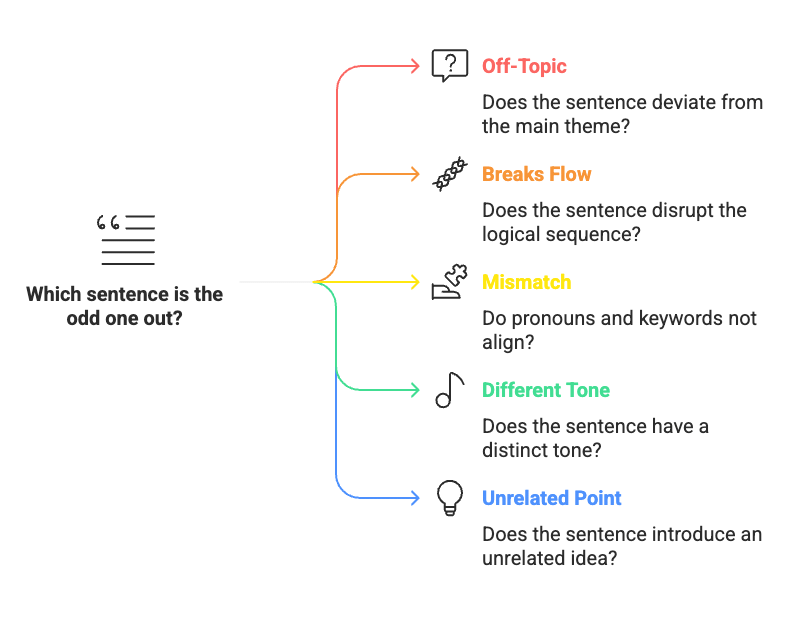
Quick Checklist for Odd Sentence Out
Before you pick the odd sentence, ask these questions:
- What’s the main theme? Does one sentence go off-topic?
- Do the sentences flow logically? Does one break the flow?
- Do pronouns and keywords match? Is there a mismatch?
- Is the tone the same? Does one sentence feel different?
- Can four sentences make a paragraph? Which one is left out?
- Does one sentence add an unrelated point or contradict the focus?
Extra Tips for Success
- Beware of Deceptive Proximity: Question setters sometimes choose an odd sentence that, in the original source text, was very close to the sentences forming the paragraph. Its topical relevance can be a trap. Focus on its role (or lack thereof) within the given set of five sentences.
- Don't Expect Perfect Prose: The four sentences forming the paragraph will be coherent, but they won't necessarily be a masterpiece of writing. The goal is to find the sentence that least fits, not to critique the writing style of the coherent set.
- Practice Deconstructive Analysis: When you review practice questions (both those you got right and those you got wrong), don't just look at the answer. Actively try to understand why the correct answer is the odd one out and, equally importantly, how the other four sentences connect. Consider the common patterns of question construction, such as the removal of connectors or the combination of multiple ideas into single sentences.
- Time Management: While thoroughness is important, be mindful of the time. If you're stuck on a question, make your best educated guess based on the rules and move on. You can always return if time permits.
By consistently applying these golden rules and tips, you can develop a systematic and effective approach to conquering Odd Sentence Out questions and boosting your performance in verbal ability sections.
|
111 videos|452 docs|90 tests
|
FAQs on 6 Golden Rules for Odd Sentence Out - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What is an Odd Sentence Out question in exams? |  |
| 2. What are the 6 Golden Rules for identifying the Odd Sentence Out? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my skills in solving Odd Sentence Out questions? |  |
| 4. What is a quick checklist to use when answering Odd Sentence Out questions? |  |
| 5. What extra tips can help me succeed in Odd Sentence Out questions during exams? |  |




















