Measuring Public Opinion Chapter Notes | AP U.S Government and Politics - Grade 12 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Definition of Public Opinion |

|
| Types of Polls |

|
| Scientific Polling Methodology |

|
| How Questions Affect Poll Accuracy |

|
| Survey Methods |

|
| Limitations of Public Opinion Data |

|
Introduction
Public opinion represents the collective perspectives, preferences, and attitudes of individuals on various issues, candidates, institutions, or policies. It plays a pivotal role in shaping democratic governance by guiding elected officials in their decision-making and ensuring responsiveness to the public’s needs. Public opinion is typically captured through polls and surveys, which rely on scientific methodologies to provide reliable insights. However, the accuracy and usefulness of these tools depend on factors such as sampling techniques, question design, and survey administration. This overview explores the definition of public opinion, types of polls, scientific polling methodologies, and the limitations of public opinion data, emphasizing their significance in understanding political dynamics.
Definition of Public Opinion
- Public opinion encompasses the shared attitudes, preferences, and views held by a group of people regarding issues, candidates, institutions, or public policies. It is commonly assessed through surveys and polls that collect data on the sentiments of specific population segments. In a representative democracy, understanding public opinion is crucial, as it enables elected officials to align their actions with constituent preferences and informs policy development.
- Accurate public opinion surveys can reveal whether a proposed legislation has majority support, identify the leading candidate in an election, or highlight the issues most important to voters. However, the reliability of these surveys hinges on the use of rigorous scientific methods.
Types of Polls
- Polls vary in design and purpose, each tailored to specific objectives. The College Board identifies four key types of scientific polls that students should understand:
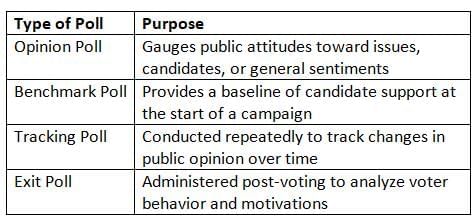
- Opinion polls are the most prevalent, capturing public sentiment on diverse topics. For instance, during discussions on gun control, an opinion poll might indicate whether most Americans favor stricter laws.
- Benchmark polls are typically conducted early in a campaign to help candidates assess their strengths and weaknesses among various voter demographics.
- Tracking polls monitor shifts in public opinion over time, enabling campaigns to evaluate the effectiveness of their strategies or make necessary adjustments.
- Exit polls are conducted immediately after voters leave polling stations, offering insights into why certain candidates were chosen and how different demographic groups voted.
Scientific Polling Methodology
Sampling Techniques
For a poll to accurately reflect the population, it must employ effective sampling methods.
Common techniques include:
- Random sampling: Ensures every individual has an equal probability of being selected.
- Stratified sampling: Divides the population into subgroups (e.g., by race, age, or region) and randomly samples from each to ensure representation.
- Cluster sampling: Segments the population into geographic clusters, with entire clusters randomly chosen for inclusion.
Margin of Error
- Every poll includes a margin of error, which indicates the potential range of uncertainty in the results.
- For example, if a candidate polls at 48% with a ±3% margin of error, their true support could fall between 45% and 51%.
How Questions Affect Poll Accuracy
Even with proper sampling, poorly designed questions can skew results. Pollsters must carefully craft questions and survey structures to ensure accuracy.
Question Type
- Closed-ended questions: Provide a limited set of response options, facilitating analysis and comparisons but potentially missing nuanced perspectives.
- Open-ended questions: Allow respondents to answer freely, offering richer insights but posing challenges for categorization and analysis.
Question Framing
Neutral wording is essential. For instance, asking “Do you support increasing taxes to fund welfare programs?” may elicit a different response than “Do you favor government initiatives to alleviate poverty through social services?”
Question Order
The sequence of questions can impact responses. A provocative question early in the survey might influence how respondents answer subsequent ones. Well-designed polls typically start with neutral, less sensitive questions before moving to more specific or controversial topics.
Survey Methods
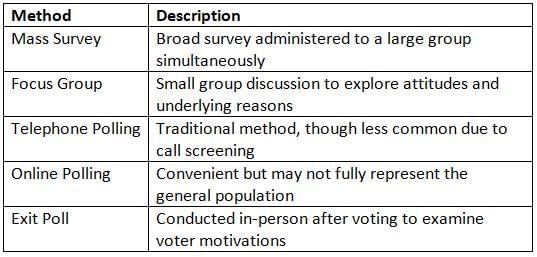
Focus groups, while not statistically representative, are valuable for uncovering the motivations behind opinions and are often paired with larger quantitative surveys.
Limitations of Public Opinion Data
Even well-executed scientific polls face challenges:
- Nonresponse bias: Respondents may differ systematically from non-respondents, skewing results.
- Timing: Public opinion can change quickly, rendering a poll conducted weeks before an election outdated.
- Misreporting: Respondents may provide inaccurate answers due to dishonesty or misunderstanding.
To mitigate these issues, it’s advisable to review multiple polls and focus on consistent patterns rather than relying on a single survey result.
FAQs on Measuring Public Opinion Chapter Notes - AP U.S Government and Politics - Grade 12
| 1. What is public opinion and why is it important in American government? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of polls used to measure public opinion? |  |
| 3. What sampling methods are commonly used in public opinion polling? |  |
| 4. How do the types and formats of questions affect polling results? |  |
| 5. How can public opinion be measured accurately? |  |














