Class 7 Science Chapter 11 HOTS Questions - Light: Shadows and Reflections
Q1: Why is it important to recycle LED lamps properly? What could happen if they end up in regular waste?
Ans: LED lamps contain small amounts of metals and electronic parts that can be harmful to the environment if thrown away carelessly. Recycling them properly ensures these materials are safely processed and reused, preventing pollution. If LED lamps go into regular trash, toxic substances can leak into soil and water, harming plants, animals, and people.
Q2: Given that light generally travels in a straight line, how do you explain the bending of light in phenomena like rainbows or when light passes through water?
Ans: Although light usually travels straight, it bends when it passes from one material to another at an angle — this is called refraction. For example, when sunlight passes through raindrops, it bends inside the drops and splits into different colors, creating a rainbow. Similarly, light bends when it moves from air into water because water is denser, changing the light’s speed and direction.
Q3: Shadow puppetry is an ancient art using shadows. How do shadows help in storytelling and what scientific concepts does it involve?
Ans: In shadow puppetry, flat puppets block light to form shadows on a screen. By moving the puppets, storytellers create characters and scenes using shadows. This involves the science of light being blocked by opaque objects to form shadows. The size and clarity of the shadows help audiences see the shapes and understand the story visually.
Q4: Imagine you are asked to create a new educational toy using the properties of light and reflection. What would it be and how would it work?
Ans: I would create a “Light Maze” toy. It would have a small laser pointer at one end and a maze made of mirrors inside a box. Children would move mirrors to reflect the laser light through the maze and hit a target. This would teach them how light travels straight and reflects off surfaces at equal angles, making learning fun and interactive.
Q5: In the design of an ambulance, why is the word "AMBULANCE" written in reverse on the front?
Ans: The word “AMBULANCE” is written backward so that drivers looking in their rear-view mirrors see the word in the correct order. This is because a plane mirror reverses images from left to right (lateral inversion). This helps drivers quickly recognize the ambulance coming behind them and move aside.
Q6: Why does changing the color of an object not affect the color of its shadow?
Ans: Shadows are formed because the object blocks light from reaching a surface. Since a shadow is simply an area with less or no light, it appears dark or black regardless of the object's color. The color of the object does not add light to the shadow, so the shadow color remains unaffected.
Q7: Why does the size and shape of a shadow change when you move the light source closer or farther from the object?
Ans: When the light source moves closer to the object, the rays spread out more, and the shadow becomes bigger and less sharp because the light is coming from a wider angle. When the light source is farther away, the rays are more parallel and the shadow becomes smaller and sharper. Also, changing the angle of the light source changes the shape of the shadow because the light hits the object differently.
Q8: You notice that sunlight reflected from a shiny surface can be directed to brighten a dark corner of your room. Explain how this happens using the reflection of light principles.:
Ans: When sunlight hits a shiny surface, like a mirror, the light bounces off the surface in a new direction. This is called reflection. By tilting or moving the mirror, you can control where the reflected light goes. So, by aiming the mirror towards a dark corner, you can send the sunlight into that space and brighten it. This happens because light changes direction but follows the rule that the angle it hits the mirror equals the angle it reflects away.
Q9: Assume, a person is standing in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 6 m. If the person moves 2 m towards the plane mirror, what would be the distance between the person and his image?
Ans:
Since, the image is 6m away from the plane mirror. So, it means that the object is also 6m away from the mirror.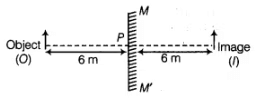
[Because OP = PI]
So, when the person moves 2 m towards the plane mirror, then the distance between the person and the plane mirror will be equal to (6 m – 2 m) = 4 m, this means that distance between the image and the mirror will be 4m.
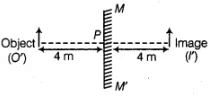 The distance between the person and his image = PO’+ PI’= 4 + 4 = 8mQ14: It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
The distance between the person and his image = PO’+ PI’= 4 + 4 = 8mQ14: It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
Ans: The lens in question is a convex lens. When the distance between an object and a convex lens decreases, the size of the image increases. This is because a convex lens converges light rays, creating a larger image as the object gets closer. As you continue to decrease the distance between the object and the lens:
- The image will initially remain clear and magnified.
- Eventually, the image may become virtual, meaning it cannot be projected onto a screen.
- At very close distances, the image may appear distorted or blurred.
Q10: Design a simple experiment at home to demonstrate that light travels in a straight line. Describe the steps.
Ans: You can try this easy experiment: Take three pieces of cardboard and make a small hole in each. Now, hold these three cardboard pieces so that the holes are perfectly lined up in a straight line.
Shine a torch or flashlight through the holes.
You will see the light pass through all three holes and form a bright spot on a wall behind.
Now, move one cardboard piece slightly so that the holes are no longer aligned.
The light spot disappears, showing that light cannot bend around the hole.
This proves that light travels in a straight line.
|
80 videos|322 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 11 HOTS Questions - Light: Shadows and Reflections
| 1. What are the main types of shadows, and how do they form? |  |
| 2. How do reflections occur in different surfaces? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the size and shape of shadows? |  |
| 4. Why do shadows change in length and direction throughout the day? |  |
| 5. How can we use shadows to tell time? |  |
















