Light and Shadows Chapter Notes | Science Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Light |

|
| Shadow |

|
| Rotation and Revolution of Earth |

|
| Formation of Day and Night |

|
| Eclipse |

|
| Terms to Know |

|
| Points To Remember |

|
Introduction
This chapter teaches us about light and how it helps us see things around us. We will learn what light is, where it comes from, and how it behaves with different objects. We will also explore shadows, how they are formed, and why they change during the day. The chapter explains the rotation and revolution of the Earth, which cause day and night, and introduces us to eclipses, which happen when the sun, moon, and Earth align in special ways.
Light

- Light is a type of energy that helps us see objects around us.
- The Sun and stars are natural sources of light because they produce their own light.
- Some living things, like fireflies, glow-worms, and lantern fish, can also produce their own light.
- Objects that produce their own light are called luminous objects.
- Humans have made sources of light, such as bulbs, tube lights, torches, and candles, which are called artificial sources of light.
- Things that do not produce light on their own, like a chair or a table, can be seen only when light falls on them.
- Objects that do not produce light but can be seen when light falls on them are called non-luminous objects.
- We cannot see objects in the dark because there is no light to make them visible.
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque Objects
Objects can be classified into three types based on how light passes through them: transparent, translucent, and opaque.

- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them completely, so we can see things clearly on the other side.
- Examples of transparent objects are glass, air, and water.
- For example, we can see through a glass window because it is transparent.
- Translucent objects allow only some light to pass through, so we see a blurred or unclear image through them.
- Examples of translucent objects are butter paper, smoked glass, and colored glass.
- For example, if we look through colored glass, we see a blurry picture because only partial light passes through.
- Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them, so we cannot see through them at all.
- Examples of opaque objects are wood, brick walls, and books.
- For example, we cannot see through a brick wall because it blocks all the light.
Shadow
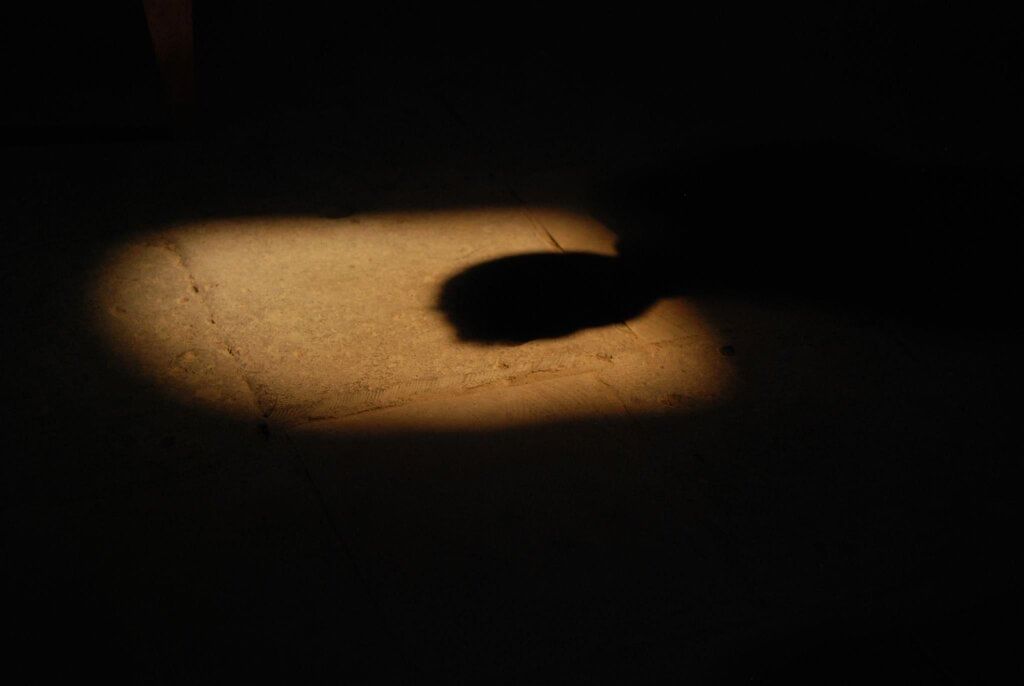

- A shadow is a dark shape formed when light falls on an opaque object and gets reflected.
- The dark shape appears on the surface on the other side of the object.
- For example, when sunlight falls on our body, our shadow forms on the ground on the opposite side of the light.
- Shadows are a natural thing that happens when light is blocked.
Conditions for the Formation of a Shadow
Three things are needed to form a shadow:
- A source of light, like the sun or a torch.
- An opaque object that blocks the light’s path.
- A screen or surface where the shadow can form, like a wall or the ground.
- Transparent objects do not form shadows because light passes through them completely.
- Translucent objects form a light shadow because some light passes through them.
Characteristic Features of the Shadow
- A shadow forms only when there is a source of light.
- The shadow always forms on the opposite side of the light source, in the area where light cannot reach.
- The shadow is always black in color, no matter the color of the object or the light.
- The size of the shadow changes depending on how far the object is from the light source.
- The shadow becomes larger when the object is closer to the light source.
- The shadow becomes smaller when the object is farther from the light source.
- The position of the shadow changes if the position of the light source changes.
Formation of Shadow at Different Times of the Day
- Shadows form only when there is a light source, so they cannot be seen in a dark room or at night.
- During the day, the Sun is the source of light, and its position changes, affecting the shadow.
- In the early morning and late evening, when the Sun is near the horizon, the shadow of an object is long.
- At midday, when the Sun is overhead, the shadow becomes shorter.
- The changing length and position of the shadow happen because of the Earth’s rotation.
Rotation and Revolution of Earth
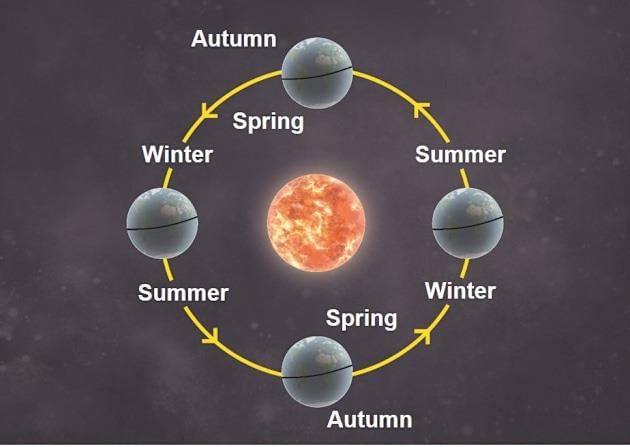
The Earth has two types of movements: rotation and revolution.
- An imaginary line running through the center of the Earth is called its axis.
- Rotation is the movement of the Earth on its axis, which takes 24 hours to complete one full turn.
- Rotation causes day and night; one half of the Earth faces the Sun and has day, while the other half is away from the Sun and has night.
- Revolution is the movement of the Earth around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit.
- The Earth takes 365¼ days to complete one revolution around the Sun, which makes one year.
- The revolution of the Earth is responsible for the change in seasons throughout the year.
Formation of Day and Night
- Day and night happen because of the Earth’s rotation on its axis.
- It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one rotation.
- The half of the Earth facing the Sun has day because it gets sunlight.
- The other half of the Earth, which is away from the Sun, has night because it does not get sunlight.
Eclipse
- An eclipse happens when the Sun’s light is blocked by either the Earth or the Moon.
- It occurs when the Sun, Moon, and Earth align in a special way, either partially or completely blocking the light.
- There are two types of eclipses: solar eclipse and lunar eclipse.
- A solar eclipse happens when the Moon blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Earth.
- A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Moon.

Solar Eclipse
- A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth.
- The Moon blocks the Sun’s light and casts its shadow on the Earth’s surface.
- When the Moon completely covers the Sun, it is called a total solar eclipse.
- In a total solar eclipse, the Sun, Moon, and Earth are in a straight line, fully blocking the Sun’s light.
- When the Moon covers only a part of the Sun, it is called a partial solar eclipse.
- A solar eclipse lasts for only a few minutes because the Moon moves quickly.
- Looking at a solar eclipse with the naked eye can harm your eyes, so special glasses are needed to watch it safely.
Lunar Eclipse
- A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon.
- The Earth blocks the Sun’s light, casting its shadow on the Moon.
- When the Earth’s shadow completely covers the Moon, it is called a total lunar eclipse.
- When the Earth’s shadow covers only a part of the Moon, it is called a partial lunar eclipse.
- A lunar eclipse can last up to one and a half hours because the Earth’s shadow is larger.
- It is completely safe to watch a lunar eclipse with the naked eye as it does not harm your eyes.
Did You Know?
Looking at a solar eclipse without special glasses can harm your eyes.
Terms to Know
- Luminous Objects: Objects that produce their own light, such as the Sun, stars, and fireflies.
- Non-Luminous Objects: Objects that do not produce their own light but can be seen when light falls on them, like a chair, table, or book.
- Transparent Objects: Objects that allow light to pass through them completely, so we can see through them clearly, such as glass, air, and water.
- Opaque Objects: Objects that do not allow light to pass through them at all, so we cannot see through them, like wood, brick walls, and books.
- Translucent Objects: Objects that allow only some light to pass through, so we see a blurred image through them, like butter paper, smoked glass, and colored glass.
- Axis: An imaginary line running through the center of the Earth, around which the Earth rotates.
- Rotation: The circular movement of the Earth on its axis, which takes 24 hours to complete and causes day and night.
- Orbit: The fixed path on which the Earth moves around the Sun during its revolution.
- Revolution: The movement of the Earth around the Sun in its orbit, which takes 365¼ days to complete and causes the change in seasons.
- Eclipse: The partial or total blocking of the Sun’s light by the Earth or the Moon, resulting in a solar or lunar eclipse.
Points To Remember
- To see things, we need a source of light, such as the Sun, bulb, tube light, burning candle, or torch.
- The Sun and stars are natural sources of light, while bulbs, tube lights, and candles are artificial sources of light.
- Objects can be classified as transparent, translucent, or opaque based on how much light passes through them.
- A shadow forms when an opaque object blocks the path of light from a source.
- The Earth’s rotation on its axis causes day and night, completing one rotation in 24 hours.
- The Earth’s revolution around the Sun takes 365¼ days and causes the change in seasons.
- An eclipse happens when the Sun’s light is partially or totally blocked by the Earth or the Moon.
|
60 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Light and Shadows Chapter Notes - Science Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What is the difference between light and shadow? |  |
| 2. How does the rotation of the Earth affect day and night? |  |
| 3. What causes an eclipse? |  |
| 4. How is a shadow formed? |  |
| 5. What are key points to remember about light and shadows? |  |















