Class 7 Science Chapter 4 HOTS Questions - The World of Metals and Non-metals
Q1. Why do you think the Iron Pillar of Delhi has not rusted even after 1600 years, while modern iron tools rust within a few years if exposed to air and water? What does this tell us about ancient Indian metallurgy?
Ans: The Iron Pillar of Delhi has not rusted because it was made using a special method that protected it from air and water. The iron used in the pillar is very pure, and a special layer formed on it naturally, which stops rusting. This shows that ancient Indian people had great knowledge and skills in making strong and long-lasting metals. They knew how to protect metals from rusting, even without modern machines or chemicals.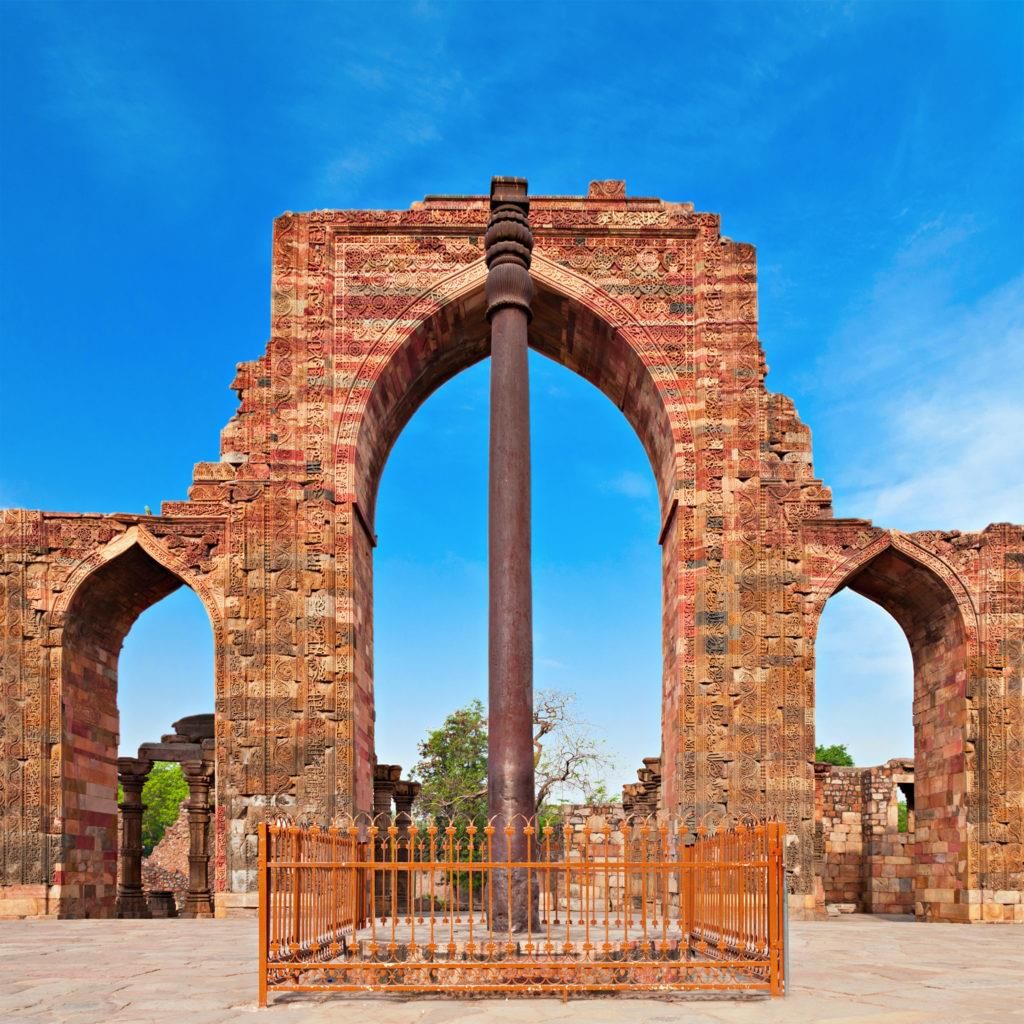
Q2. Imagine a world where all materials were non-metals. How would it affect industries like construction, transportation, or electricity supply? Give at least two examples.
Ans: If everything were made from non-metals, many things around us would not work properly. For example:
In construction, buildings and bridges would not be strong, because non-metals are weak and break easily.
In electricity supply, we could not use copper or aluminium wires, as non-metals do not let electricity pass through them.
This would make it hard to live the way we do now, as many tools and machines need metals to work properly.
Q3. If Anandi wanted to test whether a new shiny material is a metal or non-metal, what simple experiments could she perform at home or school, and why?
Ans: Anandi could try these simple tests:
She can hit the object gently with a spoon. If it makes a ringing sound, it is probably a metal.
She can check if the material shines when rubbed. Metals usually have a shiny look called lustre.
She can see if it can be flattened or bent without breaking (this shows malleability).
If she has a simple electric circuit, she can connect the material and see if it lets the bulb glow. If it does, it is a good conductor like a metal.
These small tests help her understand the properties of the material.
Q4. You are designing a kitchen utensil set. Which parts should be made of metal and which of non-metal? Explain your choices based on properties like heat conduction and malleability.
Ans: In the kitchen, cooking pans and pots should be made of metals like aluminium or iron because metals get hot quickly and help in cooking food faster (they are good conductors of heat).
The handles of these utensils should be made of non-metals like plastic or wood, because they do not get hot easily (they are poor conductors). This helps us hold the pan safely without burning our hands.
Also, metals are malleable, so they can be shaped into different cooking tools.
Q5. In your opinion, which is more crucial to human survival—metals or non-metals? Justify your answer with examples from daily life.
Ans: Non-metals are more important for our survival. For example:
Oxygen, a non-metal, is needed for breathing. Without it, we cannot live.
Carbon is found in our body and in food. It helps us grow and stay healthy.
Nitrogen is used in fertilizers that help plants grow.
Chlorine cleans water so we can drink it safely.
These non-metals are a part of our life every day, while metals are useful for making tools and machines. So, for survival, non-metals are more important.
Q6. Sodium is stored in kerosene, while phosphorus is stored in water. What does this indicate about the reactivity of these non-metals and metals? Can you think of any safety risks if these substances were stored improperly?
Ans: This shows that sodium and phosphorus are very reactive, which means they catch fire or explode easily when they come in contact with air or water.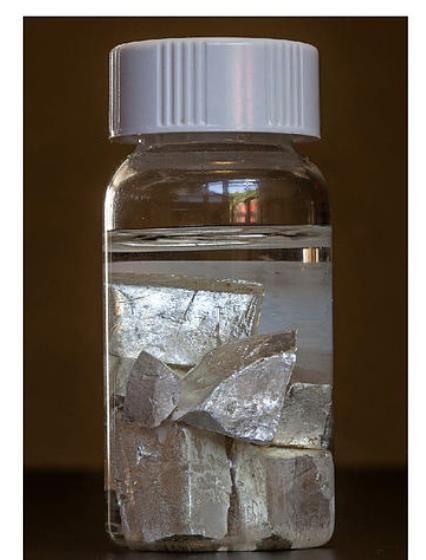
Sodium reacts quickly with air and water, so we store it in kerosene to keep it safe.
Phosphorus catches fire when exposed to air, so it is kept under water to stop it from burning.
If these materials are not stored properly, they can cause fires, burns, or accidents. That’s why it’s important to handle them carefully.
Q7. Why do you think school bells are made of metal and not plastic or wood? Can you relate this to the property of sonority?
Ans: School bells are made of metal because metals make a clear ringing sound when we hit them. This property is called sonority.
Plastic or wood do not make a loud sound. They produce dull sounds, which cannot be heard from far away.
That’s why metals are used in bells, musical instruments, and dance anklets (ghungroos), as they help produce loud and pleasant sounds.
Q8. You are an engineer designing electrical wiring for a new building. Explain why metals are used in wires and non-metals are used to cover them. What might happen if both were made of the same material?
Ans: Metals like copper and aluminium are used in wires because they allow electricity to pass through them easily.
Non-metals like plastic or rubber are used to cover the wires because they do not conduct electricity, and they protect us from getting electric shocks.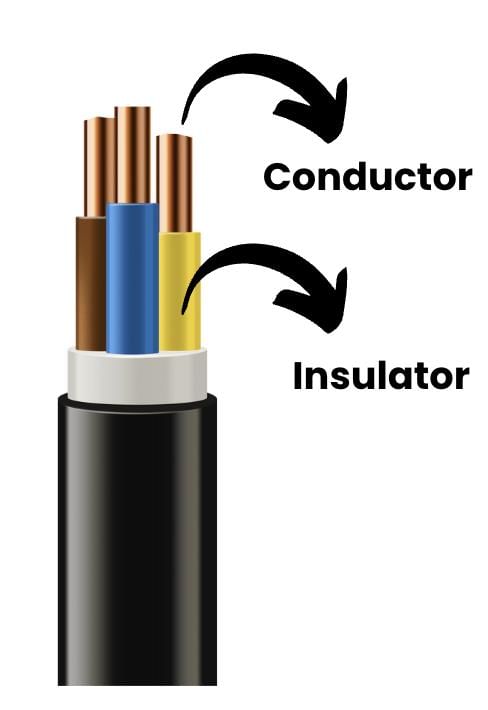 If both the wire and the covering were made of metal, the current would leak, and people might get shocked or hurt. That’s why metals and non-metals are both needed in the correct place.
If both the wire and the covering were made of metal, the current would leak, and people might get shocked or hurt. That’s why metals and non-metals are both needed in the correct place.
Q9. Rusting damages iron tools and structures. If you were a scientist, what methods would you explore (besides painting and oiling) to prevent rusting more effectively in humid coastal areas?
Ans: As a scientist, I would try these methods:
Galvanisation: Coating the iron with zinc, which protects it from rust.
Using stainless steel: This is a type of iron mixed with other metals that doesn’t rust easily.
Making a waterproof layer: Using special sprays or materials that stop air and water from touching the iron.
These methods can protect iron tools and save money spent on repairs, especially in areas near the sea where air is moist.
Q10. Why do you think both malleability and ductility are considered useful properties for metals in industries? Can you think of an example where one is more important than the other?
Ans: Metals are used in factories because they can be:
Malleable – shaped into thin sheets (like for car bodies or kitchen utensils).
Ductile – pulled into wires (like for electricity and machines).
In making aluminium foils, malleability is more important because the metal needs to be flattened.
In making electrical wires, ductility is more useful because the metal must be stretched into thin wires.
So, both properties are helpful but used in different ways.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 4 HOTS Questions - The World of Metals and Non-metals
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. Why are metals considered useful in everyday life? |  |
| 3. How do non-metals affect our health and environment? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of metals and non-metals found in nature? |  |
| 5. How can we identify whether a substance is a metal or a non-metal? |  |






















