DNA Replication Chapter Notes | Biochemistry - NEET PG PDF Download
Introduction
DNA replication is a very important process that happens in living cells. It is how cells make copies of their DNA so that when they divide, each new cell gets the same DNA. This is really important for passing on genetic information from one generation to the next.
DNA replication is the process of making a copy of the DNA molecule. During this process, the sequence of bases in the parent strand is copied to create the daughter strand, transferring genetic information from parent to offspring.
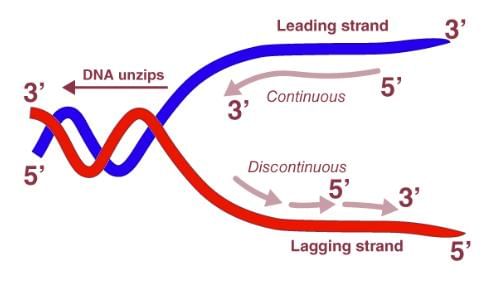
Salient Features of DNA Replication
- Timing: DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, which is when the cell is preparing to divide.
- Strand Separation: The two strands of DNA separate, and each strand serves as a template for synthesizing a complementary strand.
- Base Pairing Rule: The base pairing rule, which states that adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine, is followed during replication.
- Semiconservative Nature: DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning that half of the parent strand is kept in the daughter DNA. This was demonstrated in the Meselson and Stahl experiment.
- Direction of Synthesis: New strands are always made in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- Bidirectional Replication: DNA replication occurs in both directions from the origin of replication.
- Leading Strand: The leading strand is the strand where DNA is continuously synthesized in the same direction as the replication fork.
- Lagging Strand: The lagging strand is the strand where DNA is synthesized in pieces, called Okazaki fragments, in the opposite direction to the replication fork.
Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication
- Topoisomerases: These enzymes relieve the torsional strain that results from the unwinding of DNA by helicase.
- Nicking and Resealing Enzyme: Helicase continuously unwinds DNA, a process powered by ATP.
- Single Strand Binding (SSB) Protein: This protein prevents the premature reannealing of double-stranded DNA during replication.
- DNA Primase: This enzyme synthesizes RNA primers to initiate DNA replication. It acts as a type of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase to start the creation of RNA primers.
- DNA Polymerase: This enzyme catalyzes the process of DNA polymerization, synthesizing DNA only in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- DNA Ligase: This enzyme seals the gap between the new DNA strand and Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
DNA Polymerases
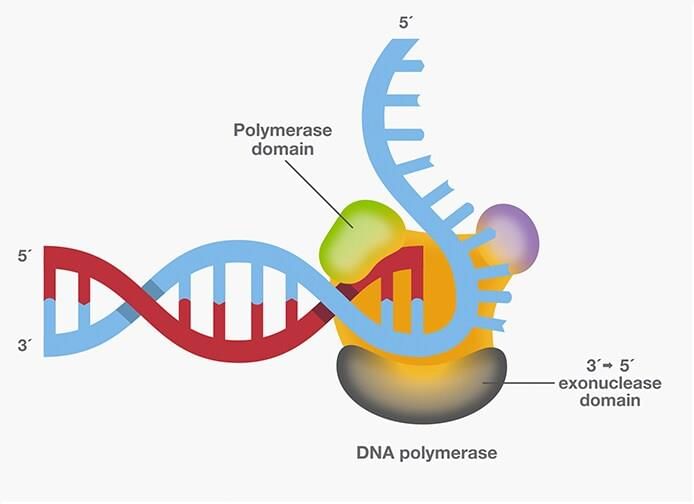
- DNA polymerases are enzymes responsible for synthesizing deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA.
- DNA polymerase requires a short RNA primer to initiate DNA synthesis.
Key Features of DNA Polymerase Complex
- Chain Elongation: Refers to the speed of polymerization, measured in nucleotides per second. DNA Pol III elongates at a rate of 20 to 50 nucleotides per second.
- Processivity: Indicates the number of nucleotides added before the polymerase detaches from the template. DNA Pol III can add from 100 to over 50,000 nucleotides before dissociating.
- Proofreading: Involves identifying and correcting errors during DNA replication. This requires 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity for proofreading and 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity for repair functions.
Prokaryotic DNA Polymerases
In prokaryotes, there are three types of DNA polymerases known as Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III.
Functions of Prokaryotic DNA Polymerase
- Removal of Primers: Prokaryotic DNA polymerase is responsible for removing RNA primers and filling in the gaps on the lagging strand.
- DNA Proofreading: It ensures the accuracy of DNA replication by proofreading the newly synthesized DNA.
- DNA Repair: Prokaryotic DNA polymerase is involved in repairing damaged DNA.
- Recombination: It plays a role in DNA recombination processes.
- Processive Leading Strand Synthesis: DNA polymerase is responsible for continuous leading strand synthesis and the synthesis of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
DNA Sliding Clamp and DNA Polymerase III
- DNA Sliding Clamp: DNA Polymerase III collaborates with two identical β subunits of the DNA sliding clamp. This clamp enhances the stability, processivity, and speed of chain elongation during DNA synthesis.
- Main Replication DNA Polymerase: DNA Polymerase III is the primary enzyme responsible for DNA replication in prokaryotes.
- Highest Rate of Chain Elongation: DNA Polymerase III is the most processive polymerase, meaning it has the highest rate of chain elongation.
- Proofreading Activity: DNA Polymerases I, II, and III possess proofreading activity, ensuring the accuracy of DNA replication.
- Repair Activity: DNA Polymerases I and II are involved in DNA repair processes.
- Gap Filling on Lagging Strand: DNA Polymerase I is responsible for filling gaps on the lagging strand.
- Okazaki Fragment Polymerization: DNA Polymerase III polymerizes Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- Leading Strand Synthesis: DNA Polymerase III is also responsible for synthesizing the leading strand.
- Kornberg’s Enzyme: DNA Polymerase I, discovered by Arthur Kornberg, is referred to as Kornberg’s enzyme.
- Discovery by Arthur Kornberg: Arthur Kornberg identified DNA Polymerase I in Escherichia coli (E. coli).
- Klenow Fragment: The Klenow Fragment is a form of DNA Polymerase I where the 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity has been removed, allowing for more specific applications in molecular biology.
Eukaryotic DNA Polymerase
- There are five main types of Eukaryotic DNA Polymerases:
- DNAP α
- DNAP β
- DNAP γ
- DNAP δ
- DNAP ε
- Eukaryotic DNA polymerase
- DNAP alpha. Initiates DNA synthesis.
- DNAP beta. Involved in DNA repair.
- DNAP gamma. Responsible for mitochondrial DNA synthesis.
- DNAP delta. Synthesizes the lagging strand and is involved in DNA repair.
- DNAP epsilon. Synthesizes the leading strand.
Remember: Eukaryotic DNA Polymerases involved in DNA repair are DNA Polymerase delta (δ) and eta (η).
Steps of DNA Replication
- Identification of the origins of replication. Fixed points on the chromosome where replication begins are called Ori.
- In E. coli. oriC
- In Bacteriophage λ. oriλ
- In Yeast. Autonomous Replicating Sequence (ARS)
- In humans. Similar to Yeast.
- Single ori in bacteria. One origin of replication.
- Multiple ori in eukaryotes. Several origins of replication.
- AT-rich sequence. Adjacent to ori, facilitating DNA unwinding.
- In eukaryotes. ~80 bp AT-rich sequence called DNA UNWINDING ELEMENT (DUE).
- Ori + dsDNA binding Protein (DNA A). Opens the DNA duplex.
- Unwinding (denaturation) of dsDNA. Provides ssDNA template.
- Ori + dsDNA binding protein. Causes local denaturation of DNA.
- Helicase. Further unwinds DNA.
Role of Single Strand Binding Protein (SSB)
- Prevents the re-annealing of the separated DNA strands.
- Human SSBs, such as Replication Protein A (RPA), are a type of SSB.
Formation of the replication fork
- Unwinding of DNA forms a replication bubble.
- A pair of replication forks forms the replication bubble.
- Primase synthesizes a primer of 100–200 ribonucleotides in length.
- Primase (DnaG) is the primase in prokaryotes.
- DNAP α has primase activity in eukaryotes.
Initiation of DNA synthesis and elongation
- Leading Strand. Synthesized continuously on the 3’ hydroxyl end of the RNA primer in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- In prokaryotes by DNA Polymerase III.
- In eukaryotes by DNA Polymerase ε.
- Lagging Strand. Synthesized discontinuously in small fragments called Okazaki Fragments in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
- By DNAP III in prokaryotes.
- By DNAP δ in eukaryotes.
- Length of Okazaki fragments in prokaryotes is 1000 to 2000 nucleotides.
- Length of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes is 100 to 250 nucleotides.
Removal of RNA Primers and gap filling of the lagging strand
- In prokaryotes—Removal of RNA Primer and gap filling by DNA Polymerase I.
- In eukaryotes—RNase H removes the primer.
- DNA P δ fills the gap where RNA Primer is removed.
Sealing the nick following gap filling
- DNA ligase. Seals the single strand nick between the nascent chain and Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- The length of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes is 100 to 250 nucleotides.
- The time required for replication in bacteria is approximately 30 minutes.
- The time taken for replication of the entire human genome is 9 hours.
Replisome
- Multimeric proteins that assemble in the replication fork are called Replisome.
- It includes: DNA helicase, Single-strand binding proteins.
Primosome
- Mobile complex between helicase and primase.
Telomeres and Telomerase
- At the 5’ end of the newly formed linear DNA, the RNA primer is removed by an enzyme known as RNase H.
- This removal creates a gap at the 5’ end of the daughter strand, resulting in incomplete synthesis.
- Essentially, the 3’ end of the leading strand is left unconstructed, leading to a gradual shortening of DNA with each cell division.
- To prevent this shortening, structures called telomeres and the enzyme telomerase are present.
Telomeres
- Telomeres are protective structures located at the ends of chromosomes.
- They are composed of short repetitive sequences, specifically T-G repeats.
- In humans, telomeres consist of a variable number of repeats of the sequence 5’ TTAGGG-3’.
Telomerase (Telomere Terminal Transferase)
- Telomerase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in preventing the shortening of DNA.
- It contains an RNA component that acts as a template for DNA synthesis.
- The enzyme exhibits Reverse Transcriptase activity, which is also known as RNA Dependent DNA Polymerase activity.
- Telomerase is primarily found in germline cells, stem cells, and a majority of cancer cells.
- However, it is typically absent in most somatic cells.
Clinical Significance of Telomerase
- The absence of telomerase is associated with premature ageing.
- In contrast, cancer cells often exhibit increased telomerase activity.
- Telomere shortening is linked to both ageing and malignancy.
- As a result, telomerase has become a target for cancer chemotherapy and drug development.
- Temin and Baltimore discovered telomerase in 1970, identifying it as an RNA Dependent DNA Polymerase.
- These polymerases synthesize new DNA strands using RNA as a template, reversing the central dogma of molecular genetics.
- This mechanism is crucial for RNA viruses, particularly retroviruses.
- Telomerase, with its reverse transcriptase activity, plays a similar role.
DNA Repair Mechanisms
DNA encounters various chemical, physical, and biological threats daily. Repairing damaged DNA is crucial for maintaining the integrity of our genetic material and preventing the propagation of mutations. Eukaryotic cells have five primary mechanisms for repairing DNA.
The mechanisms of DNA repair include:
- Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
- Mismatch Repair (MMR)
- Base Excision Repair (BER)
- Homologous Recombination (HR)
- Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ)
The following are known agents that can damage DNA:
- Ionising Radiations
- X-rays
- Anti-tumour drugs
Defects in DNA repair mechanisms:
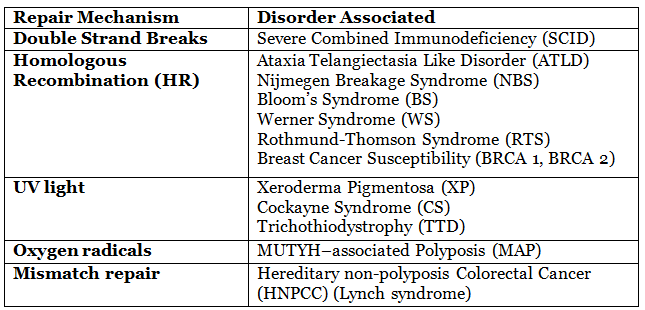
Double Strand Break Repair Mechanisms (DSB)
- Homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) are two key methods for repairing DSBs.
- Non-homologous end joining is a major way to fix DSBs in yeast.
- This method is also a primary means of DSB repair in mammals.
- This process occurs without needing homologous chromosomes.
- This repair mechanism takes place before the cell enters mitosis during the S and G2/M phases.
- This process also occurs before the cell enters mitosis in the G0/G1 phase.
|
50 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on DNA Replication Chapter Notes - Biochemistry - NEET PG
| 1. What is DNA replication and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the three important properties of DNA Polymerase Complex? |  |
| 3. What are the main mechanisms of DNA repair? |  |
| 4. How does DNA replication differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? |  |
| 5. What role do helicase and ligase play in DNA replication? |  |




















