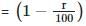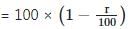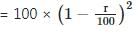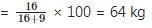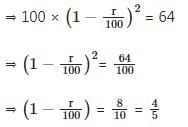Important Formulas: Alligation & Mixture | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
Mixtures and Alligation is an important concept in Quantitative Aptitude that deals with blending two or more ingredients having different characteristics, such as price, concentration, or quantity, and finding the ratio or average value of the resulting mixture.

What are Mixtures & Alligations?
- A Mixture is a combination of two or more substances (like milk & water, or different rice qualities) where they retain their individual properties.
- Alligation is a shortcut rule to find the ratio in which two or more ingredients are mixed to obtain a mixture of a desired mean value (price, % concentration, etc.).
- To solve mixture and alligation problems, you need to understand that alligation helps find the average value of a mixture when the ratio and quantity of the ingredients mixed are different.
- It also helps figure out the proportion in which the elements are mixed.

Types of Mixtures
- Simple Mixtures:- When two or more different ingredients are mixed, a simple mixture is formed. The sums based on simple mixtures are pretty easy to solve. For example,
Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals. Alloys are simple mixtures. - Compound Mixtures:- When two or more simple mixtures are mixed, a compound mixture is formed. Hence, more ratios need to be calculated while solving the sum of complex mixtures. For example,
When two metal alloys made from a combination of different elements are mixed, it leads to the formation of a complex mixture.
Rules of Alligation
- The rule of alligation helps in finding the ratio in which two or more ingredients (having different prices, percentages, or concentrations) must be mixed to obtain a mixture of a desired mean value. There are two common approaches to apply this rule:
Method 1: Formula Method
- It is given as:

- This rule can also be applied when a cheaper substance is mixed with an expensive substance.
- Example:Two types of wheat are sold at ₹45 per kg and ₹60 per kg. If a shopkeeper wants to make a mixture worth ₹54 per kg, what should be the ratio of the two types of wheat?
Ans: 2:3
Sol: Using the Formula, we get
(60 − 54) : (54 − 45) = 6 : 9 = 2 : 3
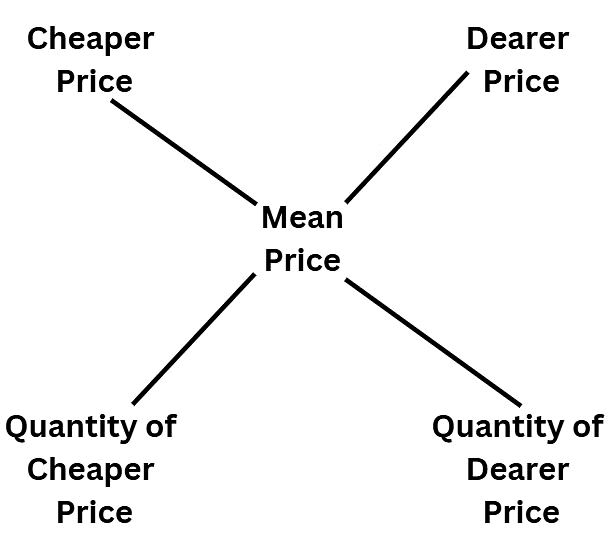
Method 2: Diagram Method
- The above method can be expressed using a diagram, which will be more convenient to understand-
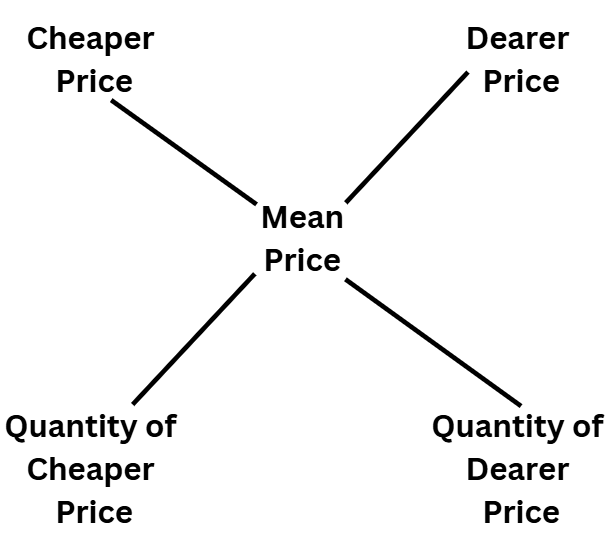
- The working of this formula is
Step 1: We take the positive difference of the mean price and the cheaper price and write the difference in the place of the Quantity of the dearer price.
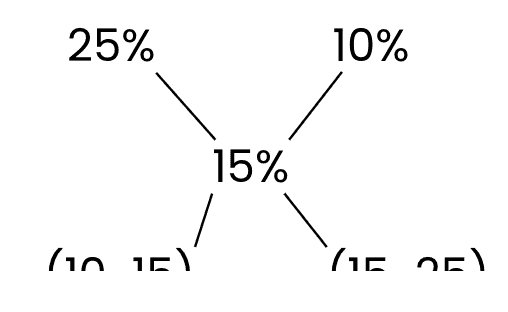
Step 2: Similarly, take the positive difference of the mean price and the dearer price and write the difference in the place of the Quantity of the cheaper price. - Example: How many litres of pure water should be added to 40 litres of 30% milk solution so that the resultant mixture is a 15% milk solution?
Sol: Taking milk as the common element in both solutions, we have 30% milk in the first and 0% milk in the second solution (i.e. pure water). On mixing them, we got 15% milk in the final solution. Therefore,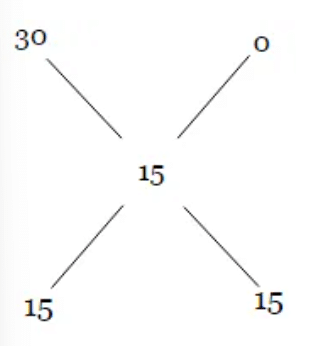 Or the ratio of the quantity of first and second solution should be 15:15 = 1:1
Or the ratio of the quantity of first and second solution should be 15:15 = 1:1Hence, 40 litres of pure water should be mixed to get the desired new solution.
[Question: 1805643]
Alligation: Reverse Weighted Average
- It is the reverse of weighted average; i.e. if the averages of two groups are separately given and the average of the whole group is given, then we can find out the ratio between the groups.
- For example, If the average weight of the boys in the class is 60 and the average weight of the girls in the class is 40 and average weight of the whole class is 52. Find the ratio between boys and the girls.
Sol: Average weight of boys = 60,
Average weight of girls = 40 and
Average weight of the whole class = 52
The data can be represented in an Alligation chart as given below and use it to find the ratio between the number of boys and girls in the class.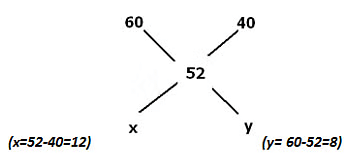 Take the difference across: x = 60-52 = 8 and y = 52-40 = 12.
Take the difference across: x = 60-52 = 8 and y = 52-40 = 12.
That is how we get the ratio between the boys and girls as 12:8 or 3:2.
Successive Replacement in Mixtures
This concept applies when a fixed quantity is repeatedly removed from a container and replaced with another substance (usually water). The key is that the replacement is done with the same volume each time.
Formula:
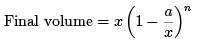
Where:
- x: Initial quantity
- a: Quantity replaced each time
- n: Number of replacements
Each time we remove and replace, the fraction of the original substance decreases multiplicatively, not linearly.
Example: A container has 40 litres of milk. 8 litres are removed and replaced with water, and this process is repeated twice. Find the final quantity of milk.
Sol: 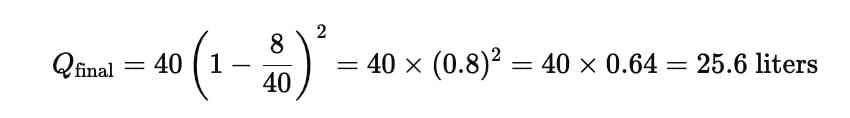
So, after two successive replacements, 25.6 litres of milk remain.
Important Formulae: A Quick Revision
As we have studied in this chapter, these are the following important formulas:
1.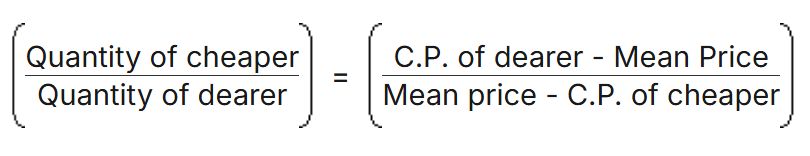
It is also called the rule of alligation and can also be represented as
2. 
3. Replacement (Same Quantity)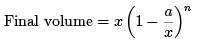
Where:
- x: Initial quantity
- a: Quantity replaced each time
- n: Number of replacements
Solved Examples
Example 1: A mixture P is formed by removing a certain amount of coffee from a coffee jar and replacing the same amount with cocoa powder. The same amount is again removed from mixture P and replaced with same amount of cocoa powder to form a new mixture Q. If the ratio of coffee and cocoa in the mixture Q is 16 : 9, then the ratio of cocoa in mixture P to that in mixture Q is [CAT 2023]
(a) 4 : 9
(b) 1 : 3
(c) 1 : 2
(d) 5 : 9
Ans: (d)
Let the initial quantity of coffee in the jar be 100 kg and r kg is replaced each time.
Since r kg out of 100 kg is removed, fraction of coffee removed = r/100
∴ fraction of coffee remaining
⇒ Quantity of coffee remaining after first replacement
And quantity of cocoa after first replacement = r kgs.
⇒ Similarly, quantity of coffee remaining after second replacement
Now, after 2nd replacement coffee and cocoa are in the ratio of 16 : 9
⇒ Quantity of coffee left after 2nd replacement
⇒ r = 20 kg
∴ 20 kg of cocoa is added after 1st replacement.
Also, quantity of cocoa after 2nd replacement
= 100 – 64 = 36 kgs
⇒ Required ratio = 20 : 36 = 5 : 9.
Hence, option (d).
Example 2: Anil mixes cocoa with sugar in the ratio 3 : 2 to prepare mixture A, and coffee with sugar in the ratio 7 : 3 to prepare mixture B. He combines mixtures A and B in the ratio 2 : 3 to make a new mixture C. If he mixes C with an equal amount of milk to make a drink, then the percentage of sugar in this drink will be [CAT 2023]
(a)21
(b)17
(c)16
(d)24
Ans: (b)
Let 20 kgs and 30 kgs of A and B are mixed.
∴ Amount of sugar in C = 2/5 × 20 + 3/10 × 30 = 17 kgs
Now we have 50 kgs of C mixed with 50 kgs of milk, i.e., 100 kgs of final solution.
⇒ Concentration of sugar in final solution = 17/(50 + 50) × 100% = 17%
Hence, option (b).
Example 3: A mixture contains lemon juice and sugar syrup in equal proportions. If a new mixture is created by adding this mixture and sugar syrup in the ratio 1 : 3, then the ratio of lemon juice and sugar syrup in the new mixture is [CAT 2022]
(a)1 : 4
(b)1 : 6
(c)1 : 5
(d)1 : 7
Ans: (d)
Let 10 units of mixture is mixed with 30 units of sugar syrup.
Amount of sugar syrup in 10 units of mixture = 5 units
Amount of lemon juice in 10 units of mixture = 5 units
∴ Total amount of lemon juice in the final mixture = 5 units, and
Total amount of sugar syrup in the final mixture = 5 + 30 = 35 units
Ratio of lemon juice and sugar syrup in final mixture = 5 : 35 = 1 : 7.
Hence, option (d).
Example 4: There are two containers of the same volume, first container half-filled with sugar syrup and the second container half-filled with milk. Half the content of the first container is transferred to the second container, and then the half of this mixture is transferred back to the first container. Next, half the content of the first container is transferred back to the second container. Then the ratio of sugar syrup and milk in the second container is [CAT 2022]
(a) 5 : 6
(b) 4 : 5
(c) 5 : 4
(d) 6 : 5
Ans: (a)
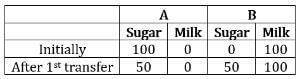
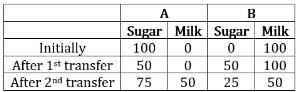
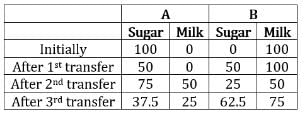
Let container A initially have 100 liters of sugar while container B have 100 liters of milk.Now the second container has sugar and milk in the ratio of 1 : 2.
When half i.e., 75 liters of it is transferred, 25 liters of sugar and 50 liters of milk will be transferred.Now the first container has sugar and milk in the ratio of 3 : 2.
When half i.e., 62.5 liters of it is transferred, 37.5 liters of sugar and 25 liters of milk will be transferred.
∴ Ratio of sugar and milk in 2nd container = 62.5 : 75 = 625 : 750 = 25 : 30 = 5 : 6
Hence, option (a).
Example 5: A glass contains 500 cc of milk and a cup contains 500 cc of water. From the glass, 150 cc of milk is transferred to the cup and mixed thoroughly. Next, 150 cc of this mixture is transferred from the cup to the glass. Now, the amount of water in the glass and the amount of milk in the cup are in the ratio [CAT 2022]
(a) 10 : 13
(b) 10 : 3
(c) 3 : 10
(d) 1 : 1
Ans: (d)
When two containers contain equal amount of milk and water respectively and then equal amounts are transferred from 1st to 2nd and then from 2nd to 1st.
The amount of milk in 1st becomes equal to amount of water in 2nd while amount of water in 1st becomes equal to amount of milk in 2nd.
Hence, option (d).
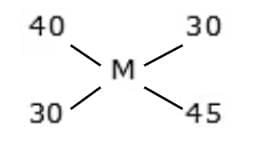
Example 6: A shopkeeper mixes 30 kg of type A rice at Rs.40/kg and 45 kg of type B rice at Rs.30/kg, then finds the price of a formed mixture of rice.
Sol:
By the rule of alligation:
(30 – M): (M – 40) = 30: 45 = 2: 3
90 – 3M = 2M – 805M = 170M = 34
Hence, price of mixture = Rs.34/kg
Note: After applying the concept of alligation on the price of the item of concentration of mixture we will get the ratio in which these two items or mixture are mixed.
Sol: Water percent in mixture A = 100% – 75% of 25%
By the rule of alligation:Required ratio = -5: -10
= 1: 2
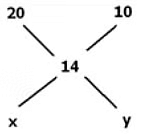
Example 8: In what ratio should a shopkeeper mix two types of rice, one costing 20 rupees/kg and another costing 10 rupees/kg to get a rice variety costing 14 rupees/kg?
Sol: Here also we can use Alligation as follows:
x = 14-10 = 4
y = 20-14 = 6
The ratio between the type 1 and type 2 rice is 4:6 or 2:3
|
167 videos|229 docs|95 tests
|