Interdependence of Living Beings - Plants and Animals Chapter Notes | Science Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Interdependence in living beings |

|
| Food Chain |

|
| Balance in Nature |

|
| Causes of imbalance in nature |

|
| Protecting the balance of nature |

|
| Points To Remember |

|
| Glossary |

|
Introduction
The chapter "Interdependence of Living Beings — Plants and Animals" explains how plants, animals, and other living things depend on each other to survive in nature. It talks about how living beings like plants and animals work together with non-living things like air, water, and sunlight to stay alive. The chapter also describes how plants make food, how animals eat plants or other animals, and how some living things clean the environment by breaking down dead matter. It highlights the importance of keeping a balance in nature and how human activities can disturb this balance, along with ways to protect it.

Our surrounding is also known as our environment
- Our environment includes all living things like plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as non-living things like air, water, sunlight, and soil.
- All living things depend on each other and on non-living things to survive.
- For example, plants need sunlight, air, water, and soil to grow, while animals need plants or other animals for food.
- At the same time, living things also depend on each other for survival.
Interdependence in living beings
- Living beings like plants, animals, and microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi depend on each other for survival.
- Plants need carbon dioxide from air, water, and nutrients from soil to make their food through a process called photosynthesis.
- In photosynthesis, plants use sunlight to make food and release oxygen into the air.
- Oxygen is very important for animals to breathe and stay alive.
- Animals breathe in oxygen and release carbon dioxide, which plants use to make more food.
- Plants also give shelter and food to many ANIMALS.
- Animals help plants by spreading their seeds to grow new plants.
- When animals die, their bodies are broken down by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi, which helps clean the environment.
- Living beings can be divided into three main groups based on their roles: producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Plants as producers
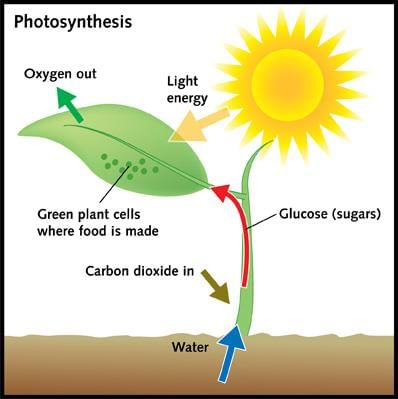
- Producers are living things that can make their own food.
- Green plants are called producers because they make their food through photosynthesis.
- In photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to make food, and they also release oxygen.
- Plants store this food in their roots, stems, and leaves.
- Humans and animals depend on plants for food and oxygen to survive.
Animals as consumers
- Consumers are living things that eat food made by producers like plants, or they eat other animals.
- All animals and humans are consumers because they cannot make their own food.
- Consumers are also called heterotrophs (hetero means other, troph means nourishment).
- Consumers can be divided into four types based on what they eat: herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and scavengers.
- Herbivores are animals that eat only plants. Examples include cows, elephants, rabbits, goats, and sheep.
- Carnivores are animals that eat only meat. Examples include lions, tigers, owls, foxes, and snakes.
- Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. Examples include bears, squirrels, and humans.
- Scavengers are animals that eat dead plants and animals, helping to clean the environment. Examples include jackals, crows, and vultures, which eat dead animals, and termites, which eat dead plants.
Decomposers
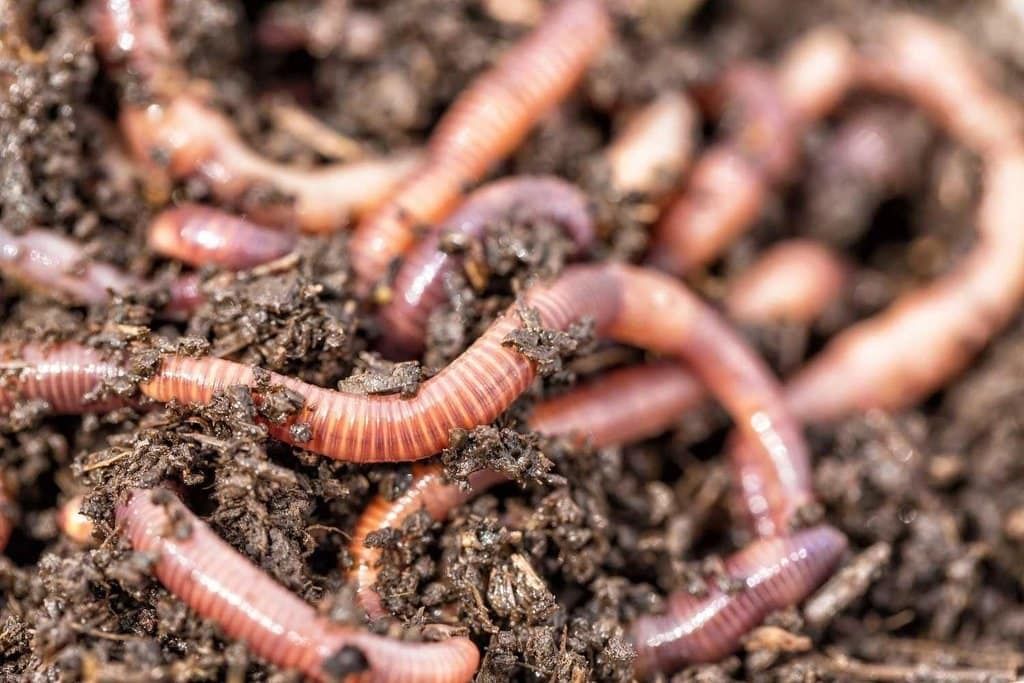

- Decomposers are living things like bacteria and fungi that break down the wastes and dead remains of plants and animals.
- They help return important nutrients to the soil, which plants use to grow.
- Without decomposers, the soil would not have enough nutrients for plants to grow properly.
- Producers, consumers, and decomposers are all interdependent, which means they need each other to survive on Earth.
Food Chain
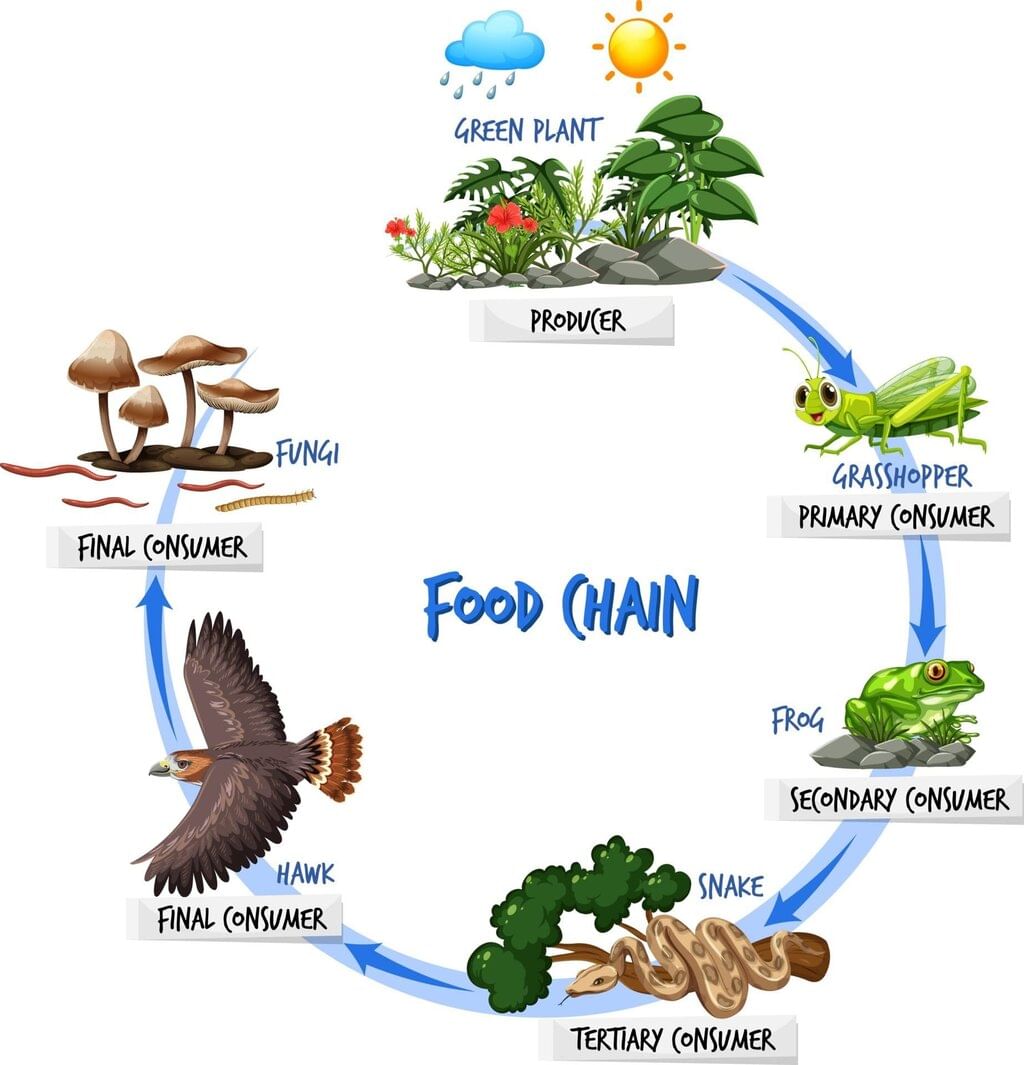
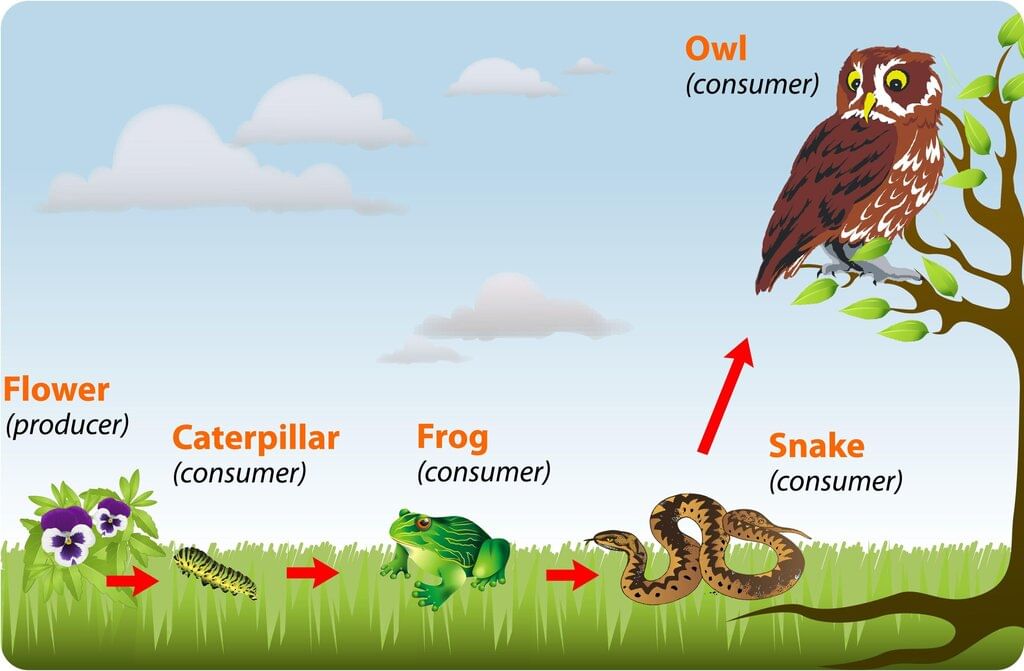
- A food chain shows how living beings depend on each other for food.
- It is a series of organisms where one organism eats another for food.
- A food chain starts with producers like plants, which make their own food.
- Plants are eaten by animals, and those animals may be eaten by bigger animals.
- Decomposers are the last stage of the food chain because they break down dead plants and animals.
Some examples of food chain
- Example 1: Fish eat sea weeds, and then humans eat fish.
- Example 2: Corn is eaten by a rat, the rat is eaten by a snake, and the snake is eaten by an eagle.
- On a larger scale, we can see how producers (plants), consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores), and decomposers work together in a food chain.
Balance in Nature

- Food chains and the interdependence of living beings help maintain a balance in nature.
- This balance is important for the survival of all living things.
- Any change in the food chain can disturb this balance and affect all living beings.
- For example, if many snakes are killed, rats will increase in number because there are fewer snakes to eat them.
- More rats can lead to more eating of crops, which may cause a shortage of food for humans and other animals.
- This shows how disturbing one part of the food chain can lead to big problems like starvation or death.
Causes of imbalance in nature
Imbalance in nature happens because of natural reasons or human activities.
Natural factors
Natural factors can cause imbalance in nature for a short time, but nature can fix itself when the situation improves.
- Flood: Too much rain can cause floods in an area, which can destroy plants and animals on a large scale.
- Forest fire: Forest fires can happen due to dry conditions or lightning strikes, killing many plants and animals in the forest.
- Drought: If there is no rain for a long time, it causes drought, which leads to the drying up of water bodies and the death of plants and animals.
Man-made causes
Human activities cause long-term imbalance in nature, which is hard to fix.
- Cutting of trees: Humans cut down trees on a large scale to get wood, like sandalwood in South India or teak for furniture.
- Forests are cleared for farming, building houses, and factories.
- Humans also cause forest fires and cut down many types of trees, which destroys animal habitats.
- Animals cannot survive without their homes and may die in forest fires.
- Fewer trees also increase carbon dioxide in the air, leading to less rain and higher temperatures.
- Cutting trees disturbs the balance of nature by affecting producers.
- Increasing number of industries and vehicles: Forests are cleared to build industries, which release harmful gases that pollute the air.
- Without enough trees, the air cannot be cleaned properly.
- Industries also release harmful chemicals and waste into water, polluting it and killing marine animals.
- Water pollution also harms human health.
- Vehicles on the roads release harmful gases and smoke, adding to air pollution and causing noise pollution.
- Hunting: Humans capture and kill animals for food, sports, or money.
- Many animals are hunted for their body parts, like rhinos for their horns, elephants for their tusks, tigers for their skin, and other animals for their paws.
- Hunting has reduced the number of these animals, disturbing the food chain and causing imbalance in nature.
- Use of plastic: Plastic is very common now, but it does not break down easily and stays in the soil for a long time.
- Since plastic cannot be broken down by decomposers, the soil loses nutrients, and plants cannot grow properly.
- Without enough plants, there is a lack of food for animals, which disturbs the entire food chain and balance of nature.
Protecting the balance of nature
- To help all living beings survive, we need to protect the balance of nature.
- Here are some steps to reduce the harmful effects of human activities:
- Plant more trees. For every tree cut down, plant three new trees in its place.
- Recycle and reuse materials like newspapers, plastic bottles, and aluminum cans.
- Save water and electricity to reduce waste.
- Do not kill animals for their products, and avoid buying things made from animal parts.
- Manage industrial wastes carefully to prevent water and land pollution.
Did you know?
When decomposers act on waste and dead matter, they break them into simpler substances. This process is called decomposition.
Points To Remember
- Our environment includes all living and non-living things around us.
- Living beings are divided into three categories: producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- Producers or autotrophs make their own food, like green plants.
- Consumers or heterotrophs eat food made by producers and are divided into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and scavengers.
- Decomposers break down dead remains of plants and animals.
- A food chain shows how one organism depends on another for food.
- Food chains and interdependence of living beings maintain balance in nature.
- Balance in nature can be disturbed due to natural factors and human activities.
- Natural factors include floods, forest fires, and droughts.
- Human activities include cutting trees, industrial pollution, and use of plastic.
- Planting more trees, recycling, reusing materials, and saving water and electricity are some ways to maintain the balance of nature.
Glossary
- Producers/Autotrophs: Living things that can make their own food, like green plants.
- Consumers/Heterotrophs: Organisms that eat food made by producers, like animals and humans.
- Herbivores: Consumers who eat only plants, like cows and rabbits.
- Carnivores: Consumers who eat only meat, like lions and tigers.
- Omnivores: Consumers who eat both plants and animals, like humans and bears.
- Scavengers: Consumers who feed on dead plants and animals, like vultures and jackals.
- Decomposers: Organisms that break down dead remains of plants and animals, like bacteria and fungi.
- Food: Overflow of a large amount of water in an area, causing destruction.
- Drought: Lack of rain for a long time, leading to drying of water bodies.
|
48 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Interdependence of Living Beings - Plants and Animals Chapter Notes - Science Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What is the food chain and why is it important in nature? |  |
| 2. How does interdependence among plants and animals contribute to ecological balance? |  |
| 3. What are some common causes of imbalance in nature? |  |
| 4. What steps can we take to protect the balance of nature? |  |
| 5. Why is it essential for students to learn about the interdependence of living beings? |  |















