The Story of Human Evolution Chapter Notes | Social Studies Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Human Evolution? |

|
| Different Stages of Human Evolution |

|
| Sources/Evidences of Human Evolution |

|
| Life of Early Humans |

|
| Points To Remember |

|
| Glossary |

|
Introduction
This chapter tells us how humans came to be what they are today. It explains how humans slowly changed over millions of years from ape-like ancestors. We will learn about the stages of human evolution, the evidence that helps us understand it, and how early humans lived.
What is Human Evolution?
- Evolution is how living things change over time from older forms to newer forms.
- Human evolution is how modern humans came from ape-like ancestors.
- Scientists think humans and apes had a common ancestor who lived in Africa about 6 million years ago.
- Humans slowly changed over millions of years through different stages, which is called human evolution.
Fun Fact
- The study of human evolution is called palaeoanthropology.
- Hominids is a term used for all early human ancestors.
Different Stages of Human Evolution
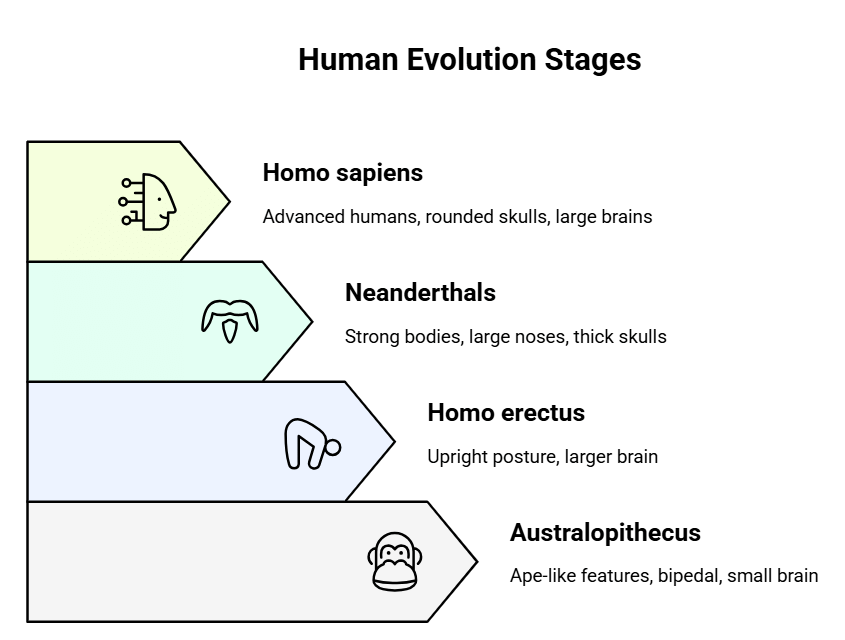
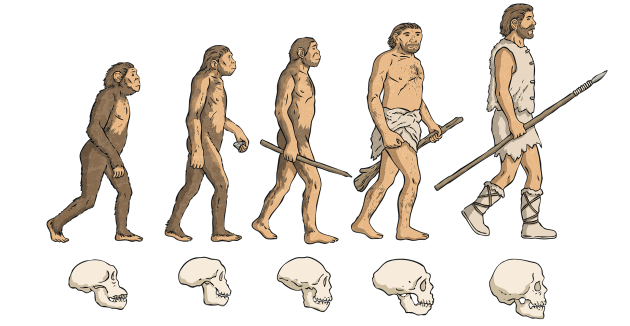
- Australopithecus: They had both human and ape-like features, walked on two legs (bipedal), but had smaller brains, longer arms, and small brains like apes.
- Homo erectus (the upright man): They were of medium height, could stand and walk straight, unlike their ancestors, and had a larger brain than Australopithecus.
- Homo neanderthalensis (Neanderthals): They looked a bit like modern humans but had shorter, stronger bodies, larger and wider noses, thicker skulls, and less rounded heads at the top, with a brain size similar to modern humans.
- Homo sapiens: They are the most advanced humans, with smaller teeth, a more defined chin, rounded skulls, and larger brains compared to earlier stages.
Sources/Evidences of Human Evolution
Archaeologists, scientists, and historians use different sources like fossils, bones, cave paintings, tools, and utensils to learn about human evolution.
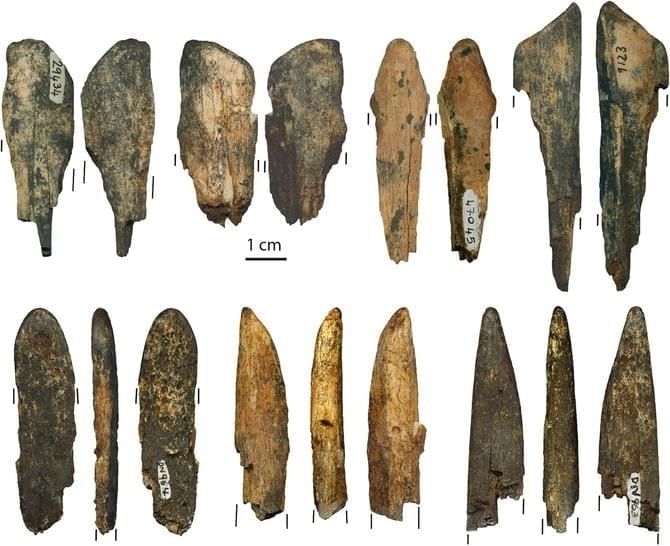

Fossils and Bones
- Fossils and bones are the main evidence used by scientists and archaeologists to study human evolution.
- They are remains of early humans found under the earth and have hardened over time.
- The study of fossils is called palaeontology, and people who study fossils are called palaeontologists.
Cave Paintings
- Early humans made paintings on cave walls in places like Bhimbetka in India and El Castillo in Spain.
- These paintings show human and animal figures, using colors made from rocks and minerals available back then.
- The paintings help us learn about the animals early humans domesticated and how they hunted.
Tools and Utensils
- Archaeologists found many tools and utensils from the prehistoric period made of stone, wood, bones, and animal horns.
- Early humans used these to cut meat and bone, remove animal skins, and chop fruits, roots, and tree bark.
- Some tools might have been attached to handles of bone or wood to make spears and arrows for hunting.
Fun Fact
The oldest human fossil, named "Lucy," was found in 1974 by Donald C. Johanson in Hadar, Ethiopia, and is dated to be more than 3.2 million years old.
Life of Early Humans
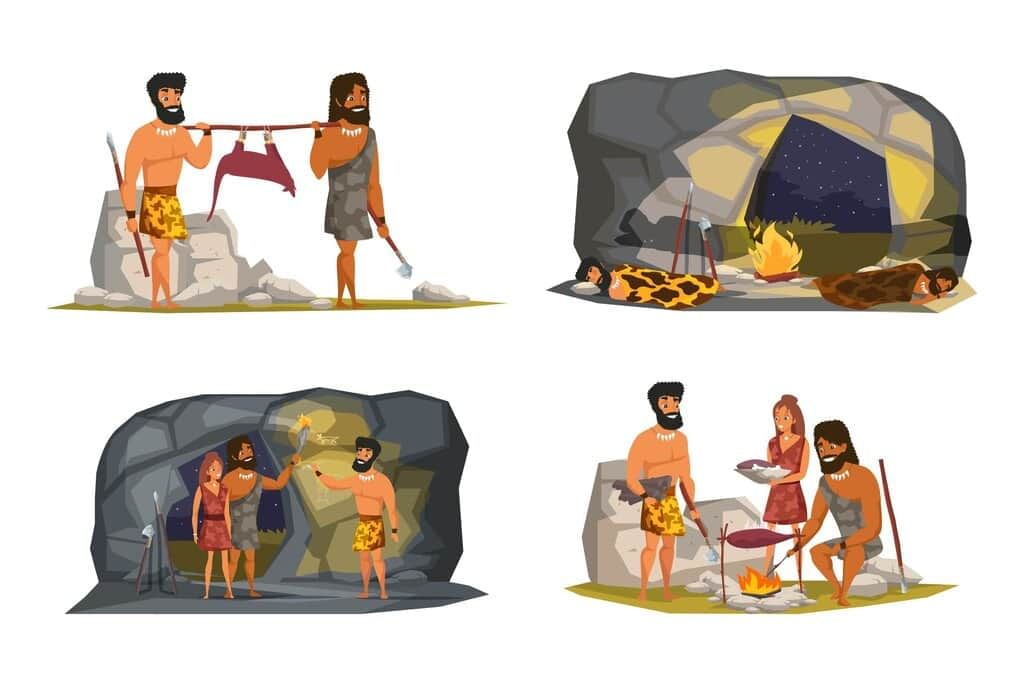

- Early humans lived a nomadic life, moving from place to place to find food and shelter.
- They were hunters and gatherers, hunting wild animals and birds, and collecting fruits, roots, nuts, seeds, and eggs for food.
- They used sharpened stones for hunting and digging roots from the ground.
- They did not wear clothes and lived in treetops or caves.
- Over time, they learned to make better tools, which made hunting easier.
Fun Fact
- Charles Darwin was an English naturalist known for his work on the theory of evolution.
- He believed all species in the world evolved over millions of years from a common ancestor.
Points To Remember
- Human beings first appeared on Earth about 6 million years ago.
- Humans evolved slowly from one stage to another, which is called human evolution.
- Scientists believe humans and apes share a common ancestor.
- Humans went through various stages of evolution until they reached their current form.
- Historians and archaeologists use fossils, bones, utensils, cave paintings, and tools to study human evolution.
- Palaeontology is the study of fossils, and people who study fossils are called palaeontologists.
- Early humans lived a nomadic life as hunters and gatherers.
Glossary
- Ancestor: A forefather, someone from whom a person comes.
- Stature: A person’s natural height.
- Erect: Standing straight.
- Stocky: Having a broad and strong build.
- Prehistoric period: The time in human history when there were no written records.
- Hunters and gatherers: People who search for food by hunting animals and collecting fruits, seeds, and other natural items.
- Nomads: People who move from one place to another and do not stay in one place permanently.
- Naturalist: A person who studies nature.
|
88 docs|20 tests
|
FAQs on The Story of Human Evolution Chapter Notes - Social Studies Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What are the main stages of human evolution? |  |
| 2. What sources of evidence do scientists use to understand human evolution? |  |
| 3. What were some major developments in human evolution? |  |
| 4. What was the life of early humans like? |  |
| 5. What are some interesting facts about human evolution for Class 5 students? |  |















