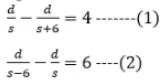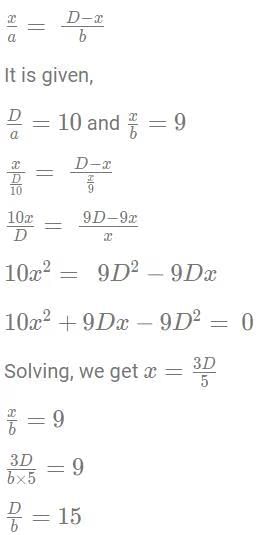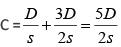CAT Previous Year Questions - Problems on Trains | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) PDF Download
2024
Q1: A train travelled a certain distance at a uniform speed. Had the speed been 6 km per hour more, it would have needed 4 hours less. Had the speed been 6 km per hour less, it would have needed 6 hours more. The distance, in km, travelled by the train is
(a) 640
(b) 780
(c) 800
(d) 720
Ans: d
Sol: Let’s assume that the distance traveled by the train is d km and the speed of the train is s km/hr.
So, T1 = d / s
T1 – T2 = 4 and T3 – T1 = 6 where
T1 is the original time
T2 is the time with increased speed
T3 is the time with decreased speed
Solving (1) and (2), we getd = 720 km.
Hence, 720 is the required answer.
2022
Q1: Trains A and B start traveling at the same time towards each other with constant speeds from stations X and Y, respectively. Train A reaches station Y in 10 minutes while train B takes 9 minutes to reach station X after meeting train A. Then the total time taken, in minutes, by train B to travel from station Y to station X is
(a) 6
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) 12
Ans: c
Sol:M - First meeting point
Let the speeds of trains A and B be 'a' and 'b', respectively.The total time taken by train B to travel from station Y to station X is 15 minutes.
The answer is option C
2021
Q1: Two trains cross each other in 14 seconds when running in opposite directions along parallel tracks. The faster train is 160 m long and crosses a lamp post in 12 seconds. If the speed of the other train is 6 km/hr less than the faster one, its length, in m, is
(a) 184
(b) 192
(c) 190
(d) 180
Ans: (c)
Sol: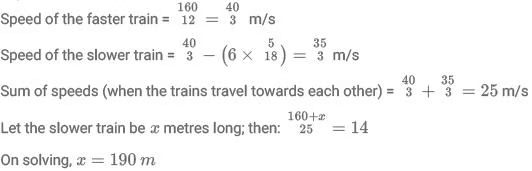
Q2: Two trains A and B were moving in opposite directions, their speeds being in the ratio 5 : 3. The front end of A crossed the rear end of B 46 seconds after the front ends of the trains had crossed each other. It took another 69 seconds for the rear ends of the trains to cross each other. The ratio of length of train A to that of train B is
(a) 3:2
(b) 5:3
(c) 2:3
(d) 2:1
Ans: (a)
Sol: Considering the length of train A = La, length of train B = Lb.
The speed of train A be 5*x, speed of train B be 3*x.
From the information provided : The front end of A crossed the rear end of B 46 seconds after the front ends of the trains had crossed each other.
In this case, train A traveled a distance equivalent to the length of train B which is Lb at a speed of 5*x+3*x = 8*x because both the trains are traveling in the opposite direction.
Hence (8*x)*(46) = Lb.
In the information provided : It took another 69 seconds for the rear ends of the trains to cross each other.
In the next 69 seconds The train B traveled a distance equivalent to the length of train A in this 69 seconds.
Hence (8*x)*(69) = La.
La/Lb = 69/46 = 3/2 = 3 : 2
2020
Q1: The distance from B to C is thrice that from A to B. Two trains travel from A to C via B.The speed of train 2 is double that of train 1 while traveling from A to B and their speeds areinterchanged while traveling from B to C. The ratio of the time taken by train 1 to that takenby train 2 in travelling from A to C is
(a) 1: 4
(b) 7: 5
(c) 5: 7
(d) 4: 1
Ans: (c)
Sol: Given,Let the speed of train 1 from A to B be s.
Then the speed of train 2 from A to B is 2s.
Time taken by train 1 to cover A toAnd, time taken by train 2 to cover A to C
Q2: A and B are two railway stations 90 km apart. A train leaves A at 9:00 am, heading towards B at a speed of 40 km/hr. Another train leaves B at 10:30 am, heading towards A at a speed of 20 km/hr. The trains meet each other at
(a) 11 : 45 am
(b) 10 : 45 am
(c) 11 : 20 am
(d) 11 : 00 am
Ans: (d)
Sol: The distance travelled by A before B starts his journey = 40 x 1.5 = 60
The time taken by them to meet each otherRequired answer =10: 30 a.m. +30 min =11: 00 a.m.
|
167 videos|229 docs|95 tests
|
FAQs on CAT Previous Year Questions - Problems on Trains - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant)
| 1. What are some common formulas used to solve problems related to trains in competitive exams? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the time taken for a train to cross a stationary object? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of understanding the concept of relative speed in train problems? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a typical train problem encountered in exams? |  |
| 5. What strategies can students use to improve their problem-solving skills for train-related questions? |  |